OBD2 DTC reader codes are essential for diagnosing car problems. This guide explores everything you need to know about these codes, from their meaning and how to read them to using them effectively for troubleshooting and repair. Learn how to interpret these codes and empower yourself to understand your vehicle’s health. Let’s dive in!
What are OBD2 DTC Reader Codes?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system that allows you to access diagnostic information from your vehicle’s computer. DTC, or Diagnostic Trouble Code, is a code that indicates a specific malfunction within a vehicle system. These codes are essential for mechanics and car owners alike, providing a starting point for diagnosing and fixing car issues. An excel obd2 scanner app can be incredibly useful for organizing and tracking these codes.
How Do OBD2 DTC Reader Codes Work?
When your car’s computer detects a problem, it stores a corresponding DTC. These codes are five-character alphanumeric sequences that follow a specific structure. The first character represents the system where the fault occurred (e.g., “P” for Powertrain, “B” for Body, “C” for Chassis, “U” for Network). The second character indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific. The remaining three characters specify the exact nature of the problem. Understanding this structure allows you to quickly identify the area and type of malfunction.
How to Read OBD2 DTC Reader Codes?
Reading OBD2 DTC reader codes is easier than you think. You’ll need an OBD2 scanner, which you can plug into your car’s OBD2 port (usually located under the dashboard). The scanner will retrieve the stored DTCs. You can then look up the meaning of these codes online, in a repair manual, or using specialized software. Understanding how use obd2 scanners and interpret the codes can save you time and money in the long run.
What do the different characters in an OBD2 code mean?
The standardized format makes understanding the basics of OBD2 codes simple. Let’s break down the five characters:
- Character 1: System. P (Powertrain), B (Body), C (Chassis), U (Network).
- Character 2: Type. 0 (Generic – Standardized across all makes and models), 1 (Manufacturer specific).
- Characters 3-5: The specific problem. These digits pinpoint the exact nature of the malfunction within the identified system.
Common OBD2 DTC Reader Codes and Their Meanings
There are thousands of potential OBD2 DTC reader codes. Some of the more common ones include:
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
Understanding these codes and their potential causes can empower you to address issues effectively. Check out our resources on pending obd2 code to learn more about codes that haven’t yet triggered a check engine light.
What are some common causes of OBD2 codes?
From loose gas caps to faulty sensors, many issues can trigger OBD2 codes. Some common culprits include problems with the oxygen sensors, catalytic converter, mass airflow sensor, and spark plugs.
“A proper diagnosis is crucial. Don’t jump to conclusions based on just the code,” advises John Smith, Senior Automotive Technician at Acme Auto Repair. “Use the codes as a starting point, then perform a thorough inspection to pinpoint the root cause.”
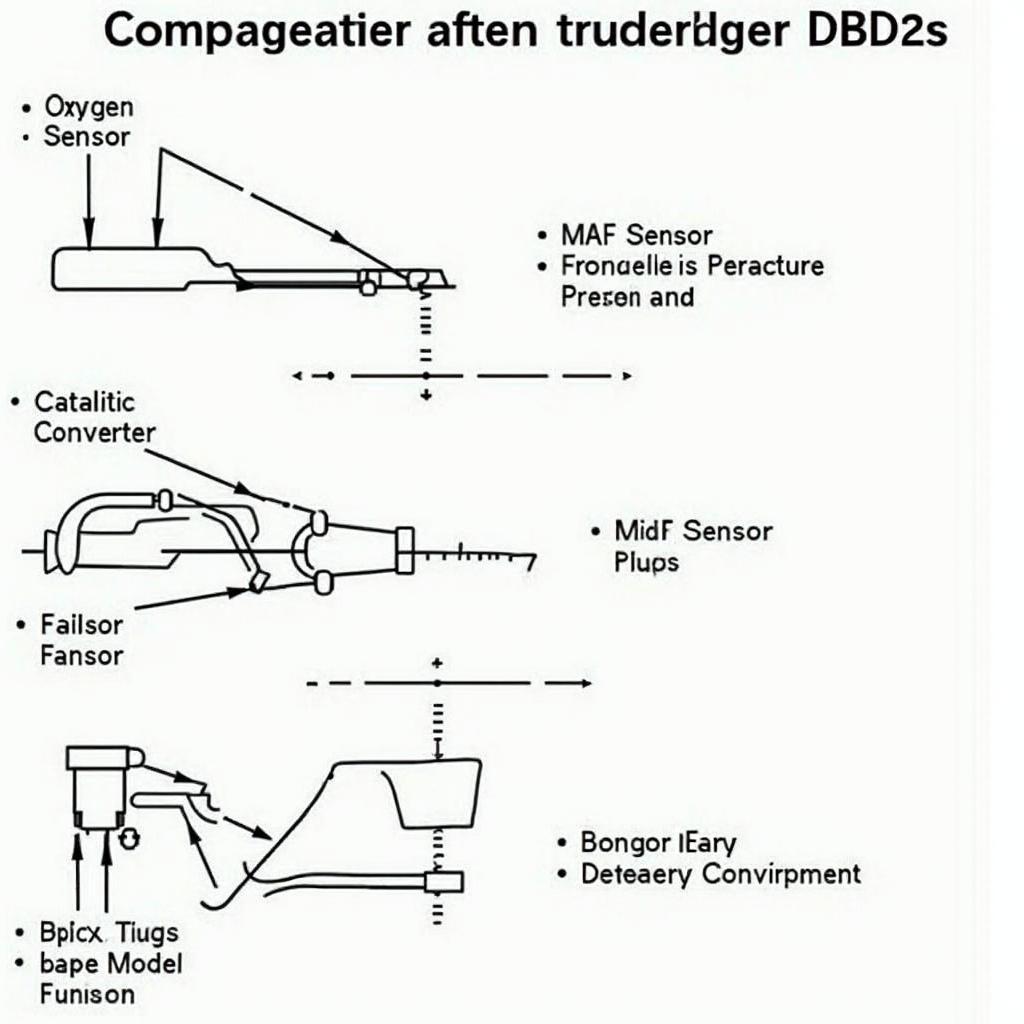 Common OBD2 Code Causes
Common OBD2 Code Causes
Using OBD2 DTC Reader Codes for Troubleshooting
OBD2 DTC reader codes are invaluable tools for troubleshooting car problems. They help narrow down the potential causes, saving you time and potentially costly diagnostic fees. However, it’s important to remember that these codes are only indicators, not definitive diagnoses. Further investigation is always necessary. For instance, knowing the regulations surrounding obd2 cars usa can help you understand the legal requirements related to emissions and diagnostics.
How can I use OBD2 codes to fix my car?
While OBD2 codes provide valuable clues, they don’t offer a complete repair solution. Consult a reliable repair manual or seek professional assistance for complex issues. Remember, accurate diagnosis is the first step towards a successful repair.
“Understanding these codes is like having a secret language to communicate with your car,” says Jane Doe, Automotive Engineer at Innovative Auto Solutions. “They give you a head start in understanding what might be going wrong and help you make informed decisions about repairs.”
Conclusion
OBD2 DTC reader codes are essential for understanding your vehicle’s health. By learning how to read and interpret these codes, you can effectively troubleshoot car problems and make informed repair decisions. While understanding codes related to specific models, like the 2018 audi obd2 system, can be helpful, understanding the general principles of OBD2 codes is crucial for any car owner. This knowledge empowers you to take control of your car maintenance and avoid unnecessary expenses.
FAQ
- What does OBD2 stand for? On-Board Diagnostics II
- Where can I find the OBD2 port in my car? Usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Do all cars have OBD2 ports? Most cars manufactured after 1996 in the US are OBD2 compliant.
- Can I fix my car just by knowing the OBD2 code? Codes are indicators, not solutions. Further investigation is always needed.
- How much does an OBD2 scanner cost? Prices vary, but affordable options are available.
- What if I clear the code and it comes back? The underlying problem hasn’t been fixed and needs further diagnosis.
- What should I do if I don’t understand the OBD2 code? Consult a repair manual or seek professional advice.
Need Help? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer support team is available 24/7.