OBD2 continuous monitors are essential for ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. These diagnostic tests, constantly running in the background, keep a close watch on various systems, alerting you to potential problems before they become major headaches. This article will delve into the intricacies of OBD2 continuous monitors, explaining their function, importance, and how they contribute to a healthier, better-performing vehicle. Learn how to interpret the data from these monitors and gain valuable insights into your car’s overall health.
Understanding how these continuous monitors work can save you money on costly repairs down the line and help you keep your car in tip-top shape. From emissions control to fuel system efficiency, these monitors play a vital role in modern vehicle diagnostics. Let’s explore how they work and what they mean for you. Are you ready to take a deeper dive into the world of OBD2 continuous monitors? Let’s get started!
What are OBD2 Continuous Monitors?
OBD2 continuous monitors are diagnostic tests that constantly run in your vehicle’s background, checking the functionality of various emission-related systems. Unlike the one-time checks performed by other OBD2 diagnostics, these monitors operate continuously while the engine is running, providing real-time feedback on the performance of crucial components. This constant monitoring allows the OBD2 system to detect subtle changes and potential issues that might be missed by one-time scans.
These monitors play a crucial role in maintaining your vehicle’s emission control systems and overall performance. They act like a silent guardian, constantly assessing various systems and alerting you to any irregularities through the check engine light. Think of them as a preventative measure, helping you address minor problems before they escalate into major and costly repairs. They are an integral part of your car’s onboard diagnostic system, constantly working to ensure optimal performance and minimize emissions.
If a continuous monitor detects a problem, it sets a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and illuminates the check engine light. However, not all DTCs trigger the check engine light immediately. Some monitors require multiple driving cycles with the same fault detected before the light comes on. This is why understanding how these monitors work is so important.
After the first paragraph, you might be interested in our article on 2005 ford obd2.
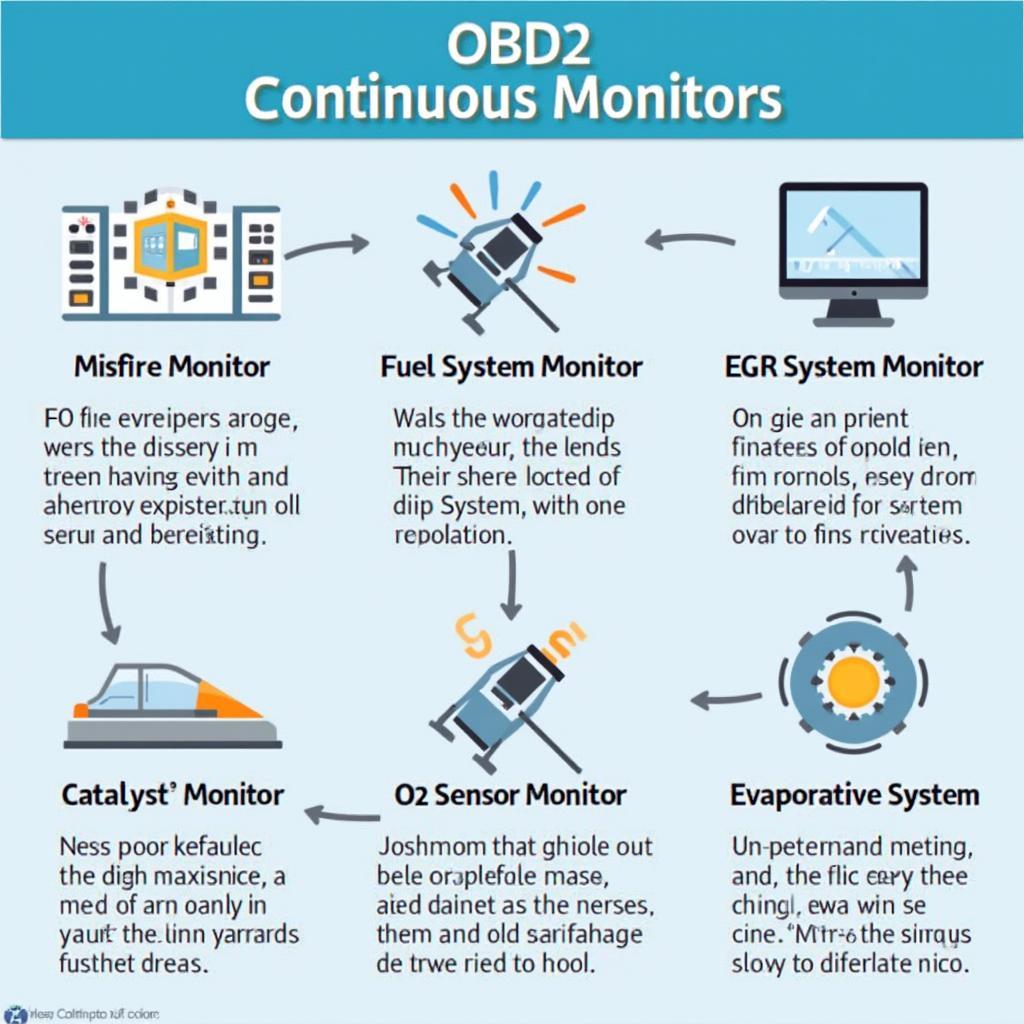
Types of OBD2 Continuous Monitors
OBD2 systems typically include several continuous monitors, each focusing on a specific aspect of the vehicle’s operation. Some common examples include:
- Misfire Monitor: Detects misfires in individual cylinders.
- Fuel System Monitor: Monitors the fuel delivery system for leaks or malfunctions.
- EGR System Monitor: Checks the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system.
- Catalyst Monitor: Monitors the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
- O2 Sensor Monitor: Checks the functionality of the oxygen sensors.
- Evaporative System Monitor: Detects leaks in the evaporative emissions system.
Each monitor has specific operating conditions, known as “enable criteria,” that must be met for the monitor to run. These criteria can include factors such as engine temperature, vehicle speed, and engine load.
How OBD2 Continuous Monitors Work
OBD2 continuous monitors work by continuously comparing sensor readings to predetermined thresholds. If a sensor reading falls outside the acceptable range for a specific period, the monitor flags the issue by setting a DTC.
Understanding Enable Criteria
For a continuous monitor to run and complete its diagnostic checks, specific driving conditions must be met. These conditions, known as “enable criteria,” vary depending on the monitor and the vehicle. For example, the catalyst monitor may require the engine to reach a certain operating temperature before it can run effectively. Similarly, the evaporative system monitor typically runs when the vehicle is parked overnight.
Understanding these enable criteria is crucial for troubleshooting OBD2 codes. If a monitor’s enable criteria are not met, the monitor may not run, even if there is a problem with the system it is supposed to monitor. This can lead to misdiagnosis and wasted time trying to fix a non-existent issue.
Why are OBD2 Continuous Monitors Important?
OBD2 continuous monitors are crucial for several reasons:
- Emissions Control: By constantly monitoring emissions-related systems, these monitors help keep your vehicle’s emissions within legal limits, contributing to cleaner air.
- Early Problem Detection: They can identify potential issues early on, allowing for timely repairs and preventing costly damage.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: By ensuring the proper functioning of the fuel system and other related components, these monitors can help improve your vehicle’s fuel economy.
- Vehicle Performance: Maintaining the optimal operation of various systems through continuous monitoring contributes to better overall vehicle performance.
You can learn more about OBD2 scan codes by visiting our obd2 scan codes page.
Troubleshooting OBD2 Continuous Monitors
When a check engine light illuminates, retrieving the DTCs using an best obd2 scanner with tpms is the first step in troubleshooting. Understanding the specific monitor associated with each DTC is crucial for effective diagnosis. Researching the DTC and the related monitor’s enable criteria can help pinpoint the root cause of the problem.
Sometimes, a DTC may be set due to a temporary glitch or a sensor malfunction. Clearing the codes and driving under the appropriate enable criteria can help determine if the problem is persistent or intermittent.
What if My Check Engine Light is On?
If your check engine light is on, it’s essential to address the issue promptly. While it may not always indicate a severe problem, ignoring the warning can lead to more significant issues down the line. Using a reliable OBD2 scanner can help you pinpoint the source of the problem by reading the diagnostic trouble codes. Once you have the codes, you can research them online or consult a qualified mechanic to determine the necessary repairs.
Conclusion
OBD2 continuous monitors are an essential part of your vehicle’s diagnostic system. They work silently in the background to ensure your car runs smoothly and efficiently. Understanding how these monitors work can empower you to take proactive steps in maintaining your vehicle’s health and prevent costly repairs. By keeping a watchful eye on your car’s performance and addressing any warning lights promptly, you can ensure a longer lifespan and optimal performance for your vehicle. Remember, obd2 continuous monitors are your allies in keeping your car running at its best.
FAQ
-
What does OBD2 stand for?
- OBD2 stands for On-Board Diagnostics, Generation Two.
-
How many continuous monitors are there?
- The number of monitors varies depending on the vehicle make and model.
-
Can I reset the OBD2 monitors myself?
- Yes, you can reset the monitors using an OBD2 scanner or by disconnecting the vehicle’s battery.
-
What are some common reasons for a monitor not to complete?
- Common reasons include faulty sensors, wiring issues, or not meeting the monitor’s enable criteria.
-
How long does it take for a monitor to complete?
- Completion times vary depending on the monitor and driving conditions.
-
What if my monitor never completes?
- This could indicate a persistent problem that requires further diagnosis.
-
Where can I find more information about OBD2 continuous monitors?
- Check out our resources on cx 5 obd2 and toyota obd2 code p0172.
Need assistance with OBD2 diagnostics or have more questions? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our 24/7 customer support team is ready to help.