Your cart is currently empty!
Understanding the OBD2 External Coil Dizzy
An Obd2 External Coil Dizzy, also known as an external coil distributor ignition system, was a common setup in older vehicles. It played a crucial role in delivering the high voltage spark needed for combustion. While largely replaced by distributorless ignition systems (DIS) in modern cars, understanding how an external coil dizzy interacts with your OBD2 scanner can still be valuable for diagnosing issues in older vehicles.
How an OBD2 External Coil Dizzy Works
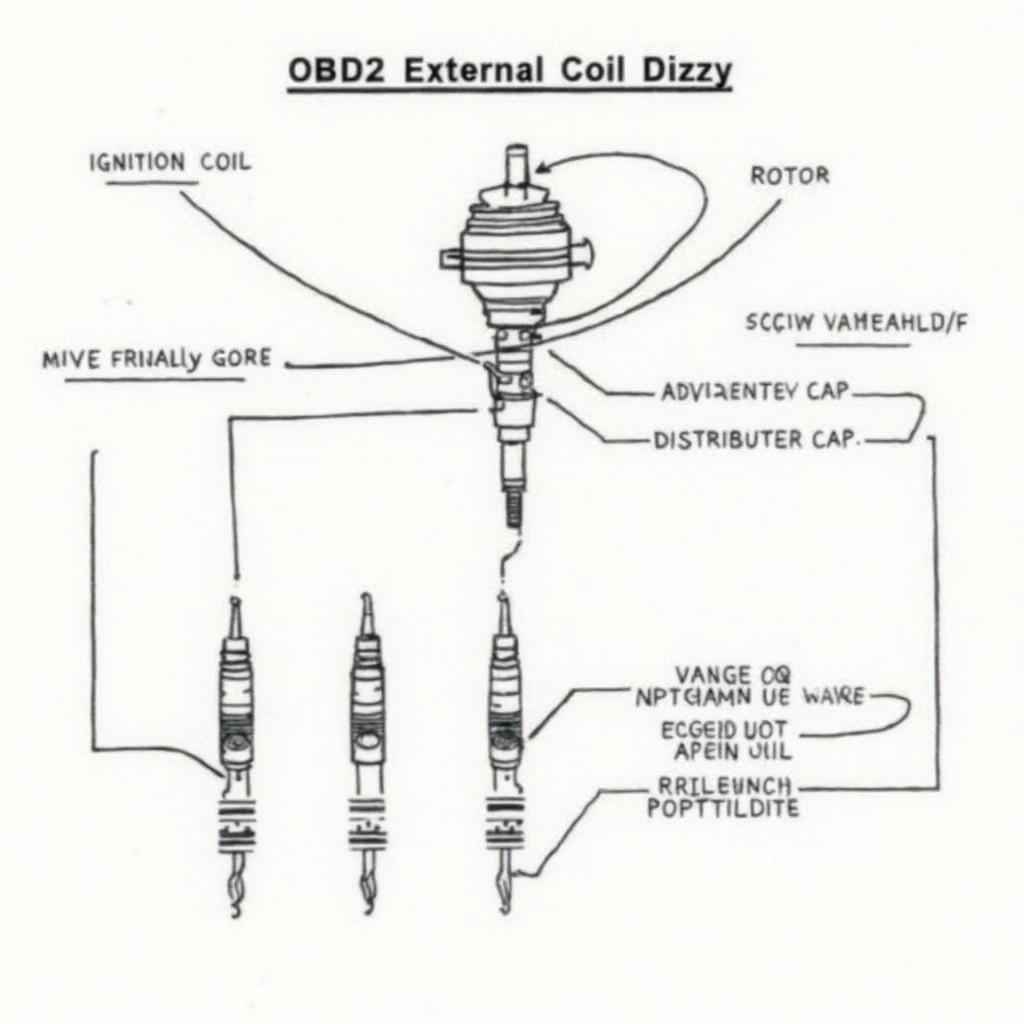
The external coil dizzy system consists of several key components working together: the ignition coil, the distributor, the rotor, and the distributor cap. The ignition coil, located externally (hence the name), takes the low voltage from the battery and steps it up to the high voltage needed to create a spark. This high voltage is then sent to the distributor. The distributor, with its rotating rotor and distributor cap, directs this high voltage to the correct spark plug at the right time. The timing of this process is critical for efficient engine operation.
 OBD2 External Coil Dizzy Components Diagram
OBD2 External Coil Dizzy Components Diagram
Diagnosing External Coil Dizzy Problems with an OBD2 Scanner
Even though the external coil dizzy itself is not directly monitored by the OBD2 system, your scanner can still provide valuable clues. The OBD2 system monitors various engine parameters, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings. Deviations in these parameters can indicate a problem with the ignition system, including the external coil dizzy. For example, misfires, rough idling, or a decrease in fuel efficiency can all be symptoms of a failing external coil, rotor, or distributor cap.
Specific OBD2 codes related to misfires (such as P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire) can help pinpoint the problem area. While these codes don’t directly identify the external coil dizzy as the culprit, they guide you towards the ignition system as a potential source of the issue.
 OBD2 Scanner Diagnosing Misfire
OBD2 Scanner Diagnosing Misfire
Common OBD2 External Coil Dizzy Issues and Solutions
Several issues commonly affect external coil dizzy systems. A cracked distributor cap can cause spark to jump between terminals, leading to misfires. A worn-out rotor can also cause similar issues. A failing ignition coil may not produce enough voltage for a strong spark.
Using your OBD2 scanner in conjunction with other diagnostic tools, like a multimeter, can help you identify the specific component causing the problem. Testing the resistance of the coil and checking for spark at the spark plugs are crucial steps in diagnosing external coil dizzy issues.
Why Modern Cars Use Distributorless Ignition Systems
Modern cars have largely moved away from the external coil dizzy in favor of distributorless ignition systems (DIS). DIS systems offer several advantages, including more precise ignition timing, improved fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. They also eliminate the mechanical wear and tear associated with the distributor, rotor, and cap.
“The move to DIS was a significant advancement in ignition technology,” says automotive engineer, Dr. Emily Carter. “It allowed for more precise control over the combustion process, leading to significant improvements in engine performance and efficiency.”
 Distributorless Ignition System Diagram
Distributorless Ignition System Diagram
Conclusion
Understanding how an obd2 external coil dizzy works and how it can be diagnosed using an OBD2 scanner is important for working on older vehicles. While modern cars have moved on to more advanced ignition systems, the principles of diagnosing ignition-related problems remain relevant. By combining your OBD2 scanner with other diagnostic tools and techniques, you can effectively troubleshoot and fix issues in vehicles equipped with this older technology.
FAQ
-
Can an OBD2 scanner directly diagnose a faulty external coil? No, but it can provide clues through misfire codes and other engine parameter readings.
-
What are the common symptoms of a failing external coil dizzy? Misfires, rough idling, decreased fuel efficiency, and difficulty starting.
-
How can I test an external coil? Using a multimeter to measure the primary and secondary resistance of the coil.
-
What are the advantages of a DIS system over an external coil dizzy? More precise ignition timing, improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and increased reliability.
-
Can I replace an external coil dizzy with a DIS system? It’s possible, but it often requires significant modifications to the vehicle’s wiring and engine management system.
“Regular maintenance and timely diagnosis are key to keeping any ignition system, including the external coil dizzy, running smoothly,” adds Dr. Carter. “Don’t ignore those warning signs – they could be telling you something important.”
For further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.

Leave a Reply