The cryptic code “OBD2 3160E” might seem like gibberish to the average car owner, but it holds valuable information about your vehicle’s health. This alphanumeric sequence is actually a specific Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) related to your car’s emissions system. Understanding what OBD2 3160E means can save you time, money, and potential headaches down the road.
Deciphering the Code: What Does OBD2 3160E Mean?
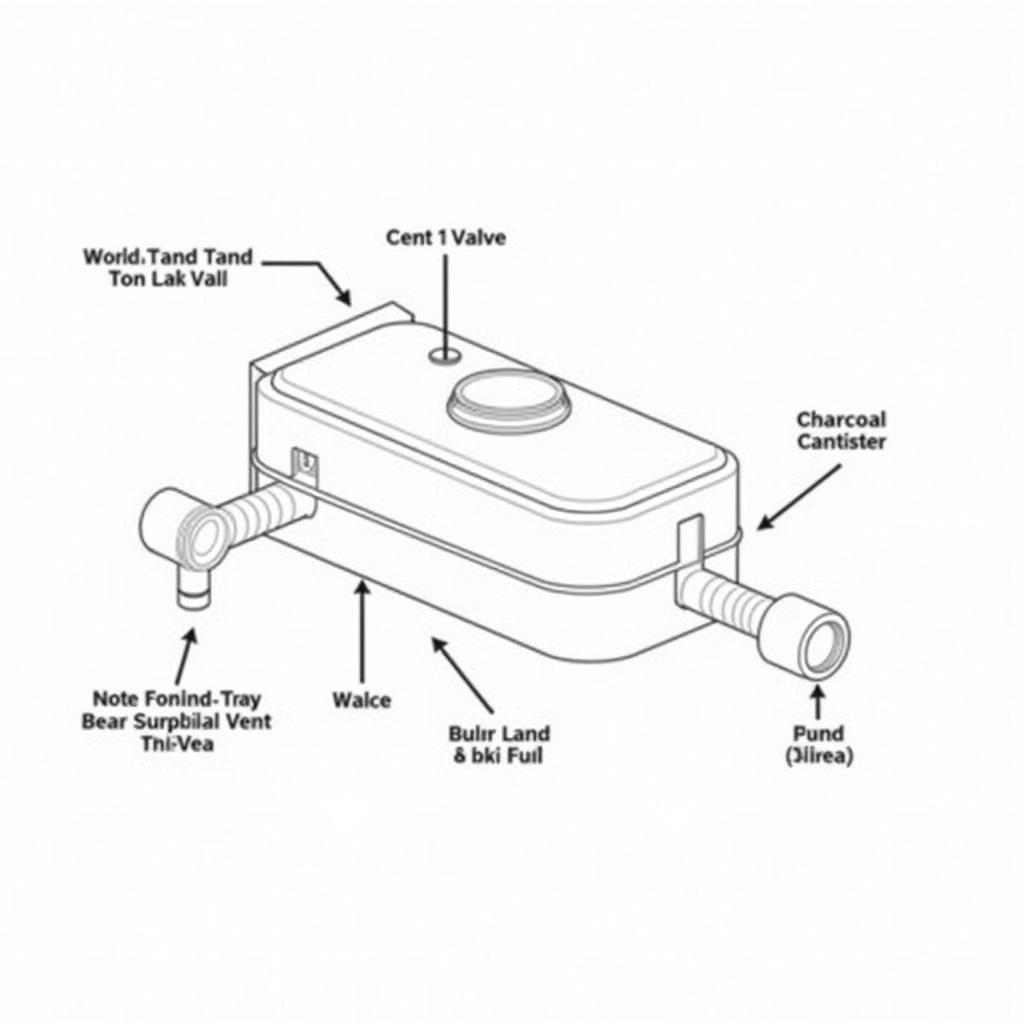
OBD2 stands for On-Board Diagnostics 2, a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and report malfunctions within various systems, including the engine and emissions control. The code 3160E specifically points to an issue with the Evaporative Emission (EVAP) system, a crucial component responsible for preventing fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere.
The EVAP system captures and stores fuel vapors from the gas tank, preventing them from being released into the air. These vapors are then purged into the engine to be burned during combustion. The “E” at the end of 3160E often signifies an electrical fault within this system.
Common Causes of OBD2 3160E
While the 3160E code points to a general issue within the EVAP system, several culprits could trigger this DTC. These include:
-
Faulty EVAP Vent Valve: This valve controls the release of pressure within the EVAP system. A malfunctioning vent valve can disrupt this pressure balance, leading to the 3160E code.
-
Damaged EVAP Purge Valve: The purge valve regulates the flow of fuel vapors from the charcoal canister to the engine for combustion. A faulty purge valve can disrupt this process, setting off the code.
-
Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring connections within the EVAP system can interrupt the electrical signals, triggering the 3160E code.
-
EVAP System Leaks: Leaks in the EVAP system, often caused by cracks in hoses or a loose gas cap, can disrupt the system’s pressure and trigger the code.
Diagnosing and Fixing OBD2 3160E
Diagnosing the exact cause of OBD2 3160E requires a systematic approach:
-
Read the Code: Using an OBD2 scanner, retrieve the specific code stored in your vehicle’s computer.
-
Research the Code: Once you have the code, consult reliable sources like OBDFree to understand its meaning and potential causes.
-
Inspect the EVAP System: Visually inspect the EVAP system components, including the vent valve, purge valve, hoses, and gas cap, for any visible damage, cracks, or loose connections.
-
Test the Components: Use a multimeter or specialized tools to test the functionality of the EVAP vent valve and purge valve.
-
Check for Leaks: Employ a smoke machine or soapy water solution to check for leaks within the EVAP system.
-
Repair or Replace: Depending on the diagnosed issue, repair or replace the faulty component.
“Addressing an EVAP system issue promptly is not just about passing emissions tests. It’s about ensuring your vehicle runs efficiently and safely,” advises John Miller, Senior Automotive Technician at CarCare Central. “Ignoring these codes can lead to more serious and costly repairs in the long run.”
Conclusion
Understanding the OBD2 3160E code empowers car owners to address potential issues proactively. By understanding the EVAP system’s function and the common causes of this code, you can take the necessary steps to diagnose and fix the problem, ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly and safely.
Need further assistance with your OBD2 codes? Contact our expert team via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880 or Email: cardiagtechworkshop@gmail.com. We’re available 24/7 to provide you with the support you need.