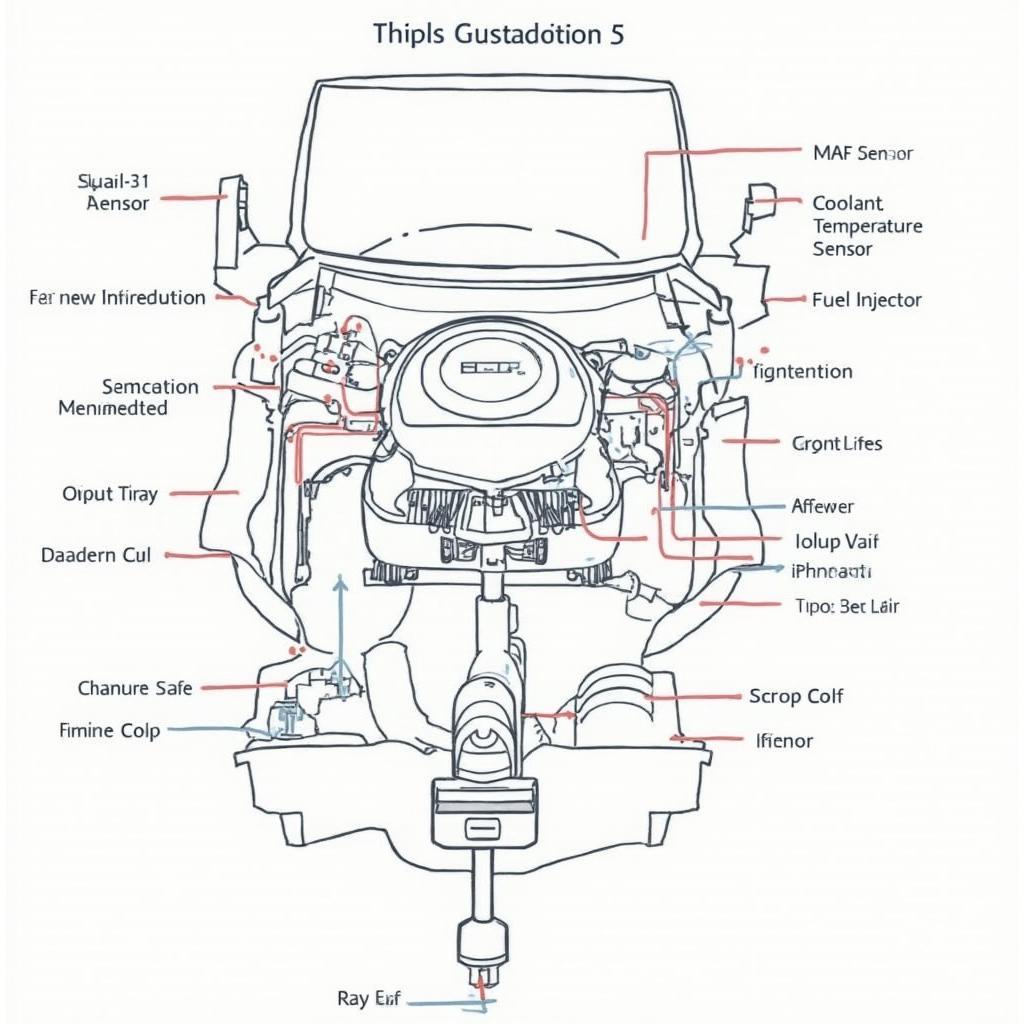
The obd2 engine computer, also known as the Engine Control Unit (ECU) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM), is the central processing unit of your vehicle’s engine management system. It’s responsible for monitoring and controlling a vast array of functions, ensuring optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. In this article, we’ll delve deep into the world of the OBD2 engine computer, exploring its functionalities, common issues, diagnostic procedures, and much more.
What is an OBD2 Engine Computer?
The OBD2 engine computer is a sophisticated electronic control unit that gathers data from numerous sensors located throughout the engine and other related systems. It uses this data to make real-time adjustments to parameters such as fuel injection timing, ignition timing, and air-fuel mixture. These adjustments optimize engine performance, minimize emissions, and ensure smooth operation. Think of it as the brain of your car, constantly making decisions to keep everything running smoothly. You can even use an obd2 for diesel engine computer.
How Does the OBD2 Engine Computer Work?
The OBD2 engine computer operates on a continuous loop of input, processing, and output. It receives input signals from various sensors, including the oxygen sensor, mass airflow sensor (MAF), manifold absolute pressure sensor (MAP), and coolant temperature sensor. The ECU then processes this data using pre-programmed algorithms and look-up tables. Based on the processed data, the ECU sends output signals to actuators, such as fuel injectors, ignition coils, and the throttle valve, controlling various engine functions.
Common OBD2 Engine Computer Problems
Like any other electronic component, the obd2 engine computer can malfunction. Common problems include:
- Failed sensors: A faulty sensor can send incorrect data to the ECU, leading to misdiagnosis and improper engine control.
- Wiring issues: Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt communication between the ECU and other components.
- Software glitches: Errors in the ECU’s software can cause erratic behavior and performance issues.
- ECU failure: In some cases, the ECU itself can fail, requiring replacement.
Diagnosing OBD2 Engine Computer Problems
Diagnosing obd2 engine computer problems requires specialized tools and knowledge. OBD2 scanners, like the ones reviewed on OBDFree, are invaluable for retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ECU’s memory. These codes provide clues about the nature of the problem and help pinpoint the faulty component. For example, you can use free cell phone obd2 apps to help you diagnose problems.
How to Reset Your OBD2 Engine Computer?
Sometimes, a simple reset can resolve minor glitches in the obd2 engine computer. This can be done by disconnecting the battery for a short period or using an OBD2 scanner to clear the DTCs. Learn more about how to reset obd2 after new ba.
The Future of OBD2 Engine Computers
OBD2 engine computers are constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and integrated with other vehicle systems. Future developments include advanced diagnostics, predictive maintenance capabilities, and enhanced cybersecurity features. Some OBD2 software can be used for obd2 computer software abs srs airbag transmission and engine. There are many interesting OBD2 projects you can explore, such as using an obd2 python example.
Conclusion
The obd2 engine computer is a critical component of modern vehicles, playing a vital role in engine management, emissions control, and overall performance. Understanding its functionalities and potential problems empowers car owners to make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs.
FAQ
- What does OBD2 stand for? On-Board Diagnostics, Second Generation.
- Can I replace my OBD2 engine computer myself? It’s recommended to have a qualified mechanic handle ECU replacement.
- How much does an OBD2 engine computer cost? Prices vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle.
- What is a DTC? A Diagnostic Trouble Code is a code stored in the ECU’s memory indicating a specific problem.
- How can I prevent OBD2 engine computer problems? Regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent many ECU issues.
- What are some signs of a failing OBD2 engine computer? Symptoms include poor fuel economy, rough idling, and check engine light illumination.
- How often should I have my OBD2 system checked? It’s a good idea to have your OBD2 system checked annually or as part of your regular vehicle maintenance.
Common OBD2 Engine Computer Situations
- Check Engine Light On: This is the most common indicator of a potential issue with your obd2 engine computer or a related component.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning ECU can lead to inefficient fuel consumption.
- Rough Idling or Stalling: The engine may idle roughly or stall due to incorrect fuel or ignition timing.
- Reduced Engine Performance: A faulty ECU can negatively impact engine power and acceleration.
Explore More OBD2 Resources on OBDFree
- Learn about OBD2 scanners for specific car makes and models.
- Find troubleshooting guides for common OBD2 problems.
- Stay updated on the latest advancements in OBD2 technology.
Need assistance? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our 24/7 customer support team is ready to help.