The dreaded check engine light has illuminated your dashboard, and your OBD2 scanner displays the cryptic code P0150. This code indicates a problem with the oxygen sensor (O2 sensor) circuit bank 2 sensor 1. But what does that mean, and how do you fix it?
This comprehensive guide will demystify OBD2 code P0150, explaining its causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions.
Understanding OBD2 Code P0150
OBD2 code P0150 specifically refers to a malfunction in the oxygen sensor circuit for bank 2 sensor 1. Let’s break down this terminology:
- Oxygen Sensor (O2 Sensor): These sensors, usually located in the exhaust manifold or exhaust pipe, measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. This information is crucial for the engine control unit (ECU) to regulate the air-fuel mixture, optimizing engine performance and emissions.
- Bank 2: In engines with two cylinder banks (typically V6, V8, etc.), bank 2 refers to the side of the engine opposite bank 1. Bank 1 usually contains cylinder #1.
- Sensor 1: This designation signifies the upstream oxygen sensor on bank 2. The upstream sensor is positioned before the catalytic converter.
Therefore, P0150 indicates an issue with the electrical circuit of the upstream oxygen sensor on the side of the engine opposite cylinder #1.
Causes of OBD2 Code P0150
A variety of factors can trigger the P0150 code. Some common culprits include:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The sensor itself may be worn out, contaminated, or damaged, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring within the sensor circuit can disrupt the signal transmission.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust manifold, exhaust pipes, or related components can introduce excess oxygen into the exhaust stream, confusing the sensor.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the engine’s vacuum system can also disrupt the air-fuel mixture, affecting sensor readings.
- Faulty Fuel Pressure Regulator: Inconsistent fuel pressure can lead to an imbalanced air-fuel mixture, impacting oxygen sensor data.
- Malfunctioning ECU: While less common, a faulty ECU can misinterpret or fail to process the oxygen sensor signals properly.
Symptoms of a P0150 Code
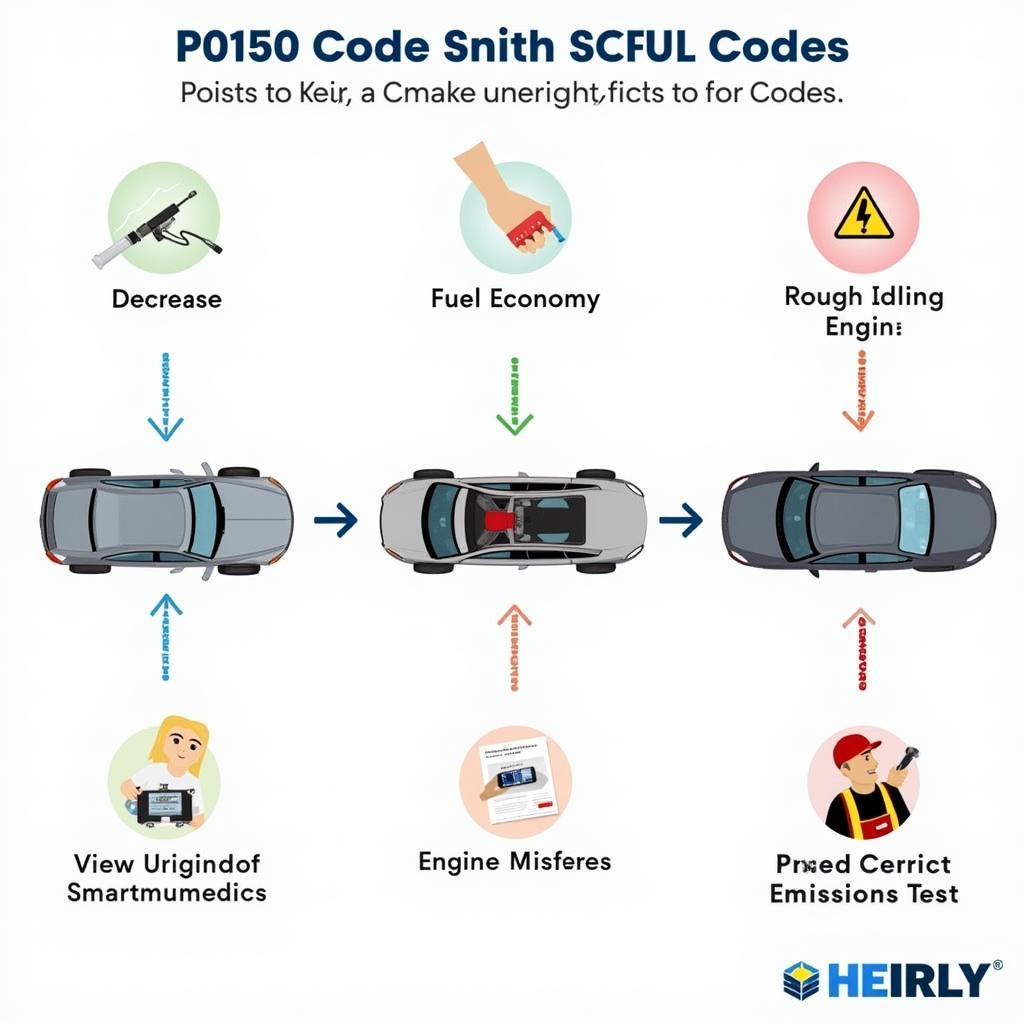
While the check engine light is the most obvious indicator, you might also experience these symptoms if you have a P0150 code:
- Decreased Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can cause your engine to run rich (too much fuel), leading to reduced fuel efficiency.
- Rough Engine Idle: The engine might idle erratically or roughly due to the imbalanced air-fuel mixture.
- Engine Misfires: In severe cases, a P0150 code can lead to engine misfires, particularly during acceleration.
- Failed Emissions Test: A faulty oxygen sensor can cause your vehicle to fail emissions testing.
 OBD2 Code P0150 Symptoms
OBD2 Code P0150 Symptoms
Diagnosing OBD2 Code P0150
Accurately diagnosing the root cause of the P0150 code requires a systematic approach:
- Read the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the stored trouble codes.
- Clear the Codes: After noting the codes, clear them using the scanner.
- Test Drive: Take your vehicle for a test drive to see if the code resets. If it does, proceed with further diagnosis.
- Inspect the Oxygen Sensor: Visually examine the bank 2 sensor 1 oxygen sensor for any visible damage, loose connections, or signs of contamination.
- Check Wiring and Connectors: Thoroughly inspect the wiring harness and connectors within the sensor circuit for any fraying, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Test Sensor Voltage: Using a multimeter, test the voltage signal from the oxygen sensor. Compare the readings with the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Inspect for Exhaust Leaks: Carefully examine the exhaust manifold, pipes, and gaskets for any signs of leaks.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect the vacuum hoses and connections for any leaks or damage.
Fixing OBD2 Code P0150
The solution to a P0150 code depends on the underlying cause. Here are some potential fixes:
- Replace the Oxygen Sensor: If the sensor is faulty, replacement is typically the most effective solution. Ensure you use a high-quality OEM or equivalent sensor.
- Repair Wiring Issues: Repair or replace any damaged, corroded, or loose wiring within the sensor circuit.
- Fix Exhaust Leaks: Address any leaks in the exhaust system by tightening connections, replacing gaskets, or repairing damaged components.
- Resolve Vacuum Leaks: Locate and repair any vacuum leaks by replacing damaged hoses, tightening clamps, or sealing leaks.
- Replace Fuel Pressure Regulator: If faulty, replace the fuel pressure regulator to restore proper fuel pressure.
- Consult a Mechanic: If the issue persists or you’re unable to diagnose it yourself, consult a qualified mechanic for further assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions about OBD2 Code P0150
1. Can I drive with a P0150 code?
While you might be able to drive short distances with a P0150 code, it’s not recommended. Ignoring the code can lead to further engine damage, reduced fuel economy, and potential emissions test failures.
2. How much does it cost to fix a P0150 code?
The repair cost varies widely depending on the underlying cause. A simple oxygen sensor replacement can cost around $100-$300, while more complex repairs like exhaust manifold replacement can range from $500 to over $1000.
3. Can a bad oxygen sensor damage my catalytic converter?
Yes, a faulty oxygen sensor can potentially damage your catalytic converter over time. The inaccurate readings can lead to an imbalanced air-fuel mixture, causing the catalytic converter to overheat and deteriorate.
4. How often should I replace my oxygen sensors?
Oxygen sensors typically have a lifespan of 60,000 to 90,000 miles, but it’s best to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific recommendations.
5. Can a loose gas cap cause a P0150 code?
While a loose gas cap can trigger other EVAP system codes, it’s unlikely to directly cause a P0150 code related to the oxygen sensor circuit.
Need More Help with OBD2 Codes?
Check out our comprehensive guide to oxygen sensor obd2 codes for more information on diagnosing and fixing oxygen sensor-related issues.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing the OBD2 code P0150 is vital for maintaining your vehicle’s performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions compliance. By following the diagnostic tips and potential solutions outlined in this guide, you can resolve the issue effectively. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable tackling the repair yourself, don’t hesitate to seek help from a qualified mechanic.
Need assistance with your car diagnostics? Contact our expert team via WhatsApp at +1(641)206-8880 or email us at cardiagtechworkshop@gmail.com. We’re available 24/7 to provide you with the support you need.