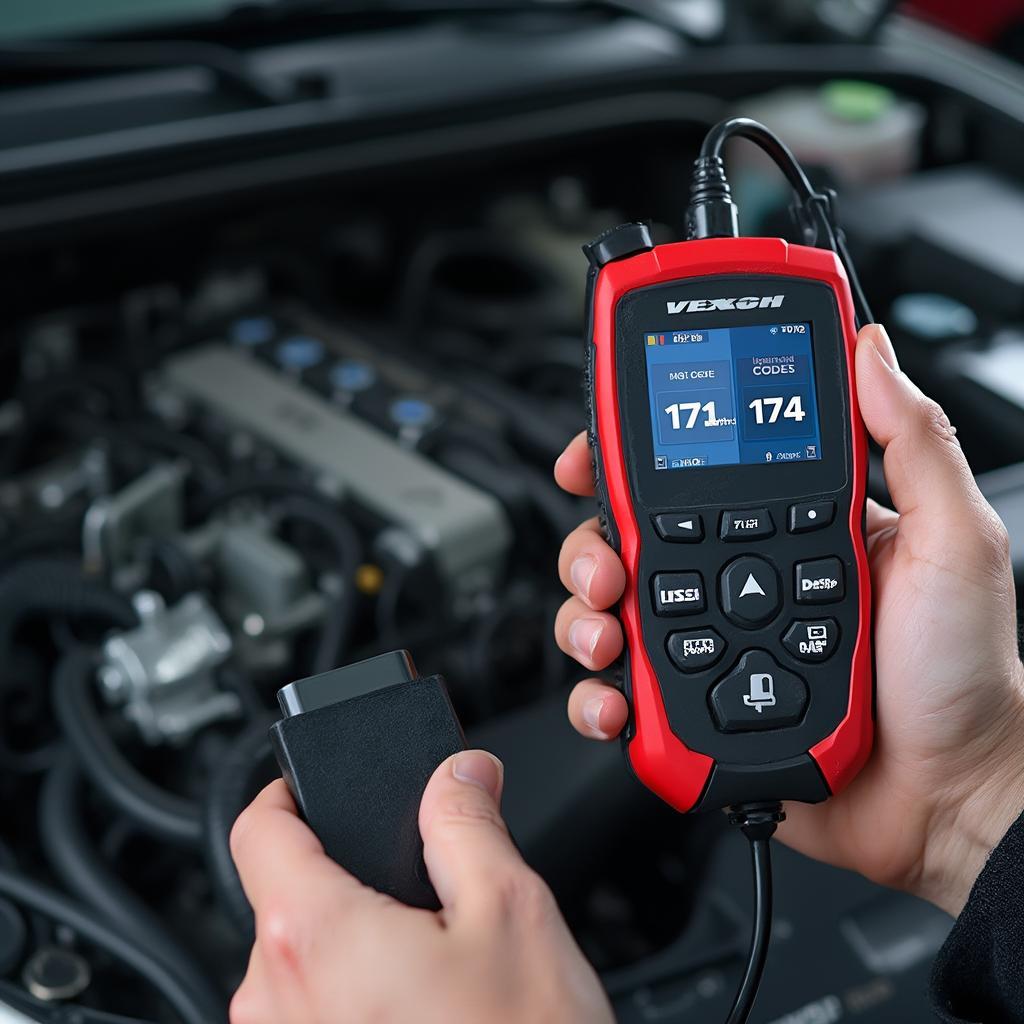
OBD2 codes 171 and 174 indicate a lean fuel mixture, a common issue that can affect various vehicle makes and models. This article will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and solutions for these trouble codes, providing you with a comprehensive guide to resolving this problem and keeping your car running smoothly.
What are OBD2 Codes 171 and 174?
These codes signal that the engine’s air-fuel mixture is lean, meaning there’s too much air compared to fuel. Code P0171 refers to a lean condition in Bank 1, while P0174 indicates the same issue in Bank 2. Most vehicles with a V6 or V8 engine configuration have two banks, each containing a separate set of cylinders. Four-cylinder engines typically only have one bank. obd2 codes p0171 and p0174
Why are Lean Conditions Harmful?
A lean air-fuel mixture can cause a range of problems, from reduced fuel efficiency and performance to engine damage. It can lead to increased combustion temperatures, potentially damaging engine components.
A lean condition can significantly impact your vehicle’s performance and longevity. For example, a lean mixture can cause misfires, rough idling, and hesitation during acceleration. In extreme cases, it can even lead to catastrophic engine damage. Think of it like trying to bake a cake with too much flour – it just won’t come out right!
Common Causes of OBD2 Codes 171 and 174
Several factors can contribute to a lean air-fuel mixture, including:
- Vacuum Leaks: A leak in the intake manifold, vacuum hoses, or other components can allow unmetered air to enter the engine.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: These sensors play a crucial role in monitoring the air-fuel mixture. A malfunctioning sensor can send incorrect data to the engine control unit (ECU), leading to a lean condition. obd2 o2 sensor readings
- Fuel System Problems: Issues like a clogged fuel filter, weak fuel pump, or faulty fuel injectors can restrict fuel flow, resulting in a lean mixture.
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor Problems: A dirty or faulty MAF sensor can provide inaccurate readings to the ECU, causing it to deliver the wrong amount of fuel.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system before the oxygen sensors can affect their readings and lead to a lean mixture.
- PCV Valve Issues: A faulty Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve can cause excessive air intake, leading to a lean mixture.
“A thorough diagnosis is crucial to pinpoint the root cause of the lean condition,” says John Miller, a seasoned automotive technician with over 20 years of experience. “Don’t just throw parts at the problem, as that can be costly and ineffective.”
Diagnosing OBD2 Codes 171 and 174
Diagnosing these codes requires a systematic approach. Start by visually inspecting for vacuum leaks, checking the condition of vacuum hoses, and looking for any loose or disconnected components. Then, use an OBD2 scanner to monitor the fuel trims, oxygen sensor readings, and MAF sensor data. obd2 ford v10
Using an OBD2 Scanner
An OBD2 scanner can be invaluable in diagnosing these codes. It allows you to monitor real-time data from various sensors, providing insights into the engine’s performance and identifying potential issues.
“Using an OBD2 scanner can save you a lot of time and money in the long run,” advises Miller. “It allows you to pinpoint the problem quickly and accurately, avoiding unnecessary repairs.”
How to Fix OBD2 Codes 171 and 174
Once you’ve identified the cause, you can take appropriate action to fix the lean condition. This might involve:
- Repairing Vacuum Leaks: Replace damaged hoses or tighten loose connections.
- Replacing Faulty Oxygen Sensors: If the sensors are malfunctioning, replacement is usually the only solution.
- Addressing Fuel System Issues: Clean or replace the fuel filter, check the fuel pump pressure, and replace faulty fuel injectors.
- Cleaning or Replacing the MAF Sensor: Clean the MAF sensor with a specialized cleaner or replace it if it’s damaged.
- Repairing Exhaust Leaks: Repair any leaks in the exhaust system before the oxygen sensors.
- Replacing the PCV Valve: If the PCV valve is faulty, replace it.
obd2 code p0402 p1131 pq0171 p0174p0455 p1151
Conclusion
OBD2 codes 171 and 174 indicate a lean air-fuel mixture, which can lead to various performance problems and potential engine damage. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures, you can effectively address this issue and keep your car running smoothly. Remember, a thorough diagnosis is crucial for accurate and efficient repairs.
FAQ
- What is a lean air-fuel mixture? A lean mixture means there’s too much air and not enough fuel in the combustion chamber.
- Can I drive with a lean condition? It’s not recommended. Prolonged driving with a lean condition can cause engine damage.
- How much does it cost to fix a lean condition? The cost varies depending on the cause and the necessary repairs.
- Can I fix a lean condition myself? Some repairs, like replacing a vacuum hose, are relatively easy. Others require more advanced knowledge and tools.
- How can I prevent a lean condition? Regular maintenance, including checking for vacuum leaks and replacing worn-out components, can help prevent lean conditions.
Need support? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected], or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer support team is available 24/7.