The OBD2 P0030 code indicates a problem with your car’s oxygen sensor heater control circuit. This can affect fuel efficiency, emissions, and overall engine performance. In the next few paragraphs, we’ll delve deep into what this code means, its common causes, how to diagnose it, and potential solutions.
What is the OBD2 P0030 Code?
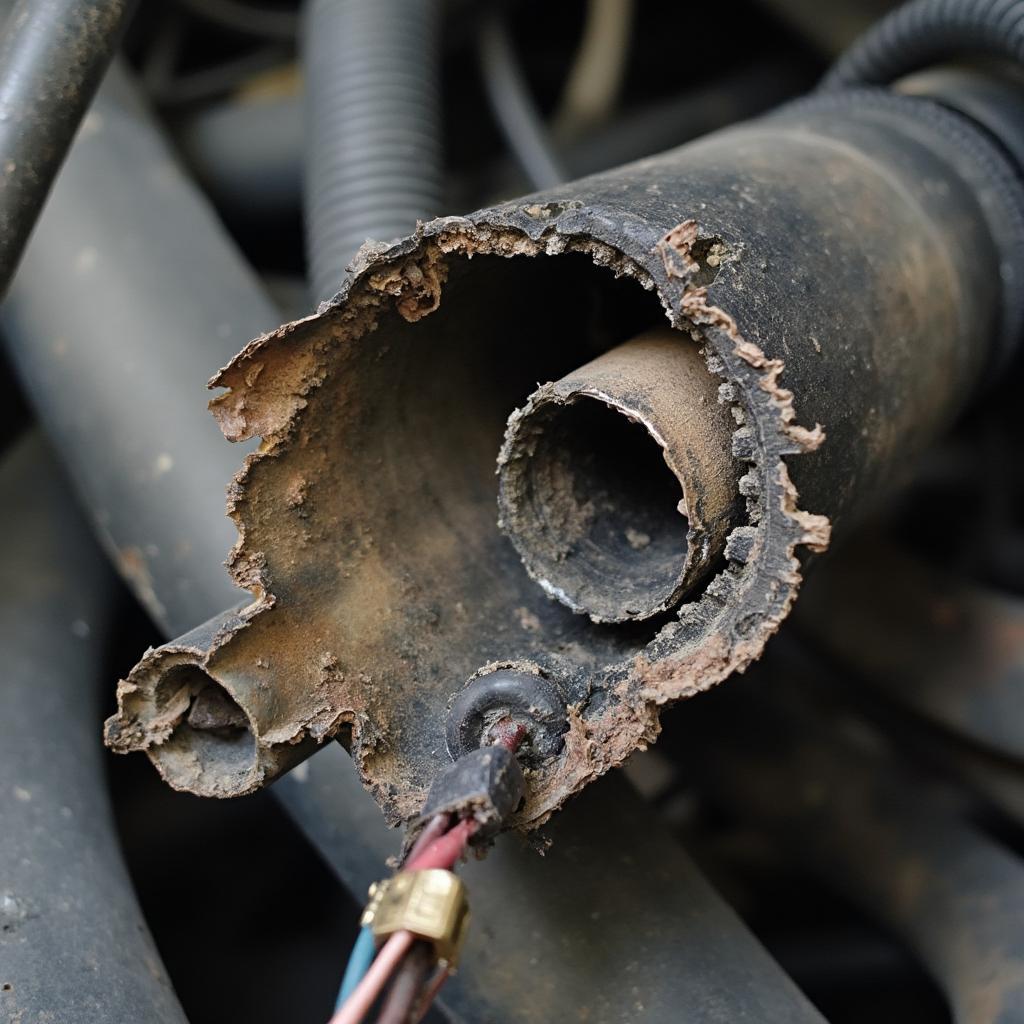
The P0030 diagnostic trouble code specifically points to a malfunction in the heater control circuit of the oxygen sensor (O2 sensor), Bank 1 Sensor 1. This sensor is located upstream of the catalytic converter, meaning it’s positioned before the exhaust gases reach the converter. Its primary function is to measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust stream, allowing the engine control module (ECM) to adjust the air-fuel ratio for optimal combustion. The heater element within the sensor ensures it reaches operating temperature quickly, providing accurate readings faster.
Causes of the OBD2 P0030 Code
Several factors can trigger the P0030 code. Understanding these potential causes is crucial for effective diagnosis and repair. These include:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 1): The most common culprit is a malfunctioning oxygen sensor itself. The heater circuit within the sensor can fail, preventing it from reaching optimal operating temperature.
- Damaged Wiring or Connectors: Wiring issues, such as breaks, shorts, or corrosion in the sensor’s wiring harness or connectors, can disrupt the heater circuit’s functionality.
- Blown Fuse: A blown fuse in the oxygen sensor heater circuit can cut off power to the heater, triggering the P0030 code.
- Faulty ECM: In rare cases, a malfunctioning ECM can cause the P0030 code. This is usually a last resort diagnosis after all other possibilities have been ruled out.
Diagnosing the OBD2 P0030 Code
Diagnosing the P0030 code requires a systematic approach. Start by using an OBD2 scanner to confirm the code and check for any other related codes. Then, visually inspect the oxygen sensor wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
Next, use a multimeter to test the sensor’s heater circuit for continuity and resistance. Check the relevant fuse for the oxygen sensor heater circuit. If the fuse is blown, replace it and recheck for the P0030 code.
How to Fix the OBD2 P0030 Code
Once the cause of the P0030 code has been identified, the appropriate repair can be made. This could involve:
- Replacing the Oxygen Sensor: If the sensor is faulty, it will need to be replaced.
- Repairing Wiring or Connectors: Damaged wiring or connectors should be repaired or replaced as necessary.
- Replacing the Fuse: A blown fuse should be replaced with a new fuse of the correct amperage.
- Replacing or Reprogramming the ECM: In rare cases, the ECM may need to be replaced or reprogrammed. This is a complex procedure best left to a qualified mechanic.
What Happens if I Ignore the OBD2 P0030 Code?
Ignoring the P0030 code can lead to further problems, including:
- Decreased Fuel Efficiency: The ECM may not be able to accurately control the air-fuel ratio, leading to reduced fuel economy.
- Increased Emissions: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can cause the engine to run rich, resulting in higher emissions.
- Damage to the Catalytic Converter: Over time, a rich fuel mixture can damage the catalytic converter.
- Engine Performance Issues: The P0030 code can eventually lead to driveability problems, such as rough idling, hesitation, or stalling.
Conclusion: Addressing the OBD2 P0030 Code for Optimal Vehicle Performance
Addressing the OBD2 P0030 code promptly is essential to maintain optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and minimize emissions. By understanding the code, its potential causes, and diagnostic procedures, you can effectively resolve the issue and prevent further complications.
FAQ
- What does Bank 1 Sensor 1 mean? Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine where cylinder number 1 is located. Sensor 1 refers to the upstream oxygen sensor, positioned before the catalytic converter.
- Can I drive my car with a P0030 code? While you may be able to drive for a short period, it’s recommended to address the issue as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
- How much does it cost to replace an oxygen sensor? The cost can vary depending on the vehicle make and model, but typically ranges from $100 to $300.
- How often should oxygen sensors be replaced? Oxygen sensors typically have a lifespan of 60,000 to 90,000 miles.
- Can a bad oxygen sensor cause my check engine light to come on? Yes, a malfunctioning oxygen sensor can trigger the check engine light.
- Can I replace the oxygen sensor myself? While possible, replacing an oxygen sensor can be challenging. If you are not comfortable working on your car, it’s best to take it to a qualified mechanic.
- What other codes are related to the P0030 code? Related codes can include P0031 (O2 Sensor Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 1)) and P0032 (O2 Sensor Heater Control Circuit High (Bank 1 Sensor 1)).
For further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We have a 24/7 customer service team.