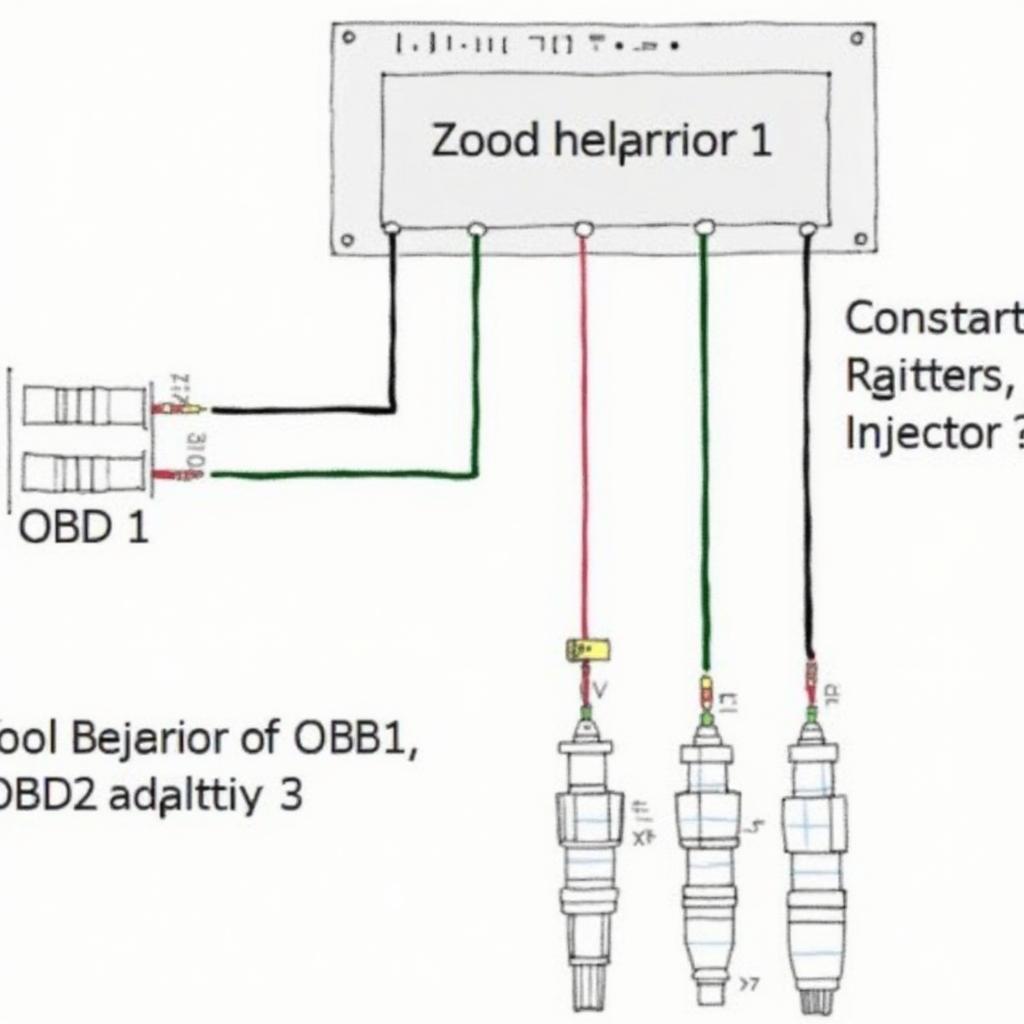
Using OBD2 injectors on an OBD1 ECU can be a popular modification, especially for performance enhancements. This article dives deep into the intricacies of this conversion, covering everything from the fundamental differences between OBD1 and OBD2 fuel injection systems to the practical steps involved in making this modification work.
Understanding the Differences: OBD1 vs. OBD2 Fuel Injection
OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics 1) and OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics 2) systems represent different eras in automotive diagnostics. OBD1, prevalent in vehicles manufactured before 1996, relies on a simpler, less standardized approach to engine management. OBD2, introduced in 1996, offers a more sophisticated and standardized diagnostic interface, enabling more precise control over fuel injection and emissions. integra obd1 to obd2 injectors offers more specific information on this conversion for Integra owners.
One key difference lies in how they control fuel injectors. OBD1 systems often utilize low-impedance injectors (also known as peak and hold injectors), which require a specific driver circuit in the ECU. OBD2 systems primarily use high-impedance injectors (saturated injectors) that operate with a simpler driver circuit. This difference in injector impedance is a crucial consideration when adapting OBD2 injectors to an OBD1 ECU.
Why Use OBD2 Injectors on an OBD1 ECU?
Despite the complexities involved, there are several reasons why someone might choose to use OBD2 injectors on an older OBD1 system. Upgraded injectors can offer better fuel atomization, leading to improved combustion efficiency and potentially increased horsepower. Additionally, OBD2 injectors are often more readily available and may be more cost-effective than sourcing older OBD1 injectors.
Making the Conversion: Key Considerations and Steps
The process of using OBD2 injectors on an OBD1 ECU typically involves using resistor packs or a specialized adapter harness. Resistor packs increase the effective resistance of the OBD2 injectors, mimicking the low-impedance characteristics expected by the OBD1 ECU. This prevents the ECU from overloading and damaging the injectors. vr6 obd2 wiring diagram provides further insights into wiring modifications.
- Resistor Packs: These are often the most cost-effective solution, but they require careful wiring and placement to ensure proper function.
- Adapter Harnesses: These pre-built harnesses simplify the installation process by providing a plug-and-play solution, eliminating the need for manual wiring and soldering.
“When using resistor packs, make sure they are rated for the correct resistance and wattage to avoid overheating and potential fire hazards,” advises John Miller, a seasoned automotive technician with over 20 years of experience.
Tuning and Calibration
After installing the OBD2 injectors and resistor packs or adapter harness, tuning the ECU is essential. This ensures that the fuel delivery matches the new injectors’ flow characteristics. Without proper tuning, the engine may run rich or lean, negatively impacting performance and fuel economy. obd2 to obd1 injector clips might be necessary for specific applications.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
While this conversion can be beneficial, it’s not without its challenges. Incorrect wiring, improper resistor pack selection, or inadequate tuning can lead to problems. “One common issue is a mismatched impedance between the injectors and the ECU, which can lead to injector failure or damage to the ECU driver circuit,” cautions Sarah Johnson, an automotive electronics specialist. full obd2 functions are not typically accessible through OBD1 systems, necessitating specific tuning methods.
Conclusion
Successfully integrating OBD2 injectors on an OBD1 ECU requires a thorough understanding of the underlying principles and meticulous attention to detail. With proper planning, execution, and tuning, this modification can offer performance gains and improved fuel efficiency. obd1 convertions obd2 inyector harnese ebay may offer pre-made solutions for this conversion.
FAQ
- Why upgrade to OBD2 injectors? For improved fuel atomization, potentially increased horsepower, and better availability.
- What are resistor packs? They increase the resistance of OBD2 injectors to match the OBD1 ECU’s requirements.
- Is tuning necessary? Yes, essential to match fuel delivery to the new injectors.
- What are common issues? Mismatched impedance, incorrect wiring, improper tuning.
- Are adapter harnesses available? Yes, they simplify the installation process.
- What are the risks? Potential injector or ECU damage if not done correctly.
- Where can I find more information? Resources like OBDFree offer valuable guides and information.
Common Scenarios
- Scenario 1: Engine misfires after the conversion. This often indicates incorrect wiring or a faulty resistor pack.
- Scenario 2: Poor fuel economy. Likely due to improper tuning or incorrect injector sizing.
- Scenario 3: Check engine light illuminates. Could be caused by various issues, including mismatched impedance or wiring problems.
Further Exploration
Explore related topics on OBDFree, such as OBD1 to OBD2 conversion guides and injector wiring diagrams.
If you need assistance, contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer support team is available 24/7.