The OBD2 P0038 code indicates a problem with your car’s heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) control circuit, specifically bank 1 sensor 2. This can impact your car’s performance and emissions. Let’s dive into what this code means, why it happens, and how to fix it.
The P0038 diagnostic trouble code refers to a malfunction in the heater control circuit of the downstream oxygen sensor, located after the catalytic converter, on bank 1. This sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the efficiency of the catalytic converter and adjusting the air/fuel mixture for optimal performance and emissions control. A faulty heater circuit can lead to inaccurate readings and potentially damage the sensor.
What Does the OBD2 P0038 Code Mean?
The P0038 code specifically points to an issue with the heater element of the oxygen sensor, not the sensor itself. The heater helps the sensor reach operating temperature faster, allowing it to provide accurate readings sooner after the engine starts. Without a properly functioning heater, the sensor may take longer to warm up, leading to inaccurate readings and potentially impacting fuel economy and emissions.
Causes of the P0038 Code
Several factors can contribute to the P0038 code appearing:
- Faulty HO2S Heater: The most common cause is a malfunctioning heater element within the oxygen sensor itself.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged, corroded, or shorted wiring in the heater circuit can disrupt the power supply to the heater.
- Blown Fuse: A blown fuse in the HO2S heater circuit can cut off power completely.
- Faulty HO2S Heater Control Module: In some cases, the module controlling the heater can malfunction, leading to improper voltage regulation.
- Exhaust Leaks: Exhaust leaks near the sensor can affect its readings and trigger the code.
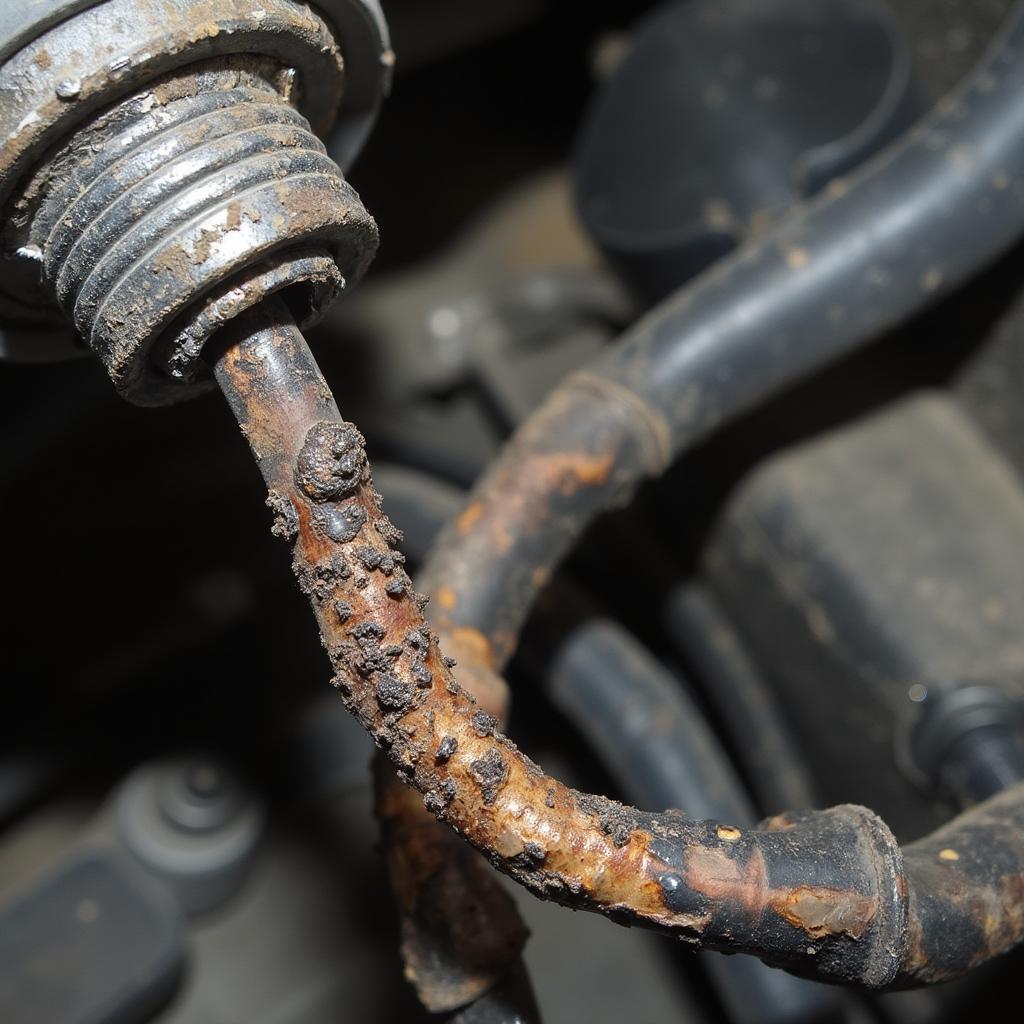 Faulty Wiring in OBD2 P0038 Code
Faulty Wiring in OBD2 P0038 Code
Symptoms of the P0038 Code
While the check engine light is the most obvious sign, other symptoms may accompany the P0038 code:
- Decreased Fuel Economy: Inaccurate readings can cause the engine to run rich or lean, affecting fuel efficiency.
- Rough Idle: A fluctuating idle speed can indicate a problem with the air/fuel mixture.
- Increased Emissions: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to higher emissions levels.
- Performance Issues: You might experience a lack of power or hesitation during acceleration.
Diagnosing the P0038 Code
Diagnosing the P0038 code requires a systematic approach:
- Check for other codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to see if any other codes are present, as they might provide additional clues.
- Visually inspect the wiring: Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections in the wiring harness leading to the sensor.
- Check the fuse: Locate and test the fuse for the HO2S heater circuit.
- Test the sensor’s heater circuit: Use a multimeter to check the resistance and voltage of the heater circuit.
- Test the HO2S heater control module: If the other components check out, the control module might be faulty.
Fixing the P0038 Code
The repair will depend on the specific cause:
- Replace the HO2S: If the sensor’s heater is faulty, replacement is usually the best solution.
- Repair the wiring: Repair or replace any damaged or corroded wiring.
- Replace the fuse: Replace a blown fuse with the correct amperage.
- Replace the HO2S Heater Control Module: If the module is malfunctioning, it will need to be replaced.
- Repair exhaust leaks: Address any exhaust leaks near the sensor.
“Regular maintenance and using a quality OBD2 scanner are key to catching potential issues early,” says Michael Evans, a certified automotive technician with over 20 years of experience. “Addressing the P0038 code promptly can prevent further damage and ensure optimal vehicle performance.”
Conclusion
The OBD2 P0038 code signifies a problem with the heater circuit of your downstream oxygen sensor on bank 1. Addressing this issue promptly can improve fuel economy, reduce emissions, and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly. Ignoring the P0038 code could lead to further damage and more costly repairs down the road.
FAQ
- What is bank 1 sensor 2? Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine with cylinder number 1. Sensor 2 is the downstream oxygen sensor, located after the catalytic converter.
- Can I drive with a P0038 code? While you can technically drive with this code, it’s not recommended. It can impact fuel economy and emissions, and potentially lead to further damage.
- How much does it cost to fix a P0038 code? The cost depends on the specific cause and can range from a simple fuse replacement to a new oxygen sensor and labor costs.
- How often should oxygen sensors be replaced? Oxygen sensors typically last between 60,000 and 90,000 miles, but it’s always best to consult your vehicle’s maintenance schedule.
- Can I fix the P0038 code myself? If you have some mechanical skills, you can potentially fix this code yourself. However, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic if you’re unsure.
- What is the difference between an upstream and downstream oxygen sensor? The upstream sensor measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gases before the catalytic converter, while the downstream sensor measures the oxygen content after the converter.
- Can a bad catalytic converter cause a P0038 code? While unlikely, a failing catalytic converter can sometimes indirectly contribute to this code.
Need help? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.