Understanding OBD2 monitors is crucial for anyone who wants to keep their car running smoothly. These diagnostic tools track your vehicle’s emission systems and other vital components, alerting you to potential problems before they become serious. This guide dives deep into the world of OBD2 monitors, explaining how they work, what they monitor, and why they’re so important.
Are you curious about what’s happening under the hood of your car? OBD2 monitors are your window into the inner workings of your vehicle’s systems. They constantly monitor various components, looking for anything out of the ordinary. This proactive approach helps prevent costly repairs and ensures optimal performance. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to understand and utilize your OBD2 system effectively.
What are OBD2 Monitors?
OBD2 monitors are self-diagnostic tests that your vehicle runs continuously. They check the various systems responsible for controlling emissions and overall performance. If a problem is detected, the monitor sets a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), which is stored in the vehicle’s computer. These codes can be retrieved using an OBD2 scanner, allowing you to identify the source of the issue. Having a grasp of these monitors can empower you to address car problems proactively.
Knowing how to interpret these codes is essential for diagnosing and fixing car problems. Resources like the differences between OBD1 and OBD2 systems guide can be immensely helpful in understanding the evolution and capabilities of each system. Check out our article diferencias entre sistemas obd1 y obd2.
Types of OBD2 Monitors
There are several types of OBD2 monitors, each focusing on a specific aspect of your vehicle’s operation. These include:
- Comprehensive Component Monitor (CCM): This monitor checks the overall functionality of the emissions system.
- Catalyst Monitor: Evaluates the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
- EGR System Monitor: Monitors the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system.
- EVAP System Monitor: Checks for leaks in the Evaporative Emission Control System.
- Fuel System Monitor: Assesses the fuel delivery system.
- Heated Catalyst Monitor: Monitors the performance of the heated catalyst.
- Misfire Monitor: Detects engine misfires.
- Oxygen Sensor Monitor: Checks the operation of the oxygen sensors.
- Secondary Air System Monitor: Monitors the secondary air injection system.
How OBD2 Monitors Work
OBD2 monitors operate by continuously analyzing data from various sensors throughout your vehicle. These sensors measure parameters like temperature, pressure, and exhaust gas composition. The data is then sent to the vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU), which compares it against predefined thresholds. If the data falls outside these thresholds, the corresponding monitor sets a DTC.
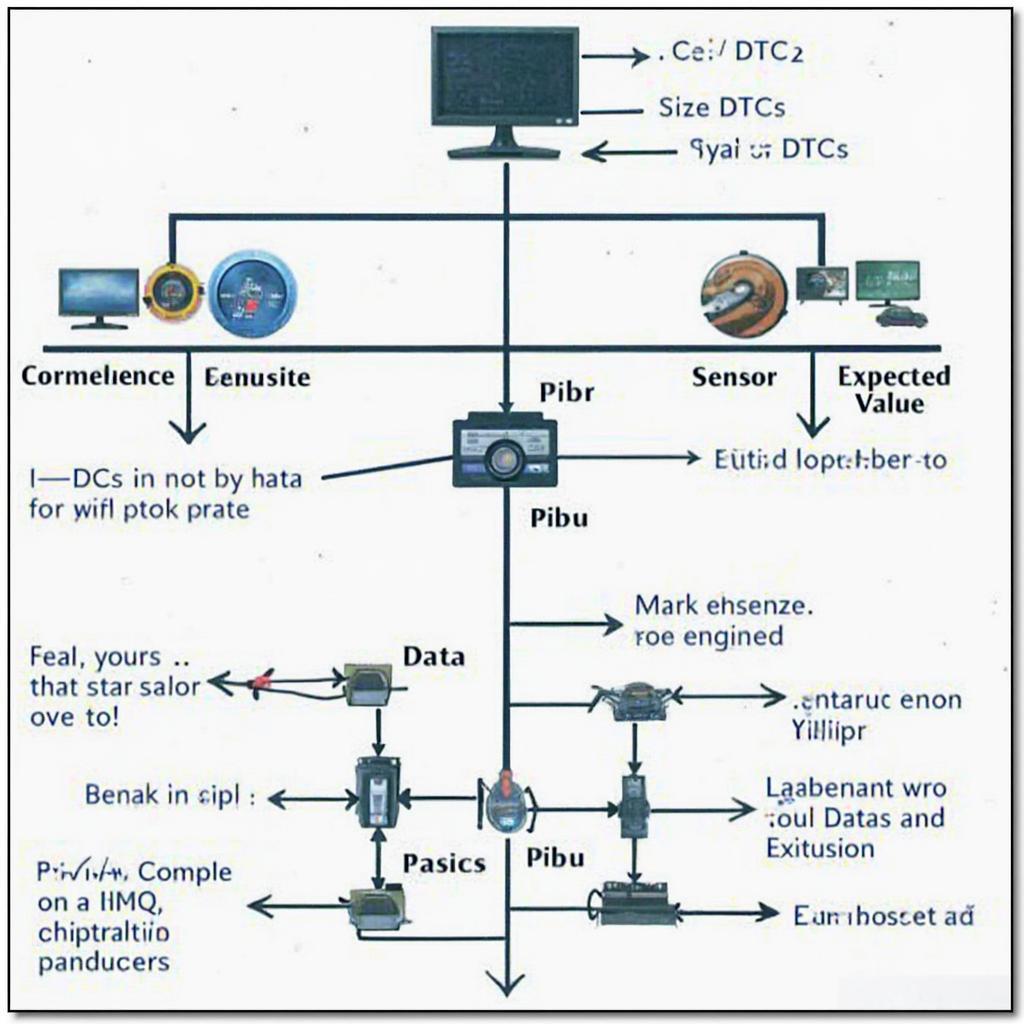 OBD2 Monitor Data Flow Chart
OBD2 Monitor Data Flow Chart
Knowing where key components like the OBD2 sensor are located can be crucial for troubleshooting. For instance, understanding the location of the OBD2 sensor on a 2012 Nissan Rogue can be beneficial for those owning this model. More information is available at obd2 sensor.on 2012 nissan roque.
Why are OBD2 Monitors Important?
OBD2 monitors play a vital role in maintaining your vehicle’s health and emissions compliance. They provide early warning signs of potential problems, allowing you to address them before they escalate into major repairs. By understanding how these monitors work, you can take proactive steps to keep your car running efficiently and minimize your environmental impact.
How do I check my OBD2 Monitors?
You can check the status of your OBD2 monitors using an OBD2 scanner. These scanners connect to your vehicle’s OBD2 port and display the DTCs stored in the computer. Some scanners also provide real-time data from the various sensors, allowing you to monitor the performance of your vehicle’s systems.
A car diagnostic tool can decode OBD2 codes, providing valuable insights into your vehicle’s health. Learn more about how car diagnostic tools can help you understand OBD2 codes by visiting car diagnostic tool can obd2 codes.
OBD2 Monitors and Emissions Testing
OBD2 monitors are a critical component of emissions testing. During an emissions test, the status of the monitors is checked to ensure that they are functioning correctly and that all required tests have been completed. If a monitor is not ready, or if a DTC is present, your vehicle may fail the emissions test.
Conclusion: Understanding OBD2 Monitors
Understanding OBD2 monitors is essential for any car owner. They provide valuable insights into the health of your vehicle’s emissions system and other vital components. By regularly checking your OBD2 monitors and addressing any detected issues promptly, you can keep your car running smoothly, minimize repair costs, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
FAQ
- What does OBD2 stand for? On-Board Diagnostics, Second Generation.
- Where is the OBD2 port located? Typically under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Can I reset my OBD2 monitors? Yes, but it’s best to address the underlying issue first.
- How often should I check my OBD2 monitors? Periodically, especially before emissions testing.
- What is a DTC? Diagnostic Trouble Code, which indicates a specific problem.
- What should I do if my OBD2 scanner shows a code? Consult a repair manual or a qualified mechanic.
- Are all OBD2 monitors the same? No, they monitor different systems and have different criteria.
Need help with your OBD2 system? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our 24/7 customer support team is ready to assist you.