The OBD2 code P01443 is a common issue that car owners may encounter. This code indicates a problem with the oxygen sensor (O2 sensor) circuit located after the catalytic converter on bank 1. Specifically, it signifies that the sensor is not sending a signal to the engine control unit (ECU) within the expected timeframe, signaling a potential issue with the sensor’s performance.
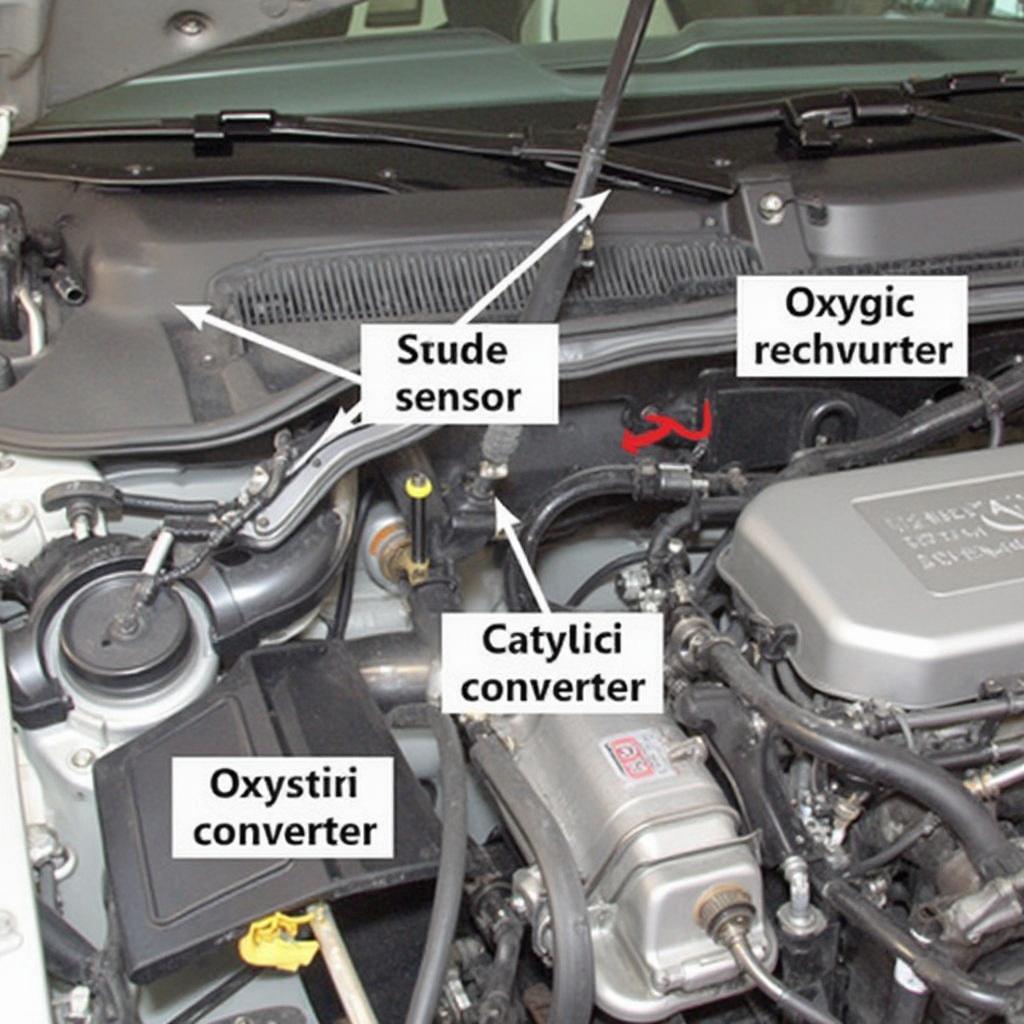 Oxygen Sensor Location Bank 1
Oxygen Sensor Location Bank 1
Understanding Oxygen Sensors and their Role
Before delving into the specifics of code P01443, it’s crucial to understand the function of oxygen sensors in your vehicle. O2 sensors are vital components of the emissions control system. They monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust stream, providing data to the ECU, which in turn adjusts the air-fuel mixture to ensure optimal engine performance and minimize harmful emissions.
A vehicle typically has two sets of oxygen sensors:
-
Upstream O2 Sensors: Located before the catalytic converter, these sensors primarily monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust gases leaving the engine, playing a crucial role in fuel management.
-
Downstream O2 Sensors: Positioned after the catalytic converter, these sensors measure the oxygen content after the exhaust gases have passed through the converter. Their primary function is to monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter in reducing harmful emissions.
Decoding the P01443 Code
The OBD2 code P01443 specifically relates to the downstream oxygen sensor on bank 1. “Bank 1” refers to the side of the engine that houses cylinder number one. This code essentially means the ECU is not receiving a signal from this particular sensor within the expected timeframe.
Common Causes of P01443
Several factors can trigger the P01443 code, ranging from simple issues to more complex problems. Here are some of the most common culprits:
-
Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The most common cause is a malfunctioning downstream oxygen sensor on bank 1. Over time, these sensors can wear out, become contaminated, or fail, leading to inaccurate readings or no signal at all.
-
Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system, particularly near the downstream oxygen sensor, can introduce fresh air into the exhaust stream, disrupting the sensor’s ability to accurately measure oxygen levels.
-
Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring connections between the oxygen sensor and the ECU can interrupt the signal transmission, triggering the P01443 code.
-
Faulty Catalytic Converter: While less common, a failing catalytic converter can also trigger this code. A clogged or inefficient converter can produce exhaust readings similar to a faulty oxygen sensor.
Symptoms of a P01443 Code
While the P01443 code itself might not cause noticeable drivability issues, it often coincides with other symptoms, including:
-
Illuminated Check Engine Light: The most apparent symptom is the illumination of the check engine light on your dashboard.
-
Decreased Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, potentially leading to reduced fuel efficiency.
-
Rough Idling or Engine Stalling: In some cases, a faulty downstream oxygen sensor might indirectly affect engine performance, causing rough idling or even engine stalling.
-
Failed Emissions Test: A stored P01443 code will likely result in a failed emissions test in areas where such inspections are mandatory.
Diagnosing and Fixing the P01443 Code
Accurately diagnosing the root cause of the P01443 code requires a systematic approach:
-
Read the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the stored code. This will confirm the presence of the P01443 code and any other related codes.
-
Inspect the Wiring: Visually examine the wiring harness connected to the downstream oxygen sensor on bank 1 for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Repair or replace any faulty wiring as needed.
-
Check for Exhaust Leaks: Inspect the exhaust system, particularly the area around the downstream oxygen sensor, for any leaks. Look for signs such as black soot deposits or listen for any unusual hissing sounds. Address any leaks before proceeding.
-
Test the Oxygen Sensor: If the wiring and exhaust system appear to be in good condition, the next step is to test the oxygen sensor itself. This typically involves using a multimeter to check the sensor’s voltage signal. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for specific testing procedures.
-
Replace the Oxygen Sensor (if necessary): If the oxygen sensor is found to be faulty, replacement is the most effective solution. Ensure you use a compatible replacement sensor that meets your vehicle’s specifications.
-
Inspect the Catalytic Converter (if necessary): If other potential causes have been ruled out, and the oxygen sensor tests within specifications, the catalytic converter might be the underlying issue. Further diagnosis of the catalytic converter’s efficiency might be necessary.
Expert Insight
“It’s important to remember that while a faulty oxygen sensor is the most frequent cause of the P01443 code, it’s not the only possibility,” says John Miller, a seasoned automotive engineer. “Thoroughly inspecting the wiring and checking for exhaust leaks are crucial steps in the diagnostic process. Overlooking these simple checks could lead to unnecessary and potentially costly part replacements.”
Conclusion
Addressing the OBD2 code P01443 is essential to ensure optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and compliance with emissions standards. While the task might seem daunting, armed with the right information and a systematic approach to diagnosis, car owners can often pinpoint the root cause and implement the necessary repairs. Remember, if you are uncomfortable working on your vehicle, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic for assistance.
FAQs
Q: Can I continue driving with a P01443 code?
A: While you might not experience immediate drivability issues, it’s advisable to address the P01443 code promptly. Driving with a faulty oxygen sensor can negatively impact fuel economy, potentially damage other components, and result in a failed emissions test.
Q: How much does it cost to replace an oxygen sensor?
A: The cost of replacing an oxygen sensor can vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle, the sensor’s location, and labor costs. On average, you can expect to pay between $100 and $300 for parts and labor.
Q: Can I replace the oxygen sensor myself?
A: Replacing an oxygen sensor is a relatively straightforward repair for those comfortable working on their vehicles. However, it’s essential to have the correct tools and follow proper safety procedures.
Q: How often should oxygen sensors be replaced?
A: Oxygen sensors typically have a lifespan of 60,000 to 90,000 miles. However, factors such as driving conditions and fuel quality can influence their lifespan.
Q: What is an OBD2 scanner, and where can I get one?
A: An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that connects to your vehicle’s OBD2 port, allowing you to read and clear trouble codes. You can purchase OBD2 scanners from auto parts stores, online retailers, or directly from manufacturers like OBDFree.
Explore More OBD2 Codes and Solutions
For more information on specific OBD2 codes and troubleshooting guides, visit OBDFree, your trusted resource for all things OBD2.
Need Help? Contact Us!
For expert assistance with your car diagnostic needs, reach out to our team at:
WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880
Email: [email protected]
We offer 24/7 customer support to help you get back on the road quickly and safely.

