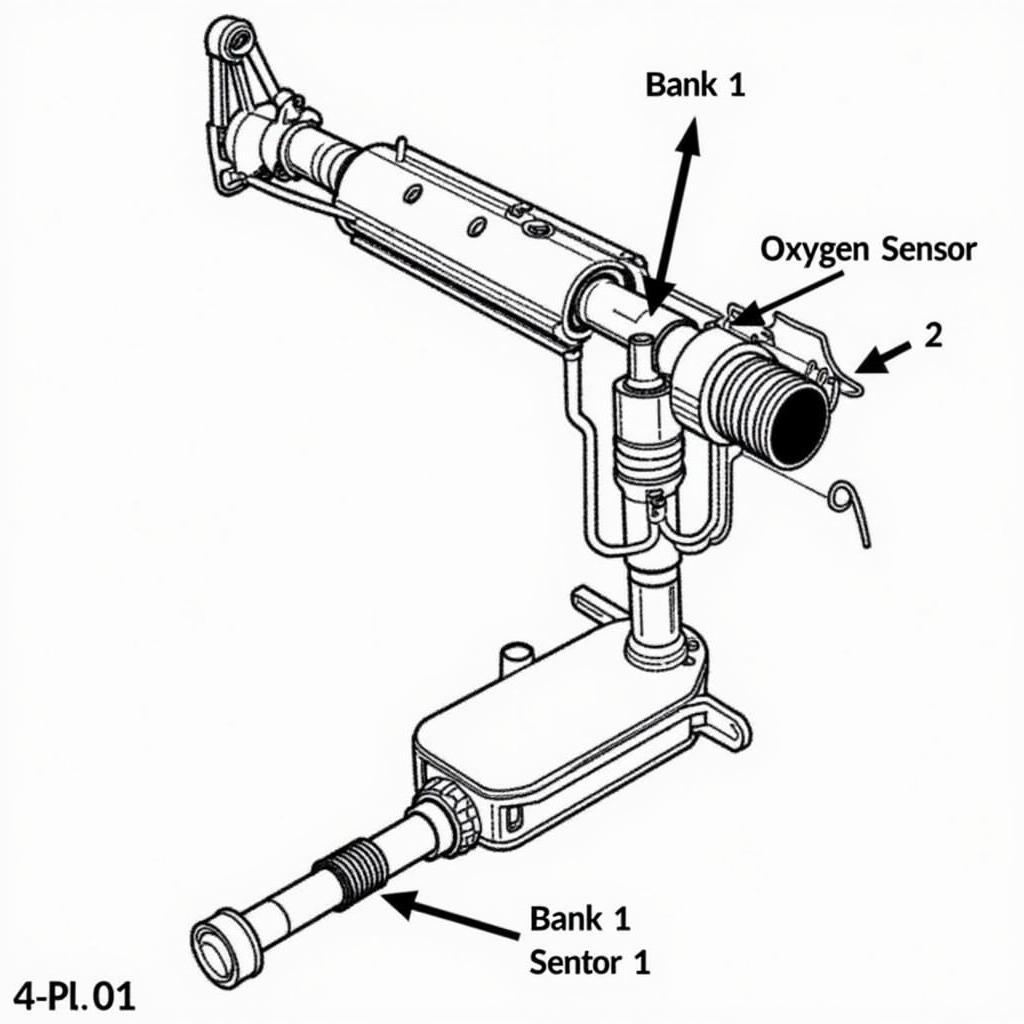
The dreaded “Check Engine” light can illuminate for a myriad of reasons, but the OBD2 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0135 points to a specific culprit: a problem with the oxygen sensor heater circuit in Bank 1, Sensor 1.
This article delves deep into the intricacies of the P0135 code, empowering you with the knowledge to understand its causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions.
Decoding the P0135 Code
The P0135 code specifically indicates a malfunction in the heating circuit of the upstream oxygen sensor (sensor 1) located on engine bank 1 (typically the bank containing cylinder #1). This sensor plays a crucial role in optimizing fuel economy and minimizing emissions.
Importance of the Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit
Modern vehicles rely on heated oxygen sensors (HO2S) for optimal performance. The heater circuit facilitates quicker sensor operation, enabling the engine control module (ECM) to enter closed-loop mode faster, especially during cold starts.
In closed-loop mode, the ECM uses data from the oxygen sensor to fine-tune the air-to-fuel ratio, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing harmful emissions.
Causes of a P0135 Code
A P0135 code can stem from a variety of issues, often related to electrical faults or sensor degradation. Common culprits include:
- Faulty oxygen sensor: A damaged or worn-out oxygen sensor is the most frequent cause. Over time, exposure to extreme temperatures and exhaust gases can degrade the sensor’s heating element.
- Damaged wiring harness: The wiring harness connecting the oxygen sensor to the ECM can become frayed, corroded, or broken, disrupting the heater circuit.
- Blown fuse: A blown fuse in the oxygen sensor heater circuit can completely cut off power to the heater.
- Faulty ECM: Although less common, a malfunctioning ECM can misinterpret sensor signals or fail to provide power to the heater circuit.
Recognizing the Symptoms
While the “Check Engine” light is a telltale sign, other symptoms might accompany a P0135 code, including:
- Decreased fuel economy: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor heater can lead to an incorrect air-fuel mixture, reducing fuel efficiency.
- Rough engine idle: An imbalanced air-fuel ratio can cause the engine to idle roughly or stall.
- Increased emissions: A rich air-fuel mixture can result in higher emissions, potentially causing your vehicle to fail emissions tests.
Diagnosing the P0135 Code
Accurately diagnosing the root cause of a P0135 code requires a systematic approach, often involving the following steps:
- Read the code: Utilize an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the stored DTCs. Verify that P0135 is present.
- Visually inspect the oxygen sensor and wiring: Examine the oxygen sensor for physical damage, debris, or excessive carbon buildup. Check the wiring harness for cuts, burns, or loose connections.
- Test the heater circuit: Using a multimeter, test for voltage and resistance in the oxygen sensor heater circuit. This step helps determine if the heater element is receiving power.
- Check the fuse: Locate and inspect the fuse associated with the oxygen sensor heater circuit. Replace if blown.
- Inspect the ECM: If other components check out, the ECM might require inspection by a qualified technician.
“A thorough diagnosis is key when addressing P0135. Start with visual inspections and progress to electrical testing to pinpoint the fault,” advises seasoned automotive diagnostician, John Miller.
Addressing the Issue
Once diagnosed, resolving a P0135 code generally involves:
- Replacing the oxygen sensor: If the sensor is faulty, replacement is the most effective solution. Always use a high-quality OEM or equivalent sensor.
- Repairing the wiring harness: Damaged wires or connections within the harness can be repaired or replaced to restore proper circuit functionality.
- Replacing the fuse: Replace a blown fuse with one of the correct amperage rating.
- Addressing ECM issues: ECM malfunctions might necessitate reprogramming or replacement, which is best handled by a qualified technician.
Preventative Measures
Preventative steps can help avoid future P0135 codes and ensure optimal oxygen sensor performance:
- Regular maintenance: Adhering to your vehicle’s recommended maintenance schedule, including timely spark plug and air filter replacements, can promote efficient combustion and prolong sensor life.
- Quality fuel: Using high-quality fuel with the recommended octane rating minimizes deposits that can contaminate the oxygen sensor.
- Addressing engine issues promptly: Promptly addressing engine performance issues, such as misfires or oil leaks, can prevent damage to the oxygen sensor and other components.
Conclusion
Understanding the OBD2 DTC P0135 is crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle performance and minimizing emissions. Early diagnosis and appropriate action can prevent further damage and costly repairs.
Remember, while this guide provides valuable insights, seeking assistance from a qualified mechanic is recommended for accurate diagnosis and repair.
FAQs about OBD2 Code P0135
1. Can I drive my car with a P0135 code?
While driving short distances with a P0135 code might be possible, it’s not recommended. Ignoring the code can lead to further damage and potentially leave you stranded.
2. How much does it cost to fix a P0135 code?
The repair cost for a P0135 code varies depending on the underlying cause. Oxygen sensor replacement typically ranges from $100 to $300, while wiring harness repairs can cost between $50 and $200.
3. Can a bad oxygen sensor damage my catalytic converter?
Yes, a malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to a rich air-fuel mixture, potentially damaging the catalytic converter over time.
4. How long does it take to replace an oxygen sensor?
Replacing an oxygen sensor is a relatively straightforward procedure, typically taking a mechanic less than an hour.
5. How can I prevent oxygen sensor problems in the future?
Following your vehicle’s recommended maintenance schedule, using high-quality fuel, and promptly addressing engine issues are key to preventing future oxygen sensor problems.
Need More Help?
For further assistance with OBD2 codes and vehicle diagnostics, explore these resources:
Still have questions? Our team of automotive experts is here to help 24/7. Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, or email: [email protected].