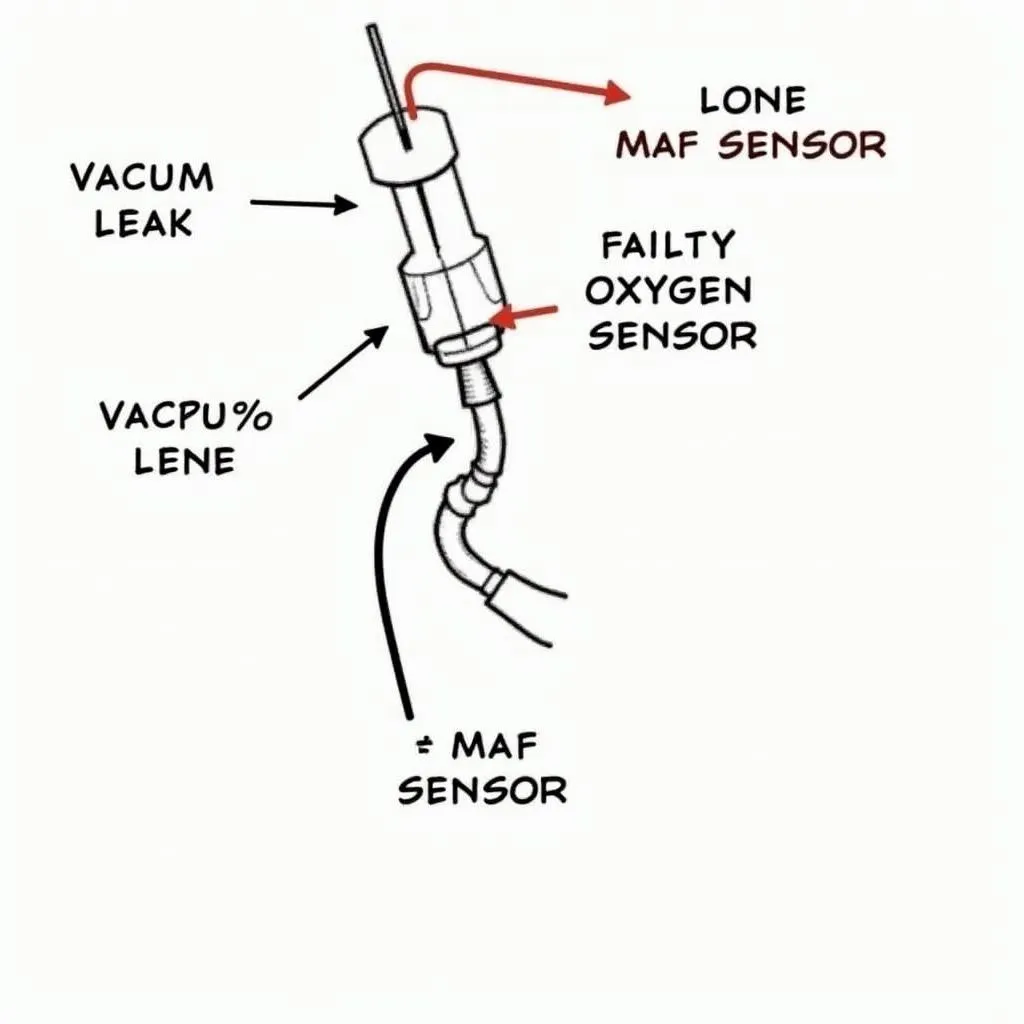
The P0170 code is a common OBD2 trouble code that indicates a problem with the fuel system in your vehicle. It stands for “Fuel Trim Malfunction (Bank 1)” and can be caused by a variety of issues, from a faulty oxygen sensor to a vacuum leak. This comprehensive guide will delve into the causes, symptoms, and fixes for the OBD2 code P0170.
Understanding the P0170 Code
Your vehicle’s engine requires a precise mixture of air and fuel to operate efficiently. The Engine Control Module (ECM) constantly monitors and adjusts this air-fuel ratio using data from various sensors, including the oxygen sensors and mass airflow sensor. When the ECM detects that it cannot maintain the ideal air-fuel ratio, specifically that the mixture is running too lean (too much air, not enough fuel) in Bank 1 of the engine (typically the side with cylinder #1), it triggers the P0170 code.
Common Causes of OBD2 Code P0170
The P0170 code can stem from various issues within your vehicle’s fuel and air intake systems. Here are some of the most common culprits:
- Vacuum Leaks: A leak in the intake manifold, vacuum hoses, or other vacuum-operated components can disrupt the air-fuel ratio, leading to a lean condition.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor(s): Oxygen sensors play a critical role in monitoring the oxygen content in the exhaust gases, which the ECM uses to adjust the air-fuel ratio. A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can provide inaccurate readings, causing the ECM to miscalculate the fuel trim.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Issues: The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. A dirty, faulty, or failing MAF sensor can send incorrect information to the ECM, resulting in an inaccurate air-fuel mixture.
- Fuel Pressure Problems: Low fuel pressure, often caused by a failing fuel pump, clogged fuel filter, or malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator, can prevent sufficient fuel from reaching the engine.
- Fuel Injector Problems: Clogged or leaking fuel injectors can disrupt the fuel spray pattern and lead to an improper air-fuel mixture.
- EVAP System Leak: A leak in the Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) system, which is responsible for capturing fuel vapors, can introduce excess air into the intake manifold.
- PCV Valve Issues: A faulty Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve can cause a vacuum leak, affecting the air-fuel ratio.
Symptoms of a P0170 Code
Recognizing the symptoms of a P0170 code can help you address the issue promptly. Here are some common signs:
- Check Engine Light: The most obvious indicator, the check engine light illuminating on your dashboard, signals a potential problem with the engine management system.
- Rough Idle: A lean air-fuel mixture can cause rough idling, making the engine sound unsteady and shaky.
- Engine Misfires: In more severe cases, the engine may misfire, especially during acceleration or under load.
- Reduced Fuel Economy: A lean condition often results in decreased fuel efficiency as the engine works harder to compensate for the lack of fuel.
- Hesitation or Stalling: The engine may hesitate during acceleration or even stall due to the incorrect air-fuel mixture.
Diagnosing and Fixing the P0170 Code
Fixing the P0170 code requires identifying the underlying cause. Here’s a step-by-step approach to diagnose and repair the issue:
- Read the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to read the trouble code stored in your vehicle’s ECM.
- Inspect for Vacuum Leaks: Carefully examine the intake manifold, vacuum hoses, and other vacuum-operated components for any signs of cracks, loose connections, or damage. Use a carburetor cleaner or a smoke machine to help locate leaks.
- Check the Oxygen Sensors: Inspect the oxygen sensors for any visible damage or contamination. Test their operation using a multimeter or consult a mechanic to analyze their readings.
- Inspect the MAF Sensor: Locate and inspect the MAF sensor for dirt or debris. Clean it with MAF sensor cleaner if necessary. You can also test its operation with a multimeter.
- Test Fuel Pressure: Connect a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel rail to measure the fuel pressure. Compare the readings to your vehicle’s specifications.
- Inspect Fuel Injectors: Check for leaking or clogged fuel injectors. You can perform a fuel injector cleaning or have them professionally tested and cleaned.
- Inspect the EVAP System: Look for any leaks in the EVAP system, including the charcoal canister, purge valve, and associated hoses.
- Check the PCV Valve: Remove the PCV valve and inspect it for clogging or sticking. Replace it if necessary.
How to Prevent P0170 Code
Regular vehicle maintenance can help prevent the P0170 code and other engine problems:
- Regular Oil Changes: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals.
- Air Filter Replacement: Replace the air filter as recommended in your owner’s manual.
- Fuel System Cleaning: Consider periodic fuel system cleaning to prevent injector clogging.
- Check Vacuum Hoses: Regularly inspect vacuum hoses for signs of wear and tear, replacing them as needed.
Importance of Addressing OBD2 Codes
Ignoring OBD2 codes like P0170 can lead to more severe engine problems and costly repairs down the line. Addressing the issue promptly ensures optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and the longevity of your vehicle.
Conclusion
The OBD2 code P0170, indicating a lean fuel mixture, can be caused by several factors ranging from minor vacuum leaks to more serious problems with oxygen sensors or fuel delivery. Prompt diagnosis and repair are crucial to prevent further engine damage and ensure optimal vehicle performance. Using an OBD2 scanner and following a systematic troubleshooting approach, you can effectively pinpoint and resolve the underlying issue. Remember, regular vehicle maintenance and addressing potential problems early on are essential for a smooth and safe driving experience.
FAQs about OBD2 Code P0170
Can I still drive my car with a P0170 code?
While you might be able to drive for a short distance with the P0170 code, it’s not advisable. Driving with a lean fuel mixture can potentially damage your engine, catalytic converter, and other components, leading to costlier repairs in the future.
How much does it cost to fix the P0170 code?
The cost of repairing the P0170 code can vary widely depending on the underlying cause and your vehicle’s make and model. A simple vacuum leak repair might cost less than $100, while replacing a faulty oxygen sensor or fuel pump could range from $200 to $800 or more.
What happens if I don’t fix the P0170 code?
Ignoring the P0170 code can lead to:
- Reduced fuel economy
- Engine damage (e.g., burnt valves, damaged pistons)
- Catalytic converter failure
- Increased emissions
Can a bad gas cap cause a P0170 code?
While a loose or damaged gas cap can sometimes trigger the check engine light, it’s unlikely to directly cause the P0170 code.
Can I fix the P0170 code myself?
If you have some mechanical experience and the right tools, you might be able to fix some of the simpler causes of the P0170 code, such as a vacuum leak or a dirty MAF sensor. However, for more complex issues like faulty oxygen sensors or fuel system problems, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic.
Are there any other OBD2 codes related to P0170?
Yes, the P0170 code often appears alongside other codes, such as:
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0172: System Too Rich (Bank 1)
- P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 2)
- P0175: System Too Rich (Bank 2)
These codes indicate similar fuel trim problems but on different engine banks.
Need More Help with OBD2 Codes?
- Explore our extensive library of OBD2 code resources.
- Learn about specific car models and their OBD2 systems, such as the OBD2 Peugeot 406 and OBD2 W210.
Contact our expert team for personalized assistance with your OBD2 code questions and concerns. Reach us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880 or email: [email protected]. We’re available 24/7 to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly.