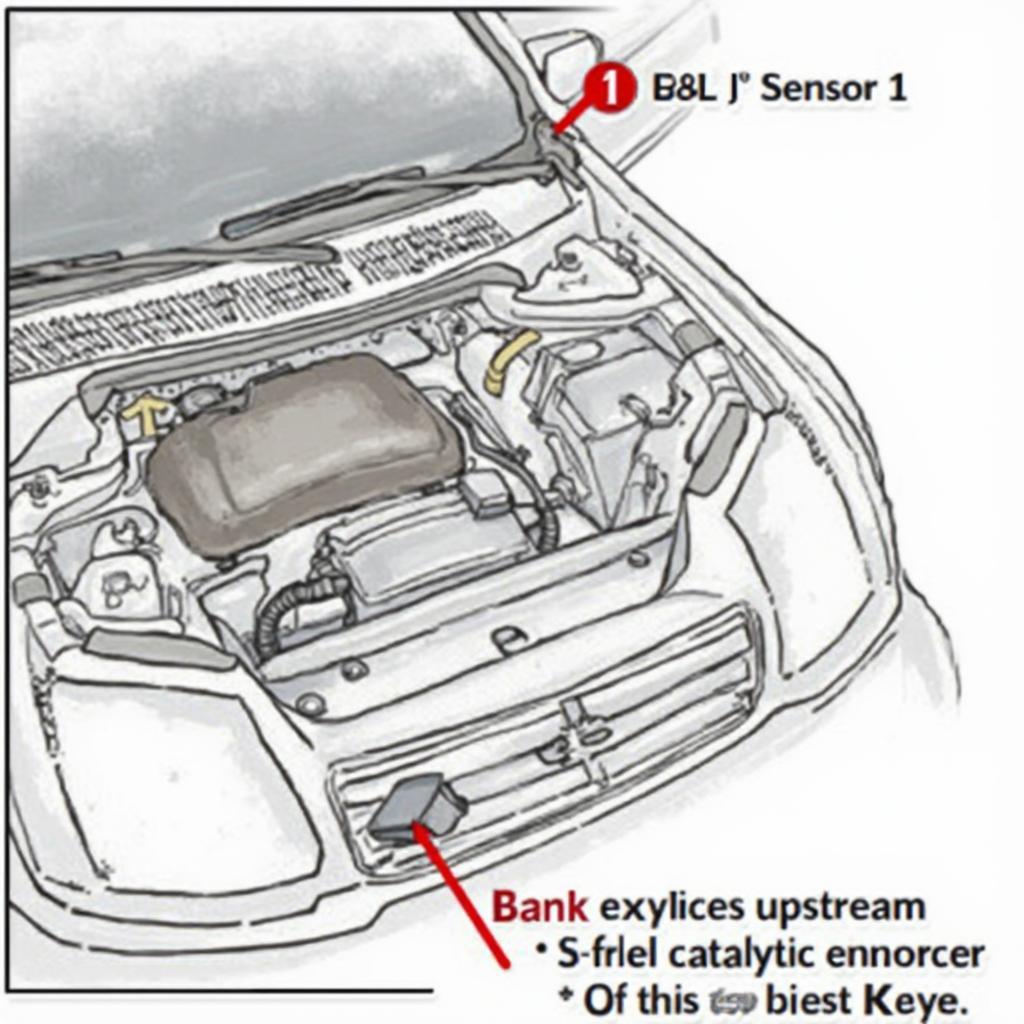
The dreaded “Check Engine” light can be a source of anxiety for any driver. One common code that can trigger this warning is OBD2 code P0030. This code indicates a problem with the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) control circuit, specifically for Bank 1 Sensor 1. Understanding this code, its causes, and potential solutions can save you time and money.
A P0030 code specifically points to a malfunction in the heater control circuit of the first oxygen sensor on Bank 1. This sensor plays a vital role in monitoring the exhaust gases leaving the engine and relaying this information to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU uses this data to adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal performance and emissions. The heater element within the sensor ensures it reaches operating temperature quickly, allowing for accurate readings soon after starting the engine. A faulty heater circuit can delay this process, leading to inaccurate readings and potentially impacting fuel efficiency and emissions.
What Does OBD2 Code P0030 Mean?
P0030 signifies a problem with the electrical circuit controlling the heater of the oxygen sensor. This doesn’t necessarily mean the sensor itself is faulty, but rather the signal controlling the heater’s operation is disrupted. This can be due to a variety of reasons, ranging from simple wiring issues to more complex problems within the ECU. The code specifically refers to Bank 1 Sensor 1. “Bank 1” refers to the side of the engine containing cylinder number one. “Sensor 1” indicates the upstream oxygen sensor, located before the catalytic converter.
Common Causes of OBD2 Code P0030
Several factors can contribute to a P0030 code. These include:
- Faulty oxygen sensor heater circuit wiring: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring can disrupt the electrical signal to the heater.
- Blown fuse: A blown fuse in the heater circuit can cut off power to the sensor heater.
- Faulty oxygen sensor: While the code points to the circuit, the sensor itself can sometimes be the culprit.
- Damaged ECU: In rare cases, a malfunctioning ECU can be responsible for the P0030 code.
How to Diagnose and Fix OBD2 Code P0030
Diagnosing a P0030 code requires a systematic approach. Start by visually inspecting the wiring and connector for the oxygen sensor. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Next, check the relevant fuse. If the wiring and fuse appear to be in good condition, you can use an OBD2 scanner to monitor the sensor’s readings. This can help determine if the sensor itself is faulty.
If you’re not comfortable working on your car’s electrical system, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic. They have the expertise and equipment to accurately diagnose and fix the problem.
What Happens If You Ignore OBD2 Code P0030?
Ignoring a P0030 code can lead to several problems, including:
- Decreased fuel economy: The ECU may not be able to optimize the air-fuel mixture, leading to increased fuel consumption.
- Increased emissions: A faulty oxygen sensor can cause the engine to run rich, increasing harmful emissions.
- Damage to the catalytic converter: Unburnt fuel can damage the catalytic converter over time.
“A properly functioning oxygen sensor is crucial for optimal engine performance and emissions control,” says John Smith, ASE Certified Master Technician. “Ignoring a P0030 code can lead to more costly repairs down the line.”
Conclusion
Understanding OBD2 code P0030 is essential for any car owner. Addressing this code promptly can prevent further issues and ensure your vehicle runs efficiently and cleanly. Remember, a little preventative maintenance can go a long way in saving you time and money in the long run. Addressing the P0030 code will help keep your car running smoothly and avoid potential problems down the road.
FAQ
- Can I drive with a P0030 code? While you can technically drive with a P0030 code, it’s not recommended.
- How much does it cost to fix a P0030 code? The cost can vary depending on the cause and your location.
- Can I fix a P0030 code myself? If you have some mechanical experience, you may be able to fix it yourself. However, it’s often best to consult a professional.
- What is the difference between Bank 1 and Bank 2? Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine with cylinder 1, while Bank 2 refers to the other side.
- What is the difference between Sensor 1 and Sensor 2? Sensor 1 is located before the catalytic converter, while Sensor 2 is located after.
- How often should I check my OBD2 codes? It’s a good practice to check your OBD2 codes periodically, especially if your “Check Engine” light comes on.
- Can extreme temperatures affect the oxygen sensor? Yes, extreme temperatures can affect the performance and lifespan of an oxygen sensor.
For further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.