The OBD2 checking protocol, also known as OBD-II, has revolutionized how we diagnose and troubleshoot car problems. This standardized system allows mechanics and car enthusiasts to access a vehicle’s onboard computer and retrieve valuable diagnostic information.
What is the OBD2 Checking Protocol?
The OBD2 checking protocol is a set of rules and commands that dictate how a scan tool communicates with a vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU). Imagine it as a common language that allows your scan tool to understand and interpret the data stored within your car’s computer. This data includes:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Sensor readings (e.g., oxygen sensor, mass airflow sensor)
- Engine performance parameters
- Emissions-related data
How Does the OBD2 Checking Protocol Work?
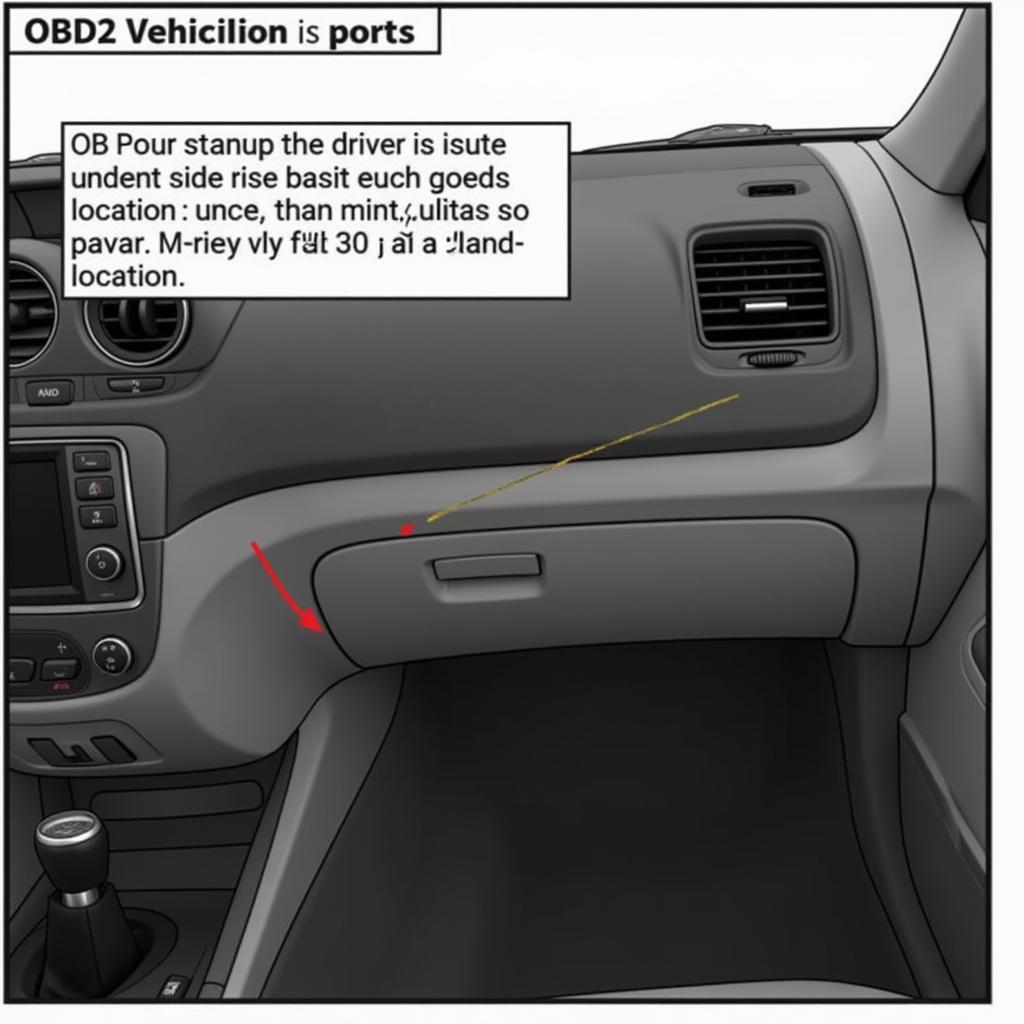
The OBD2 protocol relies on a standardized 16-pin connector, typically located under the driver’s side dashboard. When you connect an OBD2 scanner to this port, it establishes communication with the ECU and initiates a series of requests for information. The ECU responds by sending back data streams containing valuable insights into your vehicle’s health.
Why is the OBD2 Checking Protocol Important?
The implementation of the OBD2 checking protocol has significantly impacted the automotive industry, leading to:
- Faster and More Accurate Diagnostics: Mechanics can now quickly pinpoint problems, reducing diagnostic time and costs.
- Improved Emission Control: OBD2 helps monitor and regulate emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Enhanced Vehicle Maintenance: By accessing real-time data, car owners can proactively address minor issues before they escalate.
What are the Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner?
Using an OBD2 scanner, you can:
- Read and Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Identify the root cause of warning lights on your dashboard and clear them after resolving the issue.
- Monitor Real-time Sensor Data: Track engine performance parameters such as coolant temperature, RPM, and fuel pressure.
- Perform Emissions Tests: Check if your vehicle meets emission standards.
- Customize Vehicle Settings: Certain advanced scanners allow for modifications to specific vehicle settings.
Common OBD2 Checking Protocol Communication Errors
While the OBD2 protocol is generally reliable, you might encounter communication errors. Some common issues include:
- Loose or Damaged OBD2 Connector: Ensure the connector is securely plugged in and free of any physical damage.
- Blown Fuse: Check the fuse box for any blown fuses related to the OBD2 port.
- ECU Communication Issues: In rare cases, the ECU itself might have communication problems, requiring professional diagnosis.
If you suspect an issue with your vehicle’s OBD2 system, it’s always best to consult with a qualified mechanic.
Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
With countless OBD2 scanners available, choosing the right one can be overwhelming. Consider these factors:
- Functionality: Basic scanners read and clear codes, while advanced models offer live data, graphing, and other features.
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner supports your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- User Interface: Opt for a scanner with a user-friendly interface and easy-to-understand menus.
Conclusion
The OBD2 checking protocol has significantly simplified car diagnostics and empowered car owners to take charge of their vehicle maintenance. By understanding this protocol and utilizing the power of an OBD2 scanner, you can save time and money on car repairs, improve your vehicle’s performance, and contribute to a greener environment.
FAQs
1. Is my vehicle OBD2 compliant?
Vehicles manufactured in the United States after 1996 are generally OBD2 compliant. You can check your vehicle’s owner’s manual or look for the OBD2 port under your dashboard. For more information on OBD2 compliance, refer to our article: Is My Vehicle OBD2 Compliant?.
2. Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my car?
While most scanners work with a wide range of vehicles, it’s crucial to choose one compatible with your specific make, model, and year.
3. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner isn’t connecting?
First, check the connection and ensure the vehicle’s ignition is turned on. If the problem persists, refer to the scanner’s manual or contact the manufacturer for troubleshooting assistance. You can also find solutions for common OBD2 connection issues in our article: OBD2 ECU Not Connected.
4. Can an OBD2 scanner fix car problems?
OBD2 scanners are diagnostic tools, not repair tools. They help identify issues but don’t fix them.
5. Where can I learn more about my specific vehicle’s OBD2 system?
Your vehicle’s owner’s manual is a great starting point. You can also find valuable resources and guides online.
For specific questions regarding your car’s OBD2 system or to find the OBD2 port location for models like the Toyota Camry, check out our comprehensive guide: Toyota Camry OBD2 Location.
We also have a detailed guide on updating the Launch CReader 129 OBD2 scanner, which you can find here: Launch CReader 129 OBD2 Update.
If you’re unsure whether your 1995 Honda Accord is OBD1 or OBD2 compliant, our article on this topic can provide clarity: 1995 Honda Accord OBD1 or OBD2.
Need further assistance with OBD2 diagnostics?
Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected]. We have a 24/7 customer support team ready to help you!