The OBD2 code P0136 indicates a problem with the oxygen sensor circuit, specifically Bank 1 Sensor 2. This code can be confusing, so we’ll break down what it means, why it happens, and how to fix it. This article will guide you through everything you need to know about the obd2 cose p0136, helping you diagnose and resolve the issue effectively.
What Does the P0136 Code Mean?
The P0136 code refers to a malfunction in the oxygen sensor circuit for Bank 1 Sensor 2. “Bank 1” refers to the side of the engine containing cylinder #1. “Sensor 2” indicates the downstream oxygen sensor, located after the catalytic converter. This sensor monitors the efficiency of the catalytic converter. A P0136 code means the car’s computer (PCM or ECM) has detected a voltage reading outside the normal operating range for this sensor.
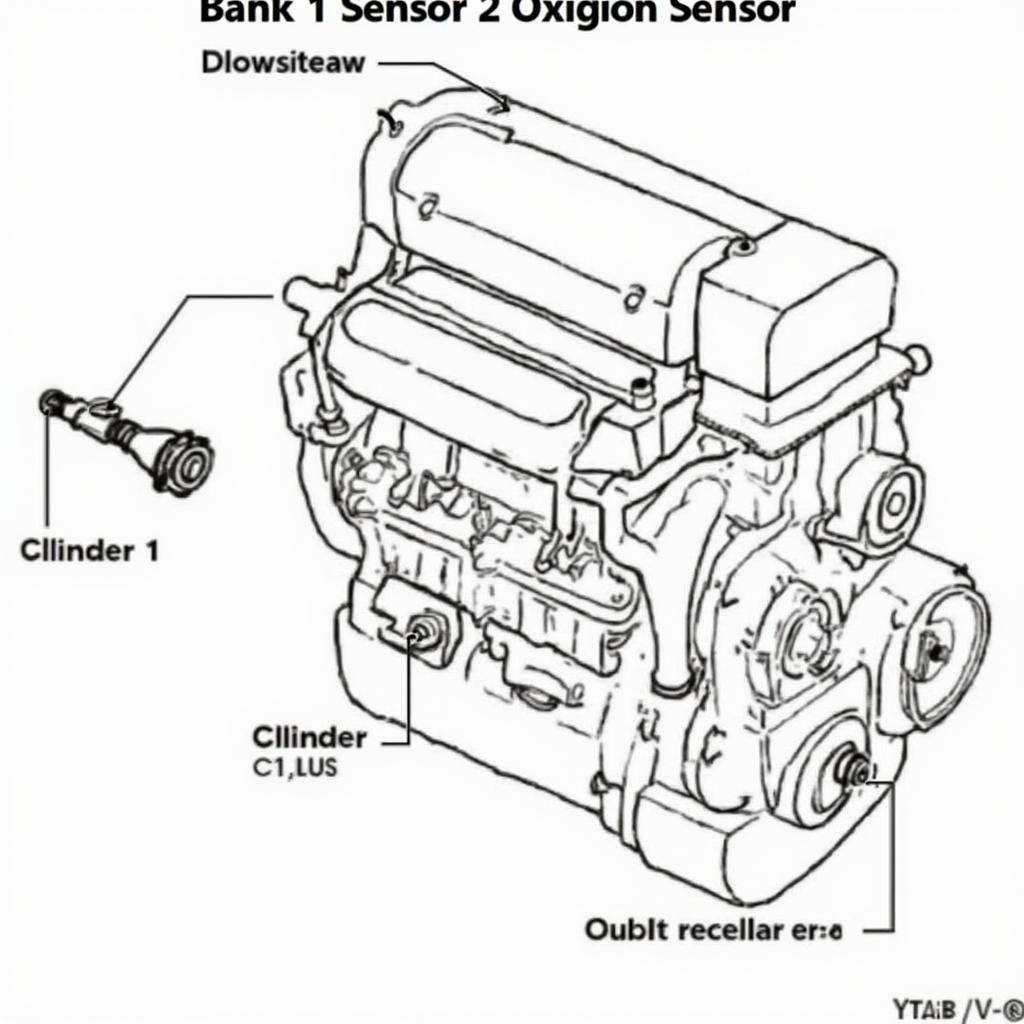 OBD2 Code P0136 Sensor Location
OBD2 Code P0136 Sensor Location
Causes of the OBD2 Code P0136
Several factors can trigger a P0136 code. Some of the most common causes include:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The sensor itself might be worn out or damaged, producing inaccurate readings.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring in the sensor circuit can disrupt the signal.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks before the sensor can introduce outside air, affecting the oxygen levels and sensor readings.
- Vacuum Leaks: These can alter the air/fuel mixture, impacting the exhaust gases and sensor readings.
- Faulty Catalytic Converter: While less common, a failing catalytic converter can also trigger this code.
- Blown Fuse: A blown fuse in the sensor circuit can interrupt power supply to the sensor.
Symptoms of a P0136 Code
While the check engine light is the most obvious symptom, other signs can indicate a P0136 issue:
- Decreased Fuel Economy: The engine might run richer to compensate for the perceived problem.
- Rough Idle or Misfires: Inaccurate sensor data can disrupt engine performance.
- Failed Emissions Test: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to higher emissions.
How to Diagnose and Fix a P0136 Code
Diagnosing a P0136 code requires a systematic approach:
-
Retrieve the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to confirm the P0136 code.
-
Inspect the Wiring: Check for any visible damage, corrosion, or loose connections in the sensor wiring and connector.
-
Check for Exhaust Leaks: Look for any holes or cracks in the exhaust system, particularly before the sensor.
-
Test the Sensor Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the sensor’s voltage output. Compare the readings with the manufacturer’s specifications.
-
Replace the Sensor (if necessary): If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one.
-
Repair Wiring or Exhaust Leaks: Address any wiring issues or exhaust leaks found during the inspection.
-
Clear the Code: After repairs, clear the code with an OBD2 scanner and verify that it doesn’t return.
“Regularly checking and maintaining your vehicle’s oxygen sensors is crucial for optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency,” says Michael Davis, ASE Certified Master Technician. “Addressing a P0136 code promptly can prevent further damage and costly repairs down the line.”
Conclusion
The obd2 cose p0136, indicating a problem with the downstream oxygen sensor, can impact your vehicle’s performance and emissions. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnostic steps, you can effectively address this issue and ensure your car runs smoothly.
“Don’t underestimate the importance of a functioning oxygen sensor,” adds Sarah Miller, Automotive Engineer. “It plays a vital role in maintaining the correct air/fuel mixture and reducing harmful emissions.”
FAQs
-
Can I drive with a P0136 code? While you might be able to drive for a short period, it’s best to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage and potential performance problems.
-
How much does it cost to replace an oxygen sensor? The cost varies depending on the vehicle and sensor type, but typically ranges from $100 to $300.
-
How often should oxygen sensors be replaced? Oxygen sensors typically last between 60,000 and 90,000 miles, but it’s best to consult your vehicle’s maintenance schedule.
-
Can a bad catalytic converter cause a P0136 code? Yes, a failing catalytic converter can sometimes trigger this code, although it’s less common than a faulty sensor.
-
What tools do I need to replace an oxygen sensor? You’ll typically need an oxygen sensor socket, a wrench set, and potentially penetrating oil.
-
Can I clear the code myself? Yes, you can clear the code with an OBD2 scanner.
-
Will the check engine light go off after replacing the sensor? The light might go off immediately, or it might take a few driving cycles.
Need Help?
For further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We have a 24/7 customer support team ready to help.
