The dreaded check engine light has illuminated your dashboard, and your OBD2 scanner reveals the cryptic code P0137. This indicates a problem with your oxygen sensor, specifically low voltage in the circuit for Bank 1, Sensor 2. Don’t panic! This article will demystify obd2 code p0137, explaining its causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions.
The P0137 code specifically refers to the downstream oxygen sensor, located after the catalytic converter. Its primary function is to monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter. A low voltage reading suggests the sensor isn’t generating the expected signal, which can lead to various performance issues and increased emissions.
What Does OBD2 Code P0137 Mean?
This code signifies that the Engine Control Module (ECM) has detected a low voltage signal from the downstream oxygen sensor (Sensor 2) on Bank 1. Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine containing cylinder number one. Understanding this terminology is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair. obd2 p0137 is a common issue, but its underlying causes can vary.
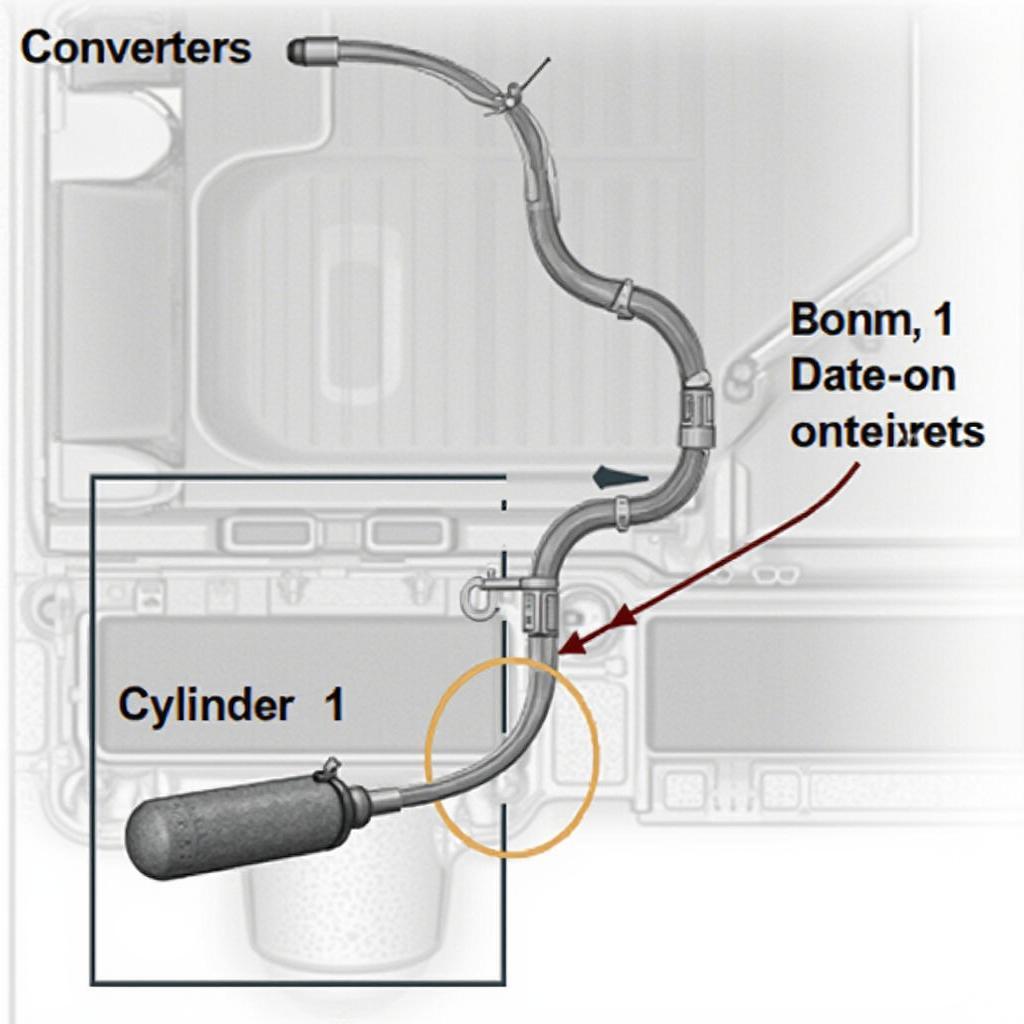 OBD2 Code P0137 Oxygen Sensor Location
OBD2 Code P0137 Oxygen Sensor Location
Common Causes of OBD2 Code P0137
Several factors can contribute to a low voltage reading from the downstream oxygen sensor. These include:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The most common culprit is a malfunctioning sensor itself, often due to age, wear, or contamination.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring in the sensor circuit can disrupt the signal transmission.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks before the sensor can introduce excess oxygen, affecting its readings.
- Vacuum Leaks: Unmetered air entering the engine can alter the air/fuel mixture and impact sensor performance.
- Fuel Delivery Problems: Issues with the fuel pump, injectors, or fuel pressure regulator can affect combustion and sensor readings.
Symptoms of P0137
While the check engine light is the most obvious symptom, you might also experience:
- Decreased Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to inefficient fuel consumption.
- Rough Idle or Stalling: The ECM might struggle to regulate the air/fuel mixture, resulting in unstable engine performance.
- Failed Emissions Test: The P0137 code directly relates to emissions control, and a faulty sensor can cause your vehicle to fail emissions testing.
Diagnosing OBD2 Code P0137
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective repair. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Retrieve the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to confirm the P0137 code.
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Check for any visible damage, corrosion, or loose connections in the sensor wiring and connector.
- Check for Exhaust Leaks: Inspect the exhaust system for leaks, particularly before the downstream oxygen sensor.
- Test Sensor Voltage: Use a multimeter to measure the sensor voltage. A consistently low reading indicates a faulty sensor.
“Accurate diagnosis is key to avoiding unnecessary repairs,” advises John Miller, a seasoned automotive diagnostician with over 20 years of experience. “Always start with a thorough visual inspection and verify the fault before replacing any components.”
obd2 scanner code p0137 can be diagnosed with a simple OBD2 scanner, available online and in auto parts stores.
How to Fix OBD2 Code P0137
Depending on the diagnosis, the solution might involve:
- Replacing the Oxygen Sensor: A faulty sensor will need to be replaced with a new one.
- Repairing Wiring or Connectors: Damaged or corroded wiring should be repaired or replaced. Loose connectors should be tightened.
- Fixing Exhaust Leaks: Address any exhaust leaks before the sensor.
- Addressing Fuel Delivery Problems: Diagnose and repair any issues with the fuel system.
Conclusion
The obd2 code p0137 indicates a low voltage issue with the downstream oxygen sensor, which can affect your vehicle’s performance and emissions. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures, you can effectively address this problem and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. Don’t hesitate to consult a qualified mechanic for assistance if needed. chevy obd2 code p0137 can be particularly challenging to diagnose and repair.
FAQ
- What is the difference between upstream and downstream oxygen sensors? Upstream sensors monitor the air/fuel mixture before the catalytic converter, while downstream sensors monitor the converter’s efficiency.
- Can I drive with a P0137 code? While you can technically drive, it’s recommended to address the issue promptly to avoid further damage and improve fuel economy.
- How much does it cost to replace an oxygen sensor? The cost varies depending on the vehicle and sensor type but typically ranges from $100 to $300.
- How often should oxygen sensors be replaced? Oxygen sensors typically last between 60,000 and 90,000 miles.
- Can a bad catalytic converter cause a P0137 code? While unlikely, a failing catalytic converter can sometimes affect the downstream sensor readings.
- How can I prevent future P0137 codes? Regular maintenance, including timely replacement of oxygen sensors, can help prevent this code. 2010 kia sedona obd2 code p013702
- What other codes are related to oxygen sensors? Other codes like P0130, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0134, P0135, P0136, P0138, and P0139 are all related to oxygen sensor issues. obd2 error code p0137
Need more information? Check out our articles on specific car models and OBD2 codes.
For immediate assistance, contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer support team is available 24/7.