The OBD2 EGAR5 incorrect ratio code, sometimes referred to as the “EGR Ratio Incorrect” code, can be a frustrating issue for vehicle owners. This code indicates a problem with the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system, specifically the ratio of exhaust gas being recirculated back into the engine. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of the EGAR5 code, its causes, symptoms, and how to diagnose and fix it.
What is the EGAR5 Code?
The EGAR5 code is triggered when the Engine Control Module (ECM), the brain of your vehicle, detects an inconsistency in the amount of exhaust gas being recirculated compared to the expected amount. The EGR system plays a crucial role in reducing harmful NOx emissions by redirecting a portion of exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber. This lowers combustion temperatures, thereby reducing NOx formation.
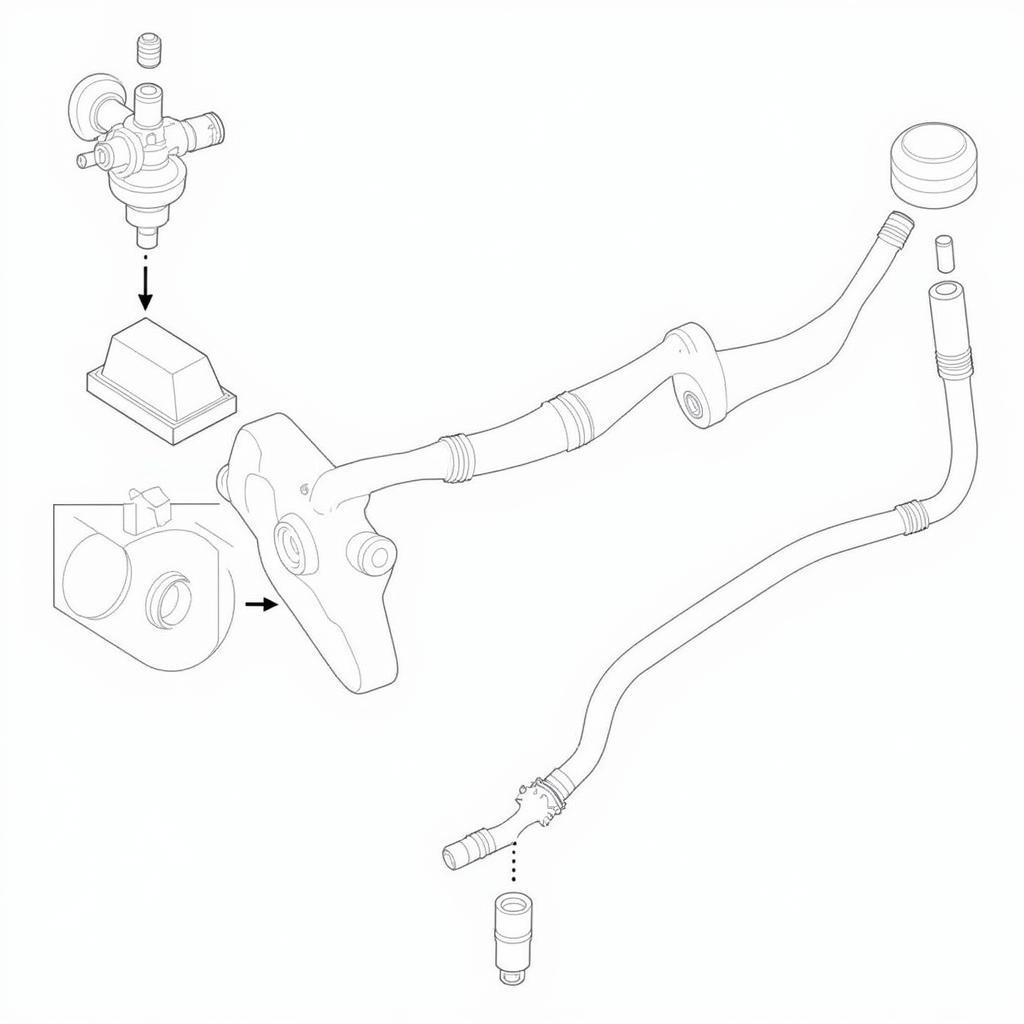 EGR System Diagram
EGR System Diagram
When the actual EGR ratio deviates significantly from the calculated value determined by the ECM, the EGAR5 code is stored, and the check engine light illuminates on your dashboard.
Causes of the EGAR5 Code
Several factors can contribute to an EGAR5 incorrect ratio code:
- Faulty EGR Valve: The EGR valve itself is a common culprit. It can become stuck open, closed, or operate erratically due to carbon buildup, vacuum leaks, or electrical issues.
- Clogged EGR Passages: Over time, carbon deposits can accumulate within the EGR passages, restricting exhaust gas flow and causing an incorrect ratio.
- Malfunctioning EGR Solenoid: The EGR solenoid controls the vacuum or electronic signal that actuates the EGR valve. A faulty solenoid can disrupt the valve’s operation.
- Vacuum Leaks: Vacuum leaks in the EGR system, particularly in hoses or the EGR valve diaphragm, can affect EGR flow and trigger the code.
- Faulty DPFE Sensor: The Differential Pressure Feedback EGR (DPFE) sensor monitors the pressure difference across the EGR valve, providing feedback to the ECM. A malfunctioning DPFE sensor can lead to inaccurate EGR ratio calculations.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring harnesses connected to EGR components can interrupt communication signals, causing erratic behavior.
Symptoms of an EGAR5 Code
While the check engine light is the most obvious symptom, other indicators might suggest an EGAR5 code:
- Rough Idle: An incorrect EGR ratio can disrupt the air-fuel mixture during idle, leading to a rough or erratic idle.
- Engine Stalling: In severe cases, excessive EGR flow can cause the engine to stall, especially at low speeds.
- Reduced Engine Performance: A malfunctioning EGR system can affect engine performance, resulting in reduced power, hesitation, or poor acceleration.
- Increased NOx Emissions: The primary function of the EGR system is to reduce NOx emissions. A faulty system can lead to increased emissions, potentially failing emissions tests.
Diagnosing the EGAR5 Code
Diagnosing the EGAR5 code requires a systematic approach:
- Read the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the specific code stored in the ECM. Note any other codes present, as they might be related.
- Inspect EGR Components: Visually inspect the EGR valve, solenoid, and associated hoses for any signs of damage, carbon buildup, or loose connections.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Use a vacuum gauge or a hand-held vacuum pump to test for leaks in the EGR system. Pay close attention to hoses and connections.
- Test EGR Valve Operation: Apply vacuum directly to the EGR valve using a hand-held pump. The valve should open, and you should notice a change in engine idle.
- Test DPFE Sensor: Consult your vehicle’s repair manual for specific DPFE sensor testing procedures. Typically, this involves checking for proper voltage signals using a multimeter.
Fixing the EGAR5 Code
The repair for the EGAR5 code depends on the underlying cause:
- Replace Faulty Components: Replace any faulty components identified during the diagnostic process, such as the EGR valve, solenoid, DPFE sensor, or damaged wiring harnesses.
- Clean EGR Passages: Use a suitable EGR system cleaner or manually clean the EGR valve and passages to remove carbon buildup.
- Repair Vacuum Leaks: Replace any cracked, loose, or damaged vacuum hoses and ensure all connections are tight.
- Consult a Mechanic: If you’re unsure about any step or the diagnosis points to a more complex issue, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic.
Preventing Future EGAR5 Codes
Regular maintenance can help prevent future EGAR5 codes:
- Regular EGR System Inspections: Include EGR system inspections during routine maintenance checks.
- Fuel System Cleaning: Using high-quality fuel and periodic fuel system cleaners can help reduce carbon buildup in the EGR system.
- Timely Repairs: Address any EGR-related issues promptly to prevent further damage or complications.
Expert Insight
“The EGR system is critical for emissions control and engine performance,” says John Smith, a certified master mechanic with over 20 years of experience. “Regular maintenance, including EGR system inspections and cleaning, can prevent costly repairs down the road.”
Conclusion
The EGAR5 incorrect ratio code signals a problem with your vehicle’s EGR system. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures, you can address the issue effectively. Remember that regular maintenance and timely repairs are crucial for keeping your EGR system functioning correctly and ensuring optimal engine performance and emissions control.
FAQs
Q: Can I still drive my car with an EGAR5 code?
A: While you might be able to drive for a short distance, it’s not advisable. Driving with a faulty EGR system can lead to further engine damage and increase emissions.
Q: How much does it cost to fix an EGAR5 code?
A: The repair cost depends on the underlying cause. A simple EGR valve cleaning might cost around $100-$200, while replacing the EGR valve or other components can range from $200 to $700 or more.
Q: Can I clean the EGR valve myself?
A: Yes, you can clean the EGR valve yourself, but it requires some mechanical aptitude. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for specific instructions.
Q: How often should I clean my EGR valve?
A: It’s generally recommended to have the EGR system inspected and cleaned every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, but consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific recommendations.
Related Resources:
For more information on OBD2 codes and car diagnostics, you can refer to these resources:
If you are experiencing issues with your vehicle and need assistance, please do not hesitate to contact us:
- WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880
- Email: [email protected]
Our team of automotive experts is available 24/7 to provide you with support and guidance.