Your cart is currently empty!
Understanding OBD2 PID 177 Formula
OBD2 PID 177, also known as Catalyst Temperature Bank 1 Sensor 2, is a crucial diagnostic parameter for understanding the health and performance of your vehicle’s catalytic converter. This article delves into the Obd2 Pid 177 Formula, exploring its significance, calculation, and potential implications for your vehicle. We’ll cover everything from the basic principles of catalytic converter operation to advanced diagnostics using OBD2 scanners.
Decoding the OBD2 PID 177 Formula
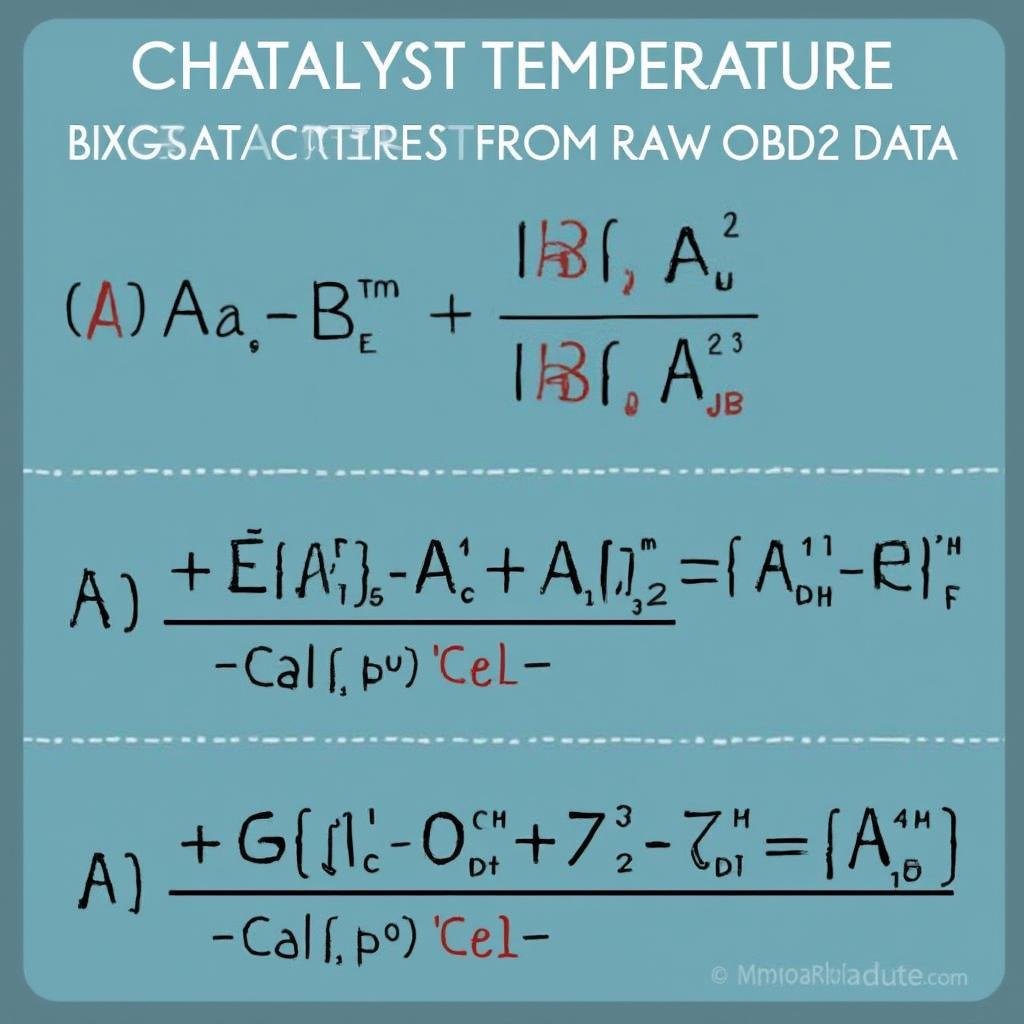
The formula for converting the raw data received from your OBD2 scanner for PID 177 into degrees Celsius is typically:
Catalyst Temperature (°C) = (A * 256 + B) / 10 - 40Where A and B represent the two bytes of data returned by the OBD2 scanner. Understanding this obd2 pid 177 formula allows you to accurately interpret the temperature readings and assess the efficiency of your catalytic converter.
 OBD2 PID 177 Formula Calculation
OBD2 PID 177 Formula Calculation
This formula is essential because it translates the raw data from the sensor into a usable temperature value. This temperature value is a key indicator of catalytic converter performance.
Why is OBD2 PID 177 Important?
The catalytic converter plays a vital role in reducing harmful emissions. Monitoring its temperature through OBD2 PID 177 helps identify potential problems, such as a failing catalytic converter, which can lead to increased emissions and even damage to other engine components. A malfunctioning catalytic converter can also trigger the check engine light and impact vehicle performance.
 Catalytic Converter Temperature Monitoring
Catalytic Converter Temperature Monitoring
By tracking the catalyst temperature, you can gain insights into the efficiency of the catalytic converter and identify potential issues early on. This preventative approach can save you time and money on costly repairs down the line.
Common Issues Related to OBD2 PID 177
Several factors can influence the readings of OBD2 PID 177. These include:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: Inaccurate oxygen sensor readings can impact the fuel mixture and consequently, the catalytic converter temperature.
- Clogged Catalytic Converter: A clogged converter restricts exhaust flow, leading to increased back pressure and higher temperatures.
- Engine Misfires: Unburnt fuel entering the converter can cause excessive heat, potentially damaging the catalyst.
- Faulty Temperature Sensor: A malfunctioning sensor can provide inaccurate temperature readings, leading to misdiagnosis.
How to Use OBD2 PID 177 for Diagnostics
Using an OBD2 scanner, you can monitor PID 177 in real-time. This allows you to observe temperature changes under various driving conditions, providing valuable insights into the converter’s performance. Compare the readings with the manufacturer’s specifications to identify any deviations.
“Regularly monitoring PID 177 can help prevent costly repairs and ensure your vehicle is running efficiently,” advises John Smith, Senior Automotive Technician at Advanced Auto Solutions.
 OBD2 Scanner Monitoring PID 177
OBD2 Scanner Monitoring PID 177
“A consistent deviation from normal operating temperatures can be an early indicator of a developing problem,” adds Smith.
Conclusion
Understanding the obd2 pid 177 formula and its implications is crucial for maintaining the health of your vehicle’s catalytic converter and reducing emissions. Regular monitoring of this parameter using an OBD2 scanner allows for proactive diagnostics and preventative maintenance, saving you time and money in the long run.
FAQ
-
What does OBD2 PID 177 measure? It measures the temperature of the catalytic converter, specifically Bank 1 Sensor 2.
-
Why is catalytic converter temperature important? It indicates the efficiency of the converter and can reveal potential problems.
-
What can cause high catalytic converter temperatures? Clogs, engine misfires, and faulty oxygen sensors are common causes.
-
How can I check OBD2 PID 177? Use an OBD2 scanner to access and monitor this parameter.
-
What should I do if PID 177 readings are abnormal? Consult a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis and repairs.
-
What is the typical operating temperature range for a catalytic converter? This varies depending on the vehicle and driving conditions but is usually between 400-800°C.
-
Can a faulty temperature sensor affect PID 177 readings? Yes, a malfunctioning sensor can provide inaccurate data.
For further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We offer 24/7 customer support.

Leave a Reply