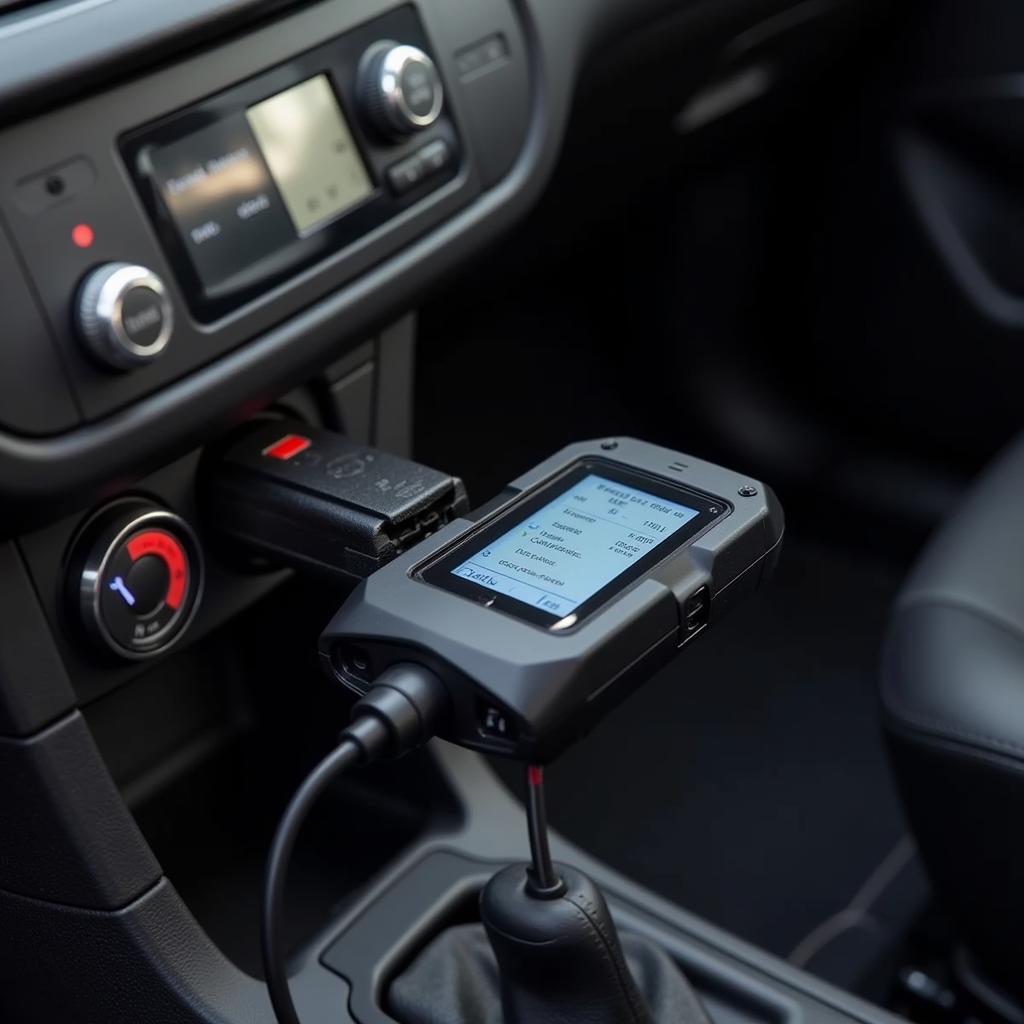
An OBD2 scanner has become an essential tool for car owners and mechanics alike. It provides a window into your car’s computer system, revealing valuable information about its health and performance. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a car enthusiast looking to understand your vehicle better, an OBD2 scanner can be your trusted companion.
What is an OBD2 Scanner and Why Do You Need One?
OBD stands for On-Board Diagnostics, and it refers to the standardized system used in vehicles to diagnose and report faults. Since 1996, all cars sold in the United States have been equipped with an OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. An OBD2 scanner, also known as a code reader, plugs into this port and allows you to communicate with your car’s computer.
So, why is an OBD2 scanner a must-have tool? Here are a few compelling reasons:
- Diagnose Engine Problems: The most common use for an OBD2 scanner is to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes are triggered when your car’s computer detects an issue with the engine or emissions system.
- Save Money on Repairs: By identifying the source of the problem, you can avoid unnecessary repairs or get a more accurate quote from a mechanic.
- Monitor Car Performance: Beyond just reading codes, many OBD2 scanners offer real-time data monitoring. You can track parameters like engine RPM, coolant temperature, speed, and fuel economy.
- Clear Check Engine Light: A glowing check engine light can be unsettling. An OBD2 scanner can help determine the cause and clear the light once the issue is resolved.
- Enhance Your Car Knowledge: Using an OBD2 scanner allows you to delve deeper into your car’s inner workings, empowering you with knowledge and understanding.
Types of OBD2 Scanners
The market offers a wide array of OBD2 scanners, each catering to different needs and budgets. Let’s break down the main types:
- Basic Code Readers: These entry-level scanners are ideal for reading and clearing basic DTCs. They are affordable and easy to use, making them suitable for casual car owners.
- Advanced Code Readers: Offering more features than basic models, these scanners can provide live data streaming, graph multiple parameters, and access manufacturer-specific codes.
- Professional Scan Tools: Used by mechanics and professional technicians, these high-end scanners offer the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. They can perform complex functions like bi-directional control, programming, and coding.
Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
With so many options available, choosing the right OBD2 scanner can seem daunting. Consider these factors:
- Your Budget: Basic code readers are affordable, while advanced and professional scanners come at a higher price point.
- Your Needs: Do you need a scanner for basic diagnostics or more advanced functionalities?
- Your Car’s Make and Model: Some scanners are designed for specific car makes, offering access to manufacturer-specific codes.
- Connectivity Options: Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and USB connections provide different levels of convenience and data transfer speeds.
How to Use an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner is relatively straightforward:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Usually found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Turn the Ignition On: Do not start the engine yet.
- Read Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the diagnostic trouble codes.
- Diagnose the Problem: Look up the codes online or in a repair manual to understand the issue.
- Clear the Codes: Once the problem is resolved, use the scanner to clear the codes.
Beyond Diagnostics: OBD2 Scanners and the Future
The role of OBD2 scanners extends beyond simple diagnostics. With the rise of connected cars and the Internet of Things (IoT), these devices are evolving to offer even more possibilities:
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing data trends, OBD2 scanners can predict potential issues before they become major problems.
- Insurance Telematics: Insurance companies can use data from OBD2 scanners to monitor driving behavior and offer personalized premiums.
- Remote Diagnostics: Mechanics can remotely access vehicle data through OBD2 scanners, providing faster and more efficient service.
Conclusion
An OBD2 scanner is a powerful tool that empowers car owners with knowledge and control over their vehicles. By demystifying your car’s inner workings, you can make informed decisions about maintenance, repairs, and even your driving habits. Whether you’re a car enthusiast or simply want peace of mind on the road, an OBD2 scanner is a worthwhile investment.