The OBD2 scan codes list can seem daunting, especially when your car throws a code like P0171. This code indicates a “System Too Lean (Bank 1)” problem, a common issue that can impact various car makes and models. Don’t worry, this article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the P0171 code, its causes, symptoms, diagnostic steps, and potential solutions.
What Does the P0171 Code Mean?
In simple terms, the P0171 code signals that the air-fuel mixture in your engine’s combustion chamber is running lean. “Lean” implies there is too much air compared to the fuel, leading to inefficient combustion. The “Bank 1” refers to the side of the engine containing cylinder #1. This code is typically triggered by the Engine Control Module (ECM) when the oxygen sensor readings indicate a lean condition beyond the acceptable parameters.
Common Causes of the P0171 Code
A variety of factors can contribute to a lean air-fuel mixture and trigger the P0171 code. Here are some of the most common culprits:
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake manifold, vacuum hoses, or other vacuum-operated components can disrupt the air-fuel ratio.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor (O2 Sensor): A malfunctioning O2 sensor can send inaccurate readings to the ECM, leading to an incorrect air-fuel mixture.
- Fuel Pressure Issues: Low fuel pressure due to a failing fuel pump, clogged fuel filter, or faulty fuel pressure regulator can starve the engine of fuel.
- Injector Problems: Clogged, dirty, or malfunctioning fuel injectors can disrupt fuel delivery, causing a lean condition.
- Air Intake System Leaks: Leaks in the air intake ductwork, after the mass airflow sensor, can allow unmetered air into the engine.
- Exhaust System Leaks: Exhaust leaks, particularly before the oxygen sensors, can introduce excess oxygen into the exhaust stream, skewing the O2 sensor readings.
- Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) System Issues: A faulty PCV valve or clogged PCV hoses can disrupt the air-fuel mixture by allowing excess air into the intake manifold.
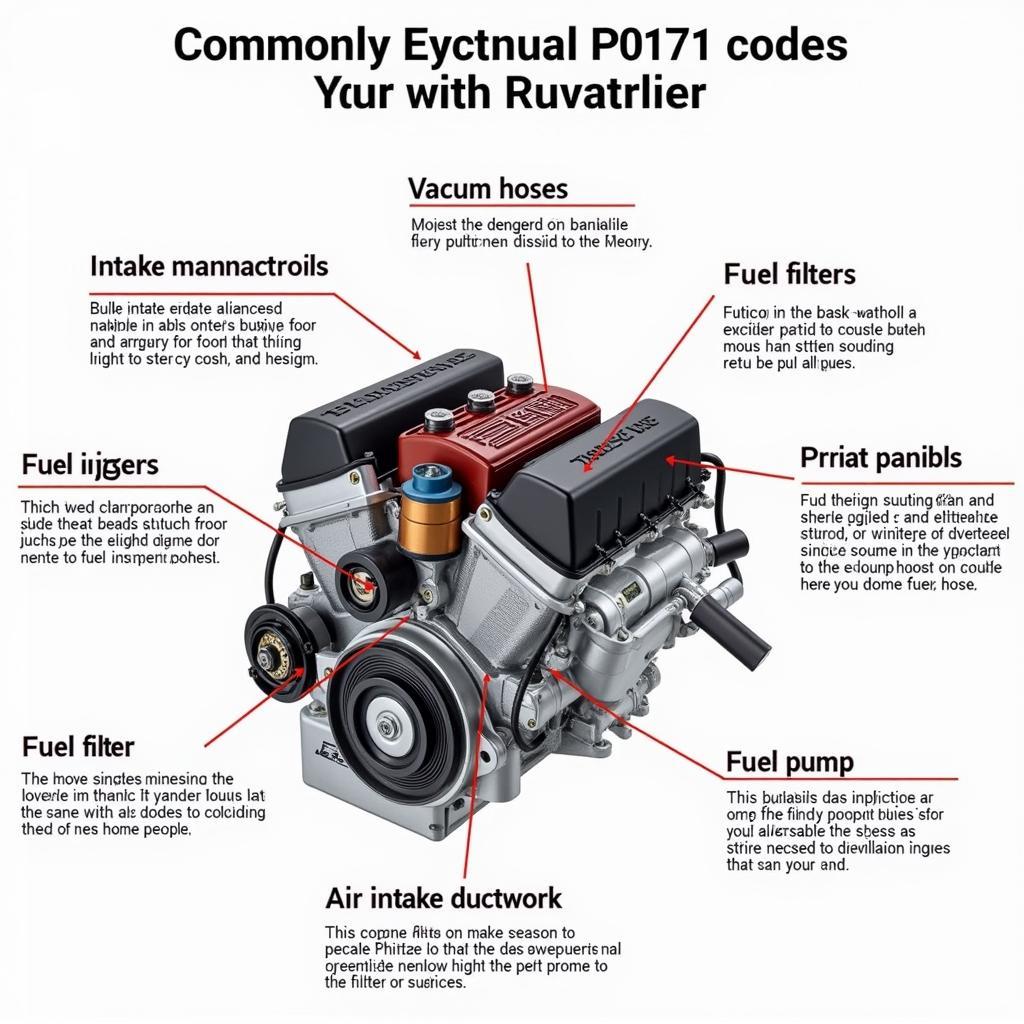 Common Causes of P0171 Code
Common Causes of P0171 Code
Symptoms of a P0171 Code
While the P0171 code illuminates the check engine light, you may experience other noticeable symptoms, such as:
- Rough Idle: A lean air-fuel mixture can cause engine misfires at idle, resulting in a rough or shaky sensation.
- Engine Hesitation: When accelerating, the engine may hesitate or stumble due to insufficient fuel.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: A lean mixture burns hotter and less efficiently, leading to decreased gas mileage.
- Engine Surging: The engine RPM may fluctuate erratically, especially at a steady speed.
- Misfires: A lean condition can cause spark plugs to misfire, resulting in a loss of power.
- Stalling: In severe cases, the engine may stall due to an extremely lean air-fuel mixture.
Diagnosing the P0171 Code
Accurately diagnosing the underlying cause of the P0171 code requires a systematic approach. Here are some diagnostic steps:
-
Read and Document the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the stored trouble code(s). Note any history codes that may provide clues.
-
Inspect for Vacuum Leaks: Visually examine vacuum hoses for cracks, splits, or loose connections. Use a vacuum gauge or spray carburetor cleaner around potential leak points while the engine is running.
-
Check Fuel Pressure: Connect a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel rail to verify that the fuel pump is delivering adequate pressure.
-
Inspect the Oxygen Sensors: Visually inspect the O2 sensors for damage or contamination. Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s voltage output.
-
Examine the Fuel Injectors: Check the fuel injectors for clogging or leaks. You can test them by listening for clicking sounds while the engine is running.
-
Inspect the Air Intake System: Look for any cracks, loose clamps, or damaged components in the air intake ductwork.
-
Examine the Exhaust System: Check for leaks in the exhaust manifold, pipes, or muffler, particularly upstream of the oxygen sensors.
Potential Solutions for the P0171 Code
Once you’ve pinpointed the root cause of the P0171 code, you can implement the necessary repairs. Here are some potential solutions:
-
Repair Vacuum Leaks: Replace any damaged or cracked vacuum hoses, tighten loose clamps, and seal any leaks in the intake manifold.
-
Replace Faulty Oxygen Sensor: If the O2 sensor is malfunctioning, replace it with a new one.
-
Address Fuel Pressure Issues: Replace a failing fuel pump, replace a clogged fuel filter, or repair/replace a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
-
Clean or Replace Fuel Injectors: Clean clogged fuel injectors using a fuel injector cleaning kit or replace them if they are beyond repair.
-
Repair Air Intake System Leaks: Seal any cracks or leaks in the air intake ductwork, tighten loose clamps, and replace any damaged components.
-
Repair Exhaust System Leaks: Repair or replace any leaking components in the exhaust system, such as the manifold, pipes, or muffler.
-
Address PCV System Problems: Replace a faulty PCV valve or clean/replace clogged PCV hoses.
Important Note: Attempting DIY repairs without proper knowledge and tools can potentially worsen the issue. If you’re unsure about any step, consult a qualified mechanic.
Conclusion
The P0171 code, indicating a lean air-fuel mixture, can be triggered by various factors. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic steps is crucial for effectively addressing the issue. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can take the necessary steps to diagnose and resolve the P0171 code, ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently.
Remember, a well-maintained vehicle is a safer and more reliable vehicle.

