The OBD2 P0300 code, indicating a random or multiple cylinder misfire, can be a frustrating issue for car owners. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, diagnosing, and resolving the P0300 code, empowering you to take control of your vehicle’s health.
What Does the P0300 Code Mean?
The P0300 code signifies that your car’s engine control module (ECM) has detected random misfires across multiple cylinders. A misfire occurs when the air-fuel mixture in a cylinder fails to ignite properly, resulting in reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and potential damage to the catalytic converter. Unlike codes like P0301 (cylinder 1 misfire), P0300 doesn’t pinpoint a specific cylinder, making diagnosis more challenging. This code often appears alongside other codes, providing additional clues for troubleshooting.
Common Causes of the P0300 Code
Several factors can contribute to the dreaded P0300 code. These include:
- Faulty Spark Plugs or Wires: Worn-out spark plugs or damaged wires can disrupt the ignition process, leading to misfires.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake manifold or vacuum hoses can disrupt the air-fuel ratio, causing misfires.
- Fuel System Problems: Issues like a clogged fuel filter, malfunctioning fuel injectors, or a weak fuel pump can starve the engine of fuel, resulting in misfires.
- Ignition Coil Problems: A failing ignition coil can prevent the spark plugs from firing correctly.
- Oxygen Sensor Issues: A faulty oxygen sensor can provide incorrect data to the ECM, leading to an improper air-fuel mixture and misfires.
- Mechanical Problems: In some cases, more severe issues like low compression, a damaged camshaft, or a faulty EGR valve can trigger the P0300 code.
Can I read the oil pressure through obd2? This is a common question, but unfortunately, not all OBD2 scanners provide this data.
Diagnosing the P0300 Code
Diagnosing the P0300 code requires a systematic approach:
- Check for Other Codes: Scan your vehicle for other diagnostic trouble codes that might provide additional clues.
- Inspect Spark Plugs and Wires: Visually inspect the spark plugs for wear and tear, and check the wires for damage or corrosion.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect vacuum hoses for cracks or leaks.
- Test Fuel Pressure: Use a fuel pressure gauge to ensure the fuel pump is delivering adequate pressure.
- Test Ignition Coils: Test the ignition coils using a multimeter or a dedicated coil tester.
- Check Oxygen Sensor Readings: Use an OBD2 scanner to monitor oxygen sensor readings.
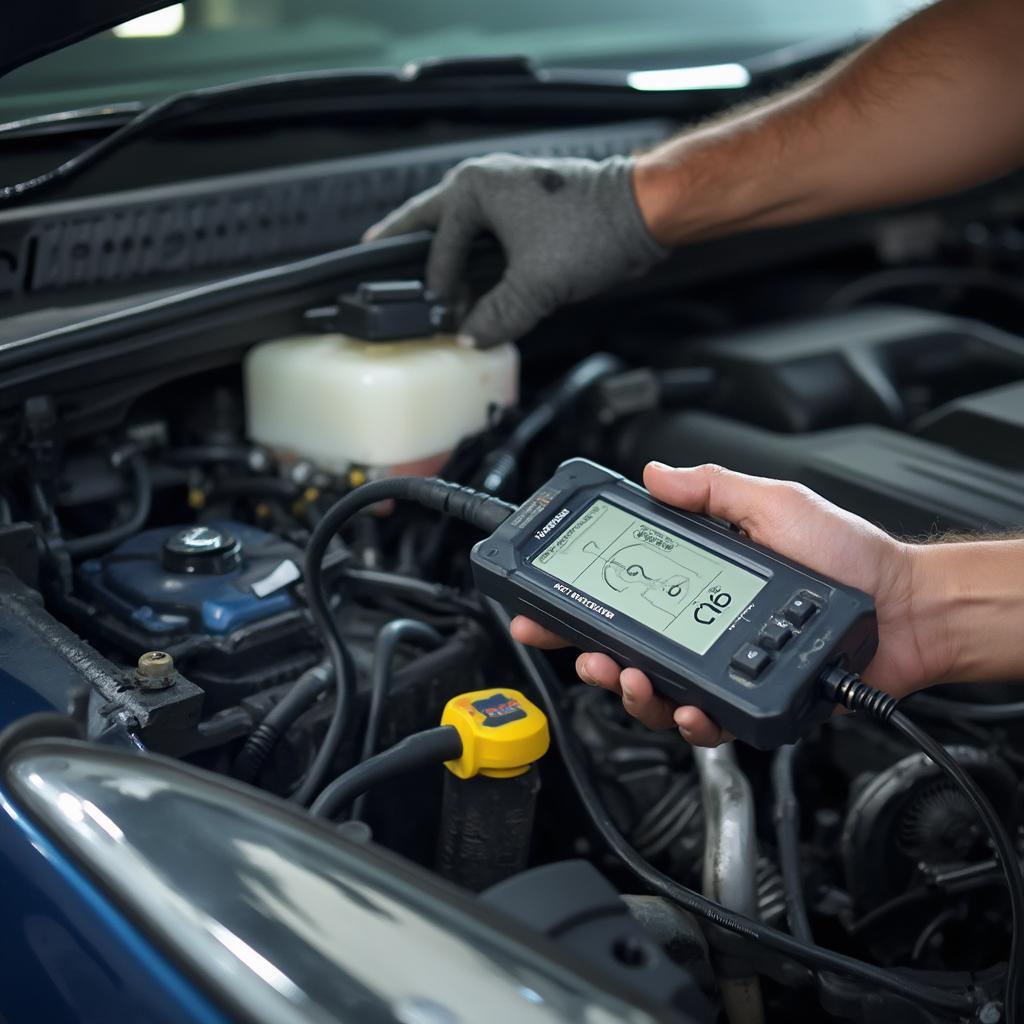 Mechanic Diagnosing Car Engine
Mechanic Diagnosing Car Engine
How to Fix the P0300 Code
Once you’ve identified the root cause, you can take the necessary steps to fix the issue. This might involve replacing faulty spark plugs, repairing vacuum leaks, or addressing fuel system problems. In some cases, more complex repairs might be necessary.
Remember, a proper diagnosis is crucial before attempting any repairs. If you’re unsure about any step, consult a qualified mechanic.
Conclusion: Tackling the OBD2 P0300 Code
The OBD2 P0300 code can be a challenging issue, but with a systematic approach to diagnosis and repair, you can get your vehicle running smoothly again. Understanding this code and its potential causes empowers you to take proactive steps towards maintaining your car’s health and performance.
FAQ
- Can I drive with a P0300 code? It’s not recommended to drive extensively with a P0300 code as it can damage your catalytic converter and reduce fuel efficiency.
- Is the P0300 code serious? While not immediately dangerous, ignoring the P0300 code can lead to more serious engine problems.
- How much does it cost to fix a P0300 code? The cost varies depending on the underlying cause, ranging from a few dollars for spark plugs to hundreds for more complex repairs.
- Can bad gas cause a P0300 code? Yes, contaminated fuel can contribute to misfires and trigger the P0300 code.
- How can I prevent the P0300 code? Regular maintenance, including tune-ups and fuel system cleaning, can help prevent misfires and the P0300 code.
- What other codes are often associated with P0300? Codes related to specific cylinder misfires (P0301-P0312) and fuel system issues are often seen alongside P0300.
- Can a faulty MAF sensor cause a P0300 code? Yes, a malfunctioning mass airflow (MAF) sensor can disrupt the air-fuel mixture and lead to misfires.
Need help? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: cardiagtechworkshop@gmail.com or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We offer 24/7 customer support.