OBD2 exhaust codes are the key to unlocking the mysteries of your vehicle’s emission system. These codes, generated by your car’s onboard diagnostic system, pinpoint issues that can impact both performance and the environment. Understanding these codes can save you time, money, and frustration.
Exhaust system problems can be tricky. A failing catalytic converter might not trigger a check engine light immediately, but it can significantly reduce fuel efficiency. Similarly, a faulty oxygen sensor can lead to increased emissions and poor engine performance. OBD2 exhaust codes provide a crucial starting point for diagnosing these problems. They are like a roadmap, guiding you towards the specific area needing attention. For instance, P0420, a common OBD2 exhaust code, indicates a problem with the catalytic converter system. Knowing this allows you to focus your troubleshooting efforts and avoid unnecessary repairs. This article will equip you with the knowledge to interpret these codes and take the necessary steps to fix them.
Decoding OBD2 Exhaust Codes: A Comprehensive Guide
OBD2 exhaust codes follow a standardized format. The first letter, “P,” indicates a powertrain code, related to the engine and transmission. The second character is either “0,” for a generic code, or “1,” for a manufacturer-specific code. The next two digits pinpoint the specific system or component involved. Finally, the last two digits further specify the exact nature of the fault.
After reading the code with an OBD2 scanner, you can search online resources or consult a repair manual to understand its meaning. For example, if you encounter a P0420 code, you’ll know it’s a generic code related to the catalytic converter system. Knowing the specific code allows you to pinpoint the problem area and start your diagnostic process. Having access to a reliable OBD2 scanner is essential for retrieving these codes. Some scanners even offer additional features, such as live data streaming and freeze frame data, which can further aid in your diagnosis.
Right after this section, we’ll provide a breakdown of some of the most common OBD2 exhaust codes. This information will help you understand the potential issues behind each code and guide you towards the appropriate solutions. A solid understanding of these codes will empower you to address emissions problems effectively and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Common OBD2 Exhaust Codes and Their Meanings
Here’s a breakdown of some frequently encountered OBD2 exhaust codes:
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1). This code often indicates a failing catalytic converter.
- P0401: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected. This code suggests a problem with the EGR system, such as a clogged valve or faulty sensor.
- P0135: O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1). This points to a problem with the heating element of the oxygen sensor, affecting its ability to provide accurate readings.
You may find that some codes are related to specific components like the DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter). You can learn more about OBD2 scanners specifically designed for DPF diagnostics by checking out our obd2 scanner dpf page.
These are just a few examples, and many other codes can relate to the exhaust system. Having issues connecting to your OBD2 port? Our article on can not connect to obd2 can help troubleshoot the problem.
What Causes OBD2 Exhaust Codes?
Various factors can trigger OBD2 exhaust codes, ranging from simple issues like a loose gas cap to more complex problems like a failing catalytic converter. Understanding the potential causes can help you narrow down the problem and determine the appropriate course of action.
Some common causes include:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: These sensors play a critical role in monitoring the exhaust gases and adjusting the fuel mixture. A malfunctioning sensor can lead to various problems, including increased emissions and poor fuel economy.
- Catalytic Converter Problems: The catalytic converter is responsible for converting harmful pollutants into less harmful substances. A failing converter can trigger codes like P0420 and lead to decreased performance and increased emissions.
- EGR System Malfunctions: The EGR system helps reduce nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine. Problems with the EGR valve or sensor can trigger codes like P0401.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake or exhaust system can disrupt the air-fuel mixture and cause various problems, including exhaust-related codes.
If you’re struggling to clear certain codes, our guide on cant clear permanent obd2 codes provides valuable insights. Addressing these issues promptly is crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle performance and minimizing environmental impact.
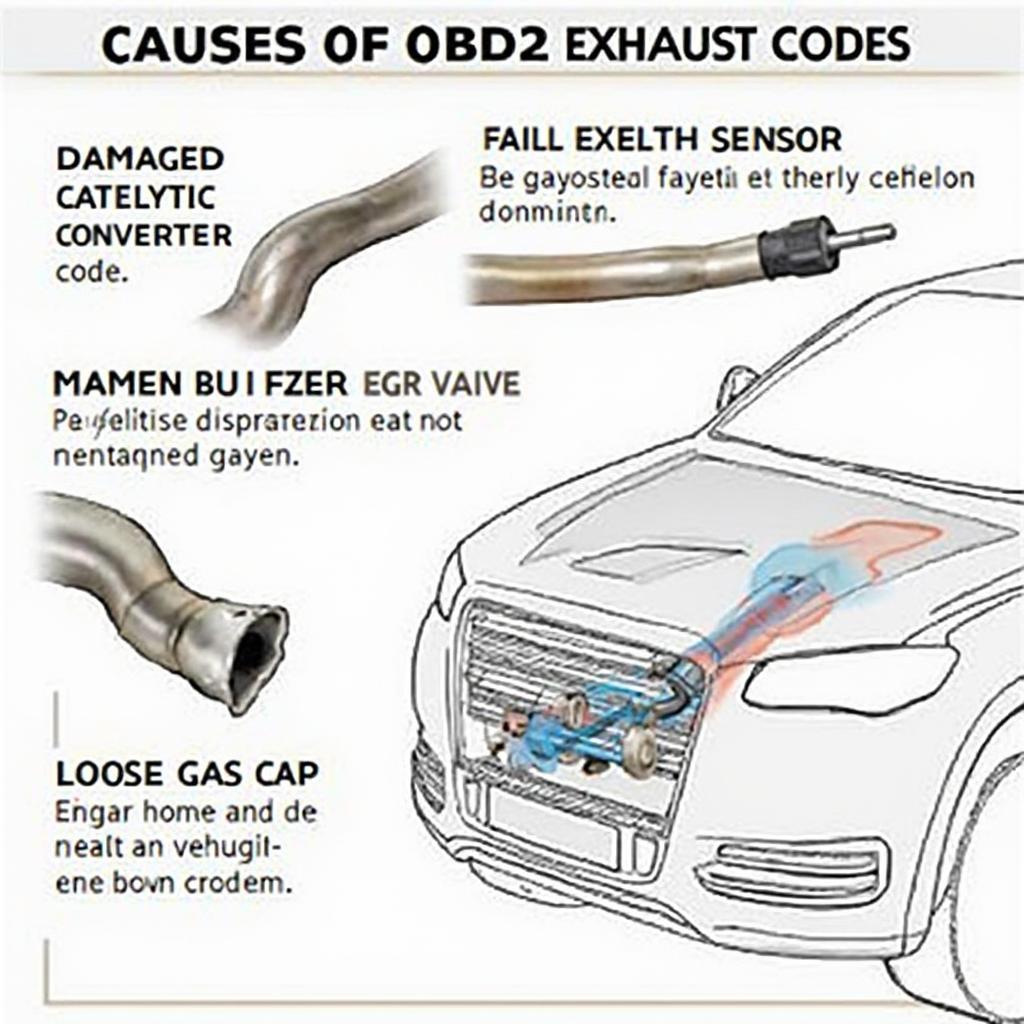 Common Causes of OBD2 Exhaust Codes in Vehicles
Common Causes of OBD2 Exhaust Codes in Vehicles
How to Diagnose and Fix OBD2 Exhaust Codes
Diagnosing and fixing OBD2 exhaust codes requires a systematic approach. First, retrieve the codes using an OBD2 scanner. Then, research the specific code to understand its meaning and potential causes. Next, perform a visual inspection of the relevant components. For example, check for any visible damage or leaks in the exhaust system.
If the problem is simple, such as a loose gas cap, tightening it might resolve the issue. However, more complex problems, like a failing catalytic converter, will require professional repair. Remember, understanding the codes is the first step towards a successful diagnosis and repair.
Interested in standalone OBD2 systems? Our defi zd standalone obd2 page offers detailed information on this topic. Taking proactive steps to address these codes can prevent further damage and ensure your vehicle runs efficiently and cleanly.
Conclusion
OBD2 exhaust codes provide valuable insights into the health of your vehicle’s emission system. Understanding these codes is essential for diagnosing and fixing problems that can impact performance, fuel efficiency, and the environment. By using an OBD2 scanner and following a systematic approach, you can effectively address these issues and keep your car running smoothly. Remember, a little knowledge about OBD2 exhaust codes can go a long way in saving you time, money, and frustration. So, equip yourself with the right tools and information to take control of your vehicle’s maintenance.
FAQ
- What does P0420 mean? P0420 typically indicates a problem with the catalytic converter system.
- How do I fix an OBD2 exhaust code? Diagnosing requires an OBD2 scanner and research. Fixes range from simple adjustments to professional repairs.
- Can a loose gas cap trigger an OBD2 code? Yes, a loose or damaged gas cap can trigger an evaporative emissions code.
- What is an oxygen sensor? Oxygen sensors monitor exhaust gases to regulate the air-fuel mixture.
- Why is my check engine light on? Various reasons, including exhaust system problems, can trigger the check engine light. Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the codes.
- Are all OBD2 exhaust codes the same? No, codes vary depending on the specific fault and manufacturer.
- Where can I find more information on specific OBD2 codes? Online resources, repair manuals, and automotive forums offer detailed information on OBD2 codes.
Do you have questions related to hcat code obd2? Explore our website for more articles.
Need help with your car’s diagnostics? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, or Email: [email protected]. Our 24/7 customer support team is ready to assist.
