Troubleshooting a no-spark condition on your 1997 Toyota can seem daunting, but with a little guidance and an OBD2 scanner, you can diagnose and potentially fix the issue yourself. This guide will walk you through the steps to identify the culprit behind your engine’s lack of spark and get you back on the road.
Before diving into the diagnostics, ensure your 1997 Toyota model year is indeed equipped with an OBD2 system. Models from 1996 onwards typically have this system.
Common Causes of a No Spark Condition
A no-spark condition means your engine isn’t receiving the electrical spark needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders. Several components could be responsible, and understanding the common culprits will guide your diagnostic journey.
- Crankshaft Position Sensor: This sensor tells the engine control unit (ECU) the position of the crankshaft, which is crucial for spark and fuel injection timing. A faulty sensor can disrupt this process, leading to a no-spark situation.
- Camshaft Position Sensor: Similar to the crankshaft sensor, the camshaft sensor relays the position of the camshaft to the ECU. This information ensures proper timing for spark and fuel delivery.
- Ignition Coil: The ignition coil is responsible for generating the high voltage needed to create the spark. If the coil fails, it won’t produce the necessary voltage.
- Distributor (If Equipped): Some older 1997 Toyota models may still use a distributor, responsible for distributing the high voltage from the ignition coil to the correct spark plug at the right time. Wear and tear can lead to a malfunctioning distributor.
- Spark Plug Wires: These wires transmit the high voltage from the distributor or coil packs to the spark plugs. Damaged or worn-out wires can cause the voltage to leak, resulting in a weak or no spark.
- Spark Plugs: Over time, spark plugs can wear down, become fouled, or have an increased gap. This can prevent them from sparking correctly.
- ECU: While less common, a faulty ECU can disrupt the spark signal.
How to Diagnose a No Spark Condition with an OBD2 Scanner
Your OBD2 scanner can be an invaluable tool in diagnosing a no-spark condition. While it won’t pinpoint the exact issue, it can reveal valuable clues. Here’s how:
- Connect your OBD2 scanner: Locate your vehicle’s OBD2 port (usually under the driver’s side dashboard) and connect your scanner.
- Turn on the ignition: Turn the key to the “on” position, but don’t start the engine.
- Read codes: Select the option to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) on your scanner. Note any codes related to the ignition system or engine sensors.
- P0335: Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- P0340: Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- P0351-P0354: Ignition Coil Primary/Secondary Circuit Malfunction
- P0300-P0304: Cylinder Misfire Detected (can be related to spark issues)
- Analyze the codes: Research the specific codes retrieved to understand which components or systems they relate to.
- Clear the codes: After noting the codes, clear them using your scanner.
- Attempt to start the engine: Try starting your Toyota. If the codes reappear, it strengthens the likelihood of a problem with the indicated component.
Further Diagnosis: Going Beyond the OBD2 Scanner
While your OBD2 scanner provides a starting point, further investigation is often needed to confirm the faulty component. Here are some additional steps:
1. Visually Inspect Key Components
Begin with a visual check of the components mentioned earlier. Look for:
- Damaged or loose wiring: Inspect the wiring harnesses around the ignition coils, distributor, and sensors for any signs of damage, burning, or loose connections.
- Worn spark plug wires: Examine the wires for cracks, burns, or excessive wear.
- Corrosion or dirt: Check the connections of the sensors, distributor cap, and spark plugs for any corrosion or dirt buildup.
2. Test the Ignition Coil
A multimeter can be used to test the resistance of the ignition coil. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for specific resistance values. If the readings are outside the specified range, the coil likely needs replacement.
3. Check for Spark
With the engine off, carefully remove a spark plug wire and insert a spark plug tester or a spare spark plug. Connect the tester or spare plug to the wire, ground the metal part of the tester or plug, and have a helper crank the engine briefly. Observe the spark plug gap for a strong, blue spark. If there’s no spark or a weak, yellow spark, it could point to a problem with the coil, distributor, or wiring.
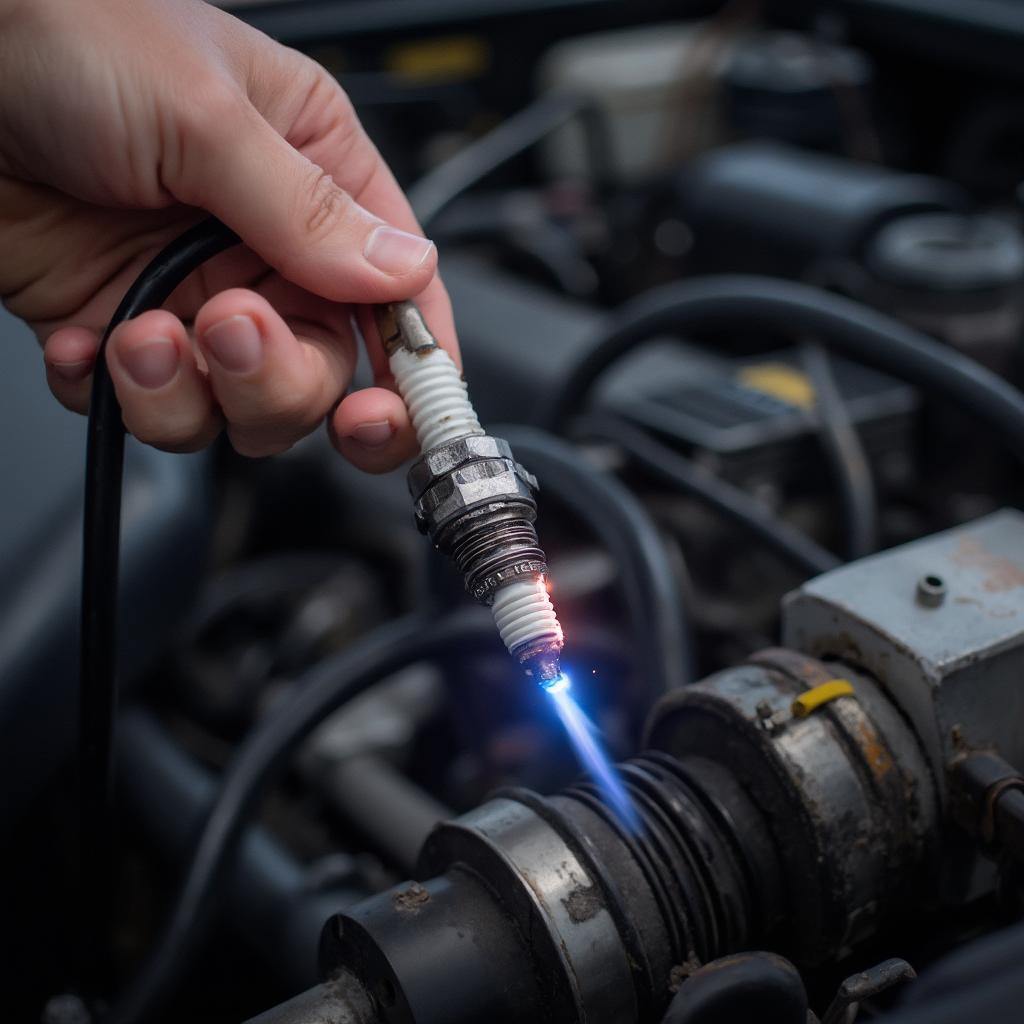 Spark Plug Tester
Spark Plug Tester
Conclusion
Diagnosing a no spark condition on your 1997 Toyota doesn’t have to be a mystery. By understanding the common causes, utilizing your OBD2 scanner effectively, and performing some basic checks, you can narrow down the problem and potentially fix it yourself. Remember to consult your vehicle’s repair manual for specific instructions and safety precautions.
If you’re uncomfortable working on your vehicle or the problem persists, consult a qualified mechanic for further assistance.
FAQs
Q: Can a bad battery cause a no spark condition?
A: While a very weak battery might struggle to power all systems, it’s unlikely to cause a complete no spark condition. The starter motor draws far more power than the ignition system.
Q: Can I drive my car with a no spark condition?
A: No, driving a car with a no spark condition is impossible as the engine will not run.
Q: How often should I replace my spark plugs?
A: Refer to your owner’s manual for specific recommendations, but generally, spark plugs should be replaced every 30,000 miles or as recommended by your manufacturer.
Need more help diagnosing your car troubles? Contact our expert team via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880 or Email: [email protected]. We offer 24/7 support to help get you back on the road.