OBD2 engineering explained involves understanding the intricate systems and protocols that allow us to diagnose vehicle problems. This article delves into the core concepts of OBD2, exploring its history, functionality, and the engineering behind this essential automotive technology. Learn how OBD2 empowers both professionals and car enthusiasts to troubleshoot and maintain their vehicles effectively.
Understanding the Basics of OBD2 Engineering
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics, second generation, is a standardized system that allows external devices to access a vehicle’s diagnostic data. At its core, OBD2 engineering revolves around the communication protocols and electronic control units (ECUs) within a vehicle. These ECUs monitor various systems, from the engine and transmission to the emissions system and airbags. When a fault occurs, the ECU stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), which can be retrieved using an obd2 code reader argos.
The Role of Protocols in OBD2 Engineering
OBD2 utilizes several communication protocols, including ISO 9141-2, KWP2000, SAE J1850 PWM, SAE J1850 VPW, and CAN (Controller Area Network). These protocols dictate how data is transmitted between the OBD2 scanner and the vehicle’s ECUs. Understanding these protocols is crucial for designing and using OBD2 diagnostic tools effectively. CAN, for instance, has become increasingly prevalent due to its higher data transfer rate and robustness.
The engineering behind OBD2 ensures that the diagnostic data is standardized, making it accessible regardless of the vehicle’s make or model. This standardization simplifies the diagnostic process for technicians and allows for the development of versatile OBD2 scanners.
“The beauty of OBD2 engineering lies in its standardization,” says automotive engineer Dr. Emily Carter. “It’s a universal language that allows any compatible scanner to communicate with any vehicle, simplifying diagnostics across the board.”
Delving into Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs are the cornerstone of OBD2 diagnostics. 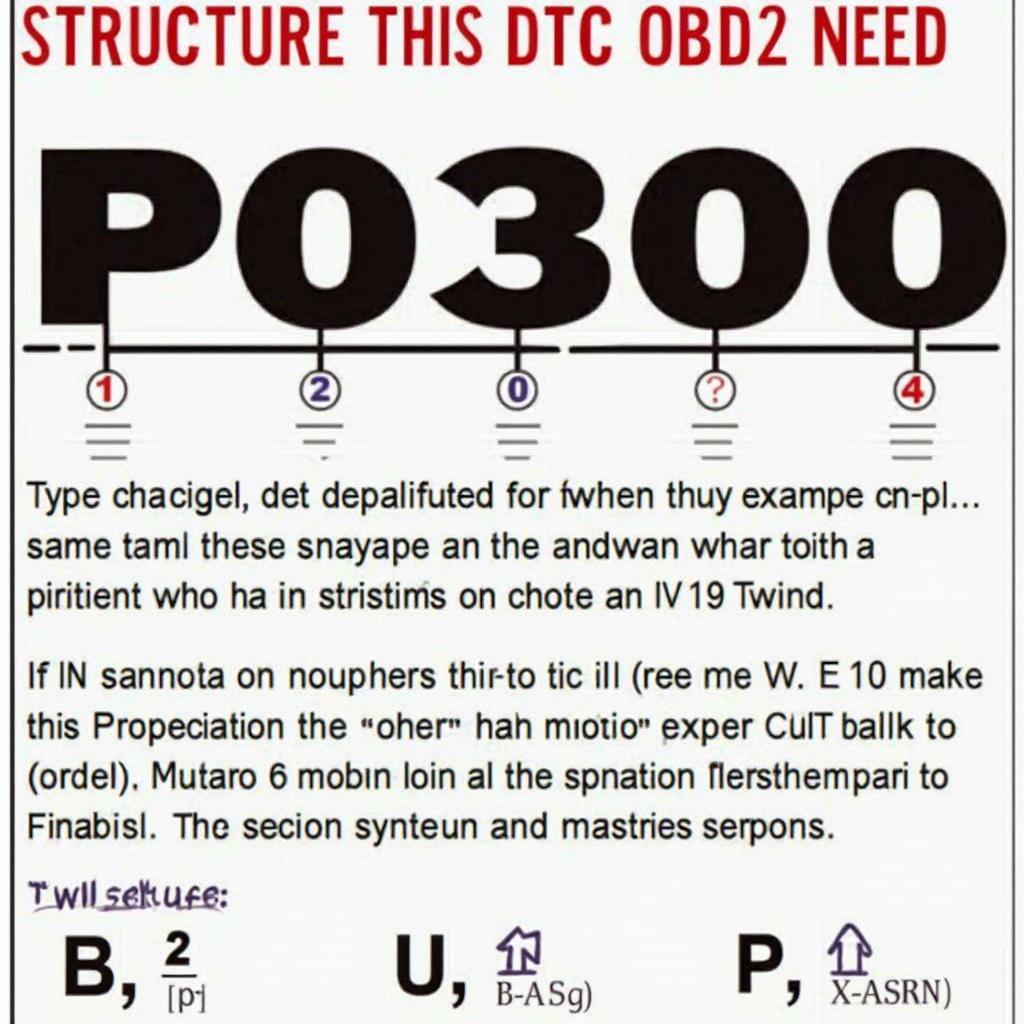 OBD2 DTC Structure Explained These codes provide specific insights into the nature and location of a vehicle fault. They consist of five characters: a letter and four numbers. The letter indicates the system affected (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network). The numbers further specify the type and area of the fault.
OBD2 DTC Structure Explained These codes provide specific insights into the nature and location of a vehicle fault. They consist of five characters: a letter and four numbers. The letter indicates the system affected (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network). The numbers further specify the type and area of the fault.
Decoding DTCs and Their Significance
Understanding how to decode DTCs is essential for effective diagnostics. kobra wireless obd2 car code reader vehicle compatibility can be valuable tools in interpreting these codes. While generic codes are standardized across all OBD2-compliant vehicles, manufacturers may also use enhanced codes specific to their models. These enhanced codes provide more granular information about the fault.
“DTCs are like clues in a detective novel,” explains Dr. Carter. “They guide you towards the root cause of the problem, helping you pinpoint the faulty component or system.”
The Future of OBD2 Engineering
OBD2 technology continues to evolve. With the rise of connected cars and the Internet of Things (IoT), OBD2 is becoming increasingly integrated with other vehicle systems. Remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and data-driven insights are just some of the emerging applications of this technology. Understanding obd2 vs obdii is also becoming increasingly important as technology advances.
What is the future of OBD2? The future lies in enhanced connectivity, enabling more sophisticated diagnostics and vehicle management capabilities.
Emerging Trends in OBD2
- Remote Diagnostics: Allows mechanics to access and analyze vehicle data remotely, enabling faster and more efficient troubleshooting.
- Predictive Maintenance: Uses OBD2 data to predict potential failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
- Data-Driven Insights: Enables manufacturers to collect valuable data on vehicle performance and usage, informing design improvements and personalized services.
“The future of OBD2 is bright,” comments Dr. David Miller, another leading automotive expert. “We’re moving towards a world where vehicles can diagnose themselves and communicate their needs proactively.”
Conclusion
OBD2 engineering is a complex yet vital aspect of modern automotive technology. Understanding its principles, from communication protocols to DTC interpretation, empowers both professionals and car enthusiasts to effectively diagnose and maintain their vehicles. As OBD2 continues to evolve, it promises to play an even more critical role in the future of the automotive industry, particularly with the growth of connected vehicles and data-driven insights. Remember to check out resources on specific OBD2 codes like the p2000 obd2 code for more detailed information.
FAQ
- What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
- How do I use an OBD2 scanner?
- What are the most common OBD2 codes?
- Can I fix my car myself using OBD2 information?
- Where can I find more information on specific OBD2 codes?
- How often should I check my car with an OBD2 scanner?
- What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
Need help with your car diagnostics? Contact us on WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.


