The dreaded check engine light can illuminate for numerous reasons, and one of the most common culprits is a faulty catalytic converter. Understanding the relationship between your OBD2 system, the catalytic converter, and that glowing check engine light is crucial for addressing the issue effectively and avoiding costly repairs. This article will dive deep into this connection, providing you with the knowledge to navigate this common automotive problem.
What is a Catalytic Converter and Why Does It Matter?
Your catalytic converter plays a vital role in reducing harmful emissions from your vehicle’s exhaust. It converts toxic gases, such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides, into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen. A malfunctioning catalytic converter not only impacts the environment but also your vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency. If you suspect a problem with your catalytic converter, understanding how your OBD2 system can help is essential. Find out more about when your obd2 mil on.
How the OBD2 System Detects Catalytic Converter Problems
The OBD2 system constantly monitors the performance of various components, including the catalytic converter. It does this by using oxygen sensors located before and after the converter. These sensors measure the oxygen levels in the exhaust stream. A healthy converter will cause a noticeable difference in the oxygen levels between these two sensors. If the OBD2 system detects that the oxygen levels are too similar, it may indicate that the converter isn’t working efficiently. This triggers the check engine light and stores a specific diagnostic trouble code (DTC) related to the catalytic converter in the system’s memory. You may encounter various Durango OBD2 codes, such as the durango obd2 codes p0134.
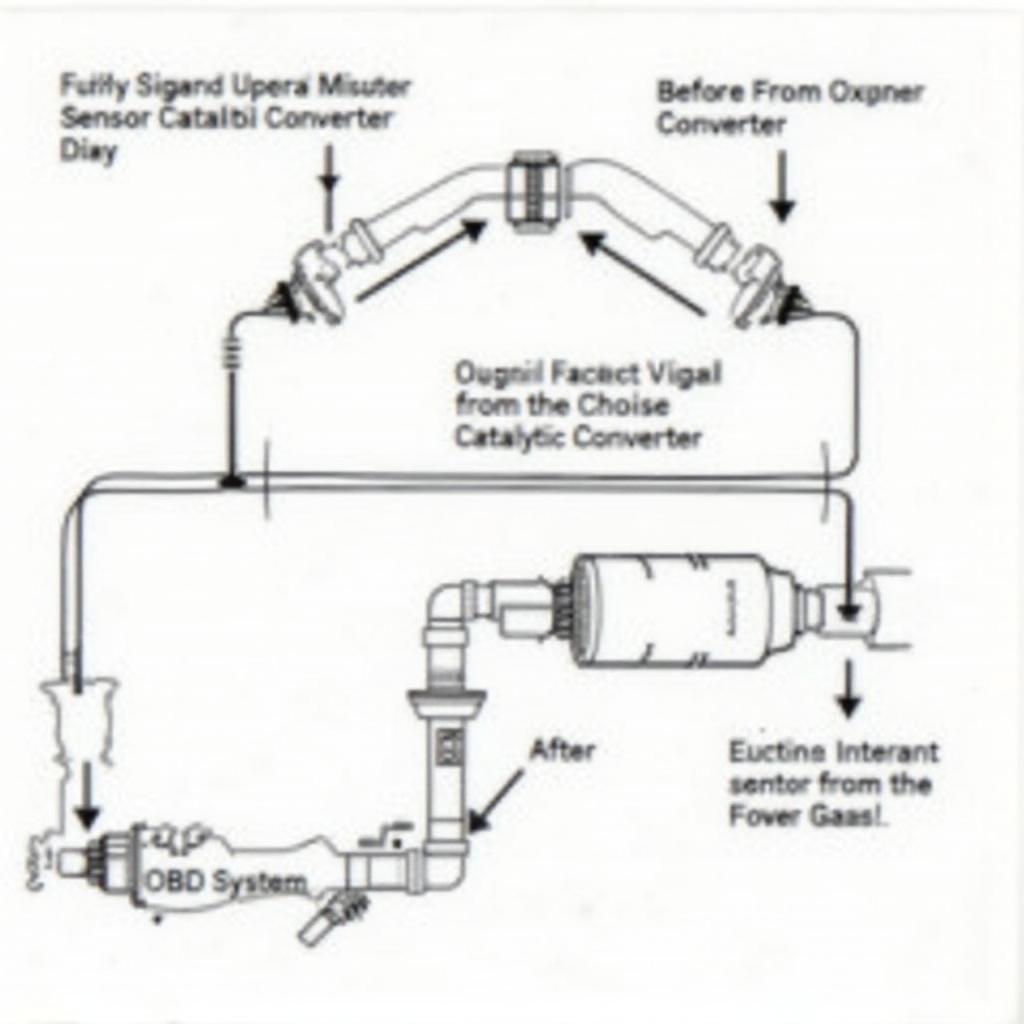 Diagram Showing Oxygen Sensor Placement and OBD2 Monitoring of Catalytic Converter Efficiency
Diagram Showing Oxygen Sensor Placement and OBD2 Monitoring of Catalytic Converter Efficiency
Common OBD2 Codes Related to Catalytic Converter Problems
Several DTCs specifically point to catalytic converter issues. The most common include:
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0430: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0421: Warm Up Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
These codes often indicate a failing catalytic converter, but other factors can trigger them as well.
“A common misconception is that a P0420 code automatically means a new catalytic converter is needed,” says automotive expert, John Miller, ASE Certified Master Technician. “It’s crucial to perform a thorough diagnosis before replacing any parts, as issues like faulty oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks, or even rich fuel mixtures can mimic a failing converter.” Learn more about specific vehicles like the 4g92 obd2.
Diagnosing the Problem
While an OBD2 scanner can identify the presence of a problem, it doesn’t pinpoint the exact cause. Further investigation is needed to determine whether the converter itself is faulty or if another issue is triggering the code. This often involves inspecting the exhaust system for leaks, checking the oxygen sensor readings, and performing a pressure test on the converter. You might be interested in learning how to bypass obd2 cat not ready.
What to Do When Your Check Engine Light Comes On
If your check engine light illuminates, don’t panic. The first step is to retrieve the DTC using an OBD2 scanner. This will give you a starting point for diagnosing the issue. If the code relates to the catalytic converter, it’s best to consult with a qualified mechanic. They have the expertise and equipment to perform a comprehensive diagnosis and recommend the appropriate repairs.
“Ignoring a check engine light related to the catalytic converter can lead to more serious problems down the road,” warns Sarah Chen, Automotive Engineer. “Addressing the issue promptly can prevent further damage to your vehicle and save you money in the long run.” Check out data stream information for specific vehicles, like the 2003 bmw 530i obd2 data stream.
Conclusion
The obd2 catalytic converter check engine light connection is a complex but crucial aspect of vehicle maintenance. Understanding how the OBD2 system detects catalytic converter problems and knowing the common related DTCs can help you address potential issues quickly and efficiently. Remember, early diagnosis and repair are key to minimizing further damage and keeping your car running smoothly.
Need help? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer support team is available 24/7.


