OBD2 stacks are the backbone of vehicle diagnostics. They represent the software layers that enable communication between an OBD2 scanner and a vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs). Understanding how these stacks function is crucial for anyone working with vehicle diagnostics, from professional mechanics to DIY enthusiasts. This guide delves into the intricacies of OBD2 stacks, exploring their architecture, functionality, and importance in the automotive world.
Decoding the Architecture of OBD2 Stacks
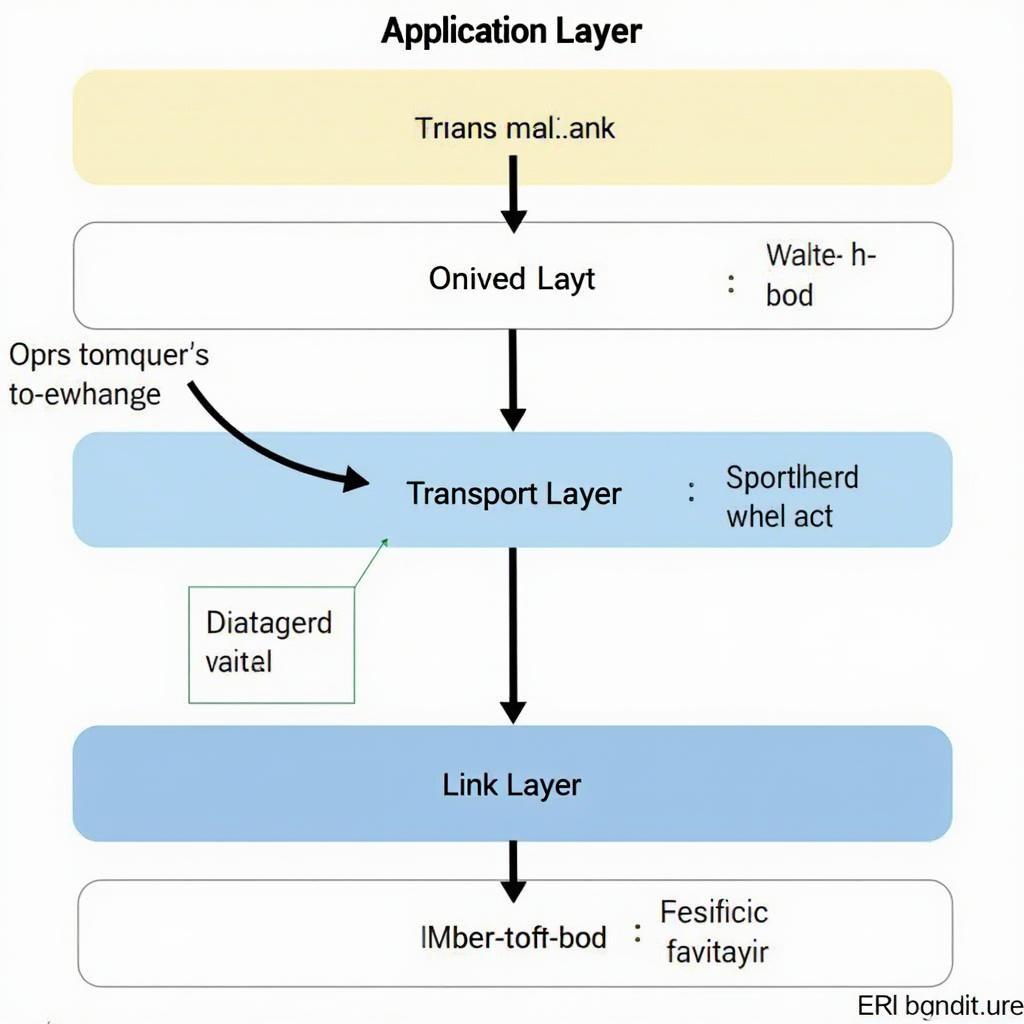
OBD2 stacks are essentially a layered software architecture designed to standardize communication between diagnostic tools and the diverse ECUs within a vehicle. They achieve this by implementing the OBD2 protocols, allowing a single scanner to interact with multiple systems, regardless of the vehicle manufacturer. This layered approach is crucial for managing the complexity of modern vehicle electronics. The typical OBD2 stack includes the application layer, the transport layer, and the link layer. Each layer performs specific functions that contribute to the overall communication process. Think of it like sending a letter: the application layer is the content of the letter, the transport layer is the envelope, and the link layer is the postal service that delivers it.
After the opening paragraph, let’s add a relevant internal link. Choosing the torque obd2 free download for pc article seems appropriate here as Torque is a popular OBD2 software application.
The Application Layer: The Brain of the Operation
This layer is the highest level of the OBD2 stack and is responsible for interpreting diagnostic requests and responses. It’s the interface that users interact with, displaying diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), sensor data, and other relevant information. This layer essentially translates the raw data from the lower layers into a user-friendly format.
The Transport Layer: Ensuring Reliable Data Delivery
The transport layer manages the flow of data between the application layer and the link layer. It ensures that data packets are transmitted reliably and in the correct order, even in the presence of network errors or interference. This layer acts as a quality control check, guaranteeing the integrity of the data being transmitted.
The Link Layer: The Physical Connection
The link layer is the lowest level of the OBD2 stack and handles the physical communication between the OBD2 scanner and the vehicle’s ECUs. This layer establishes and maintains the physical connection, ensuring that the data is transmitted accurately over the diagnostic link connector (DLC).
Why are OBD2 Stacks Important?
OBD2 stacks play a vital role in the automotive industry, facilitating diagnostics, maintenance, and repair. Without a standardized stack, communicating with different vehicle systems would be a nightmare, requiring specific tools for each make and model. OBD2 stacks simplify this process, enabling universal compatibility and streamlining the diagnostic process.
Streamlined Diagnostics: Finding the Root of the Problem
By providing a standardized communication pathway, OBD2 stacks enable mechanics and DIYers to quickly and efficiently diagnose vehicle issues. They allow access to a wealth of data, helping to pinpoint the root cause of problems and avoid unnecessary repairs.
Enhanced Maintenance: Keeping Your Car Running Smoothly
OBD2 stacks also allow for preventative maintenance. By monitoring sensor data and other parameters, mechanics can identify potential issues before they become major problems. This helps extend the life of a vehicle and minimize repair costs.
Improved Repair Efficiency: Getting Back on the Road Faster
By providing accurate and detailed diagnostic information, OBD2 stacks enable mechanics to perform repairs more efficiently. This reduces repair time and gets drivers back on the road faster. Understanding these stacks is essential for any aspiring automotive technician. Consider checking out the oxgord can obd2 ms300 scan tool for a reliable OBD2 scanner option.
Common OBD2 Stack Protocols
Several protocols exist within the OBD2 standard, each catering to specific communication needs. These include ISO 9141-2, KWP2000, ISO 14230 (KWP2000 on CAN), ISO 15765 (CAN), and SAE J1850. Understanding these protocols is vital for interpreting diagnostic data correctly.
What is ISO 9141-2?
This protocol is commonly used in older European and Asian vehicles.
What is KWP2000?
KWP2000 is also used in some European and Asian vehicles.
What is ISO 15765 (CAN)?
This is the most widely used protocol in modern vehicles, utilizing the Controller Area Network (CAN) for high-speed communication. You might be interested in learning about the v100 obd2 which utilizes this protocol.
What is SAE J1850?
This protocol is primarily used in North American vehicles.
Expert Insights
“Understanding OBD2 stacks is paramount for anyone serious about vehicle diagnostics,” says John Davis, a seasoned automotive engineer. “It’s the foundation upon which all diagnostic communication is built.”
“The layered architecture of OBD2 stacks allows for a modular and scalable approach to diagnostics,” adds Sarah Miller, a leading software developer in the automotive industry. “This ensures compatibility and simplifies the development of diagnostic tools.”
Conclusion
OBD2 stacks are essential for modern vehicle diagnostics. They provide a standardized communication framework that enables efficient troubleshooting, maintenance, and repair. By understanding the architecture, functionality, and protocols of OBD2 stacks, you can unlock the full potential of your diagnostic tools and keep your vehicle running smoothly. For a comprehensive review of a powerful diagnostic tool, check out the ancel x6 obd2 diagnostic tool review.
FAQs
- What is the purpose of an OBD2 stack? To standardize communication between diagnostic tools and vehicle ECUs.
- What are the main layers of an OBD2 stack? Application, transport, and link layers.
- Why are OBD2 stacks important? They facilitate streamlined diagnostics, enhanced maintenance, and improved repair efficiency.
- What are some common OBD2 protocols? ISO 9141-2, KWP2000, ISO 15765 (CAN), and SAE J1850.
- How do OBD2 stacks benefit DIYers? They allow access to diagnostic information and enable basic troubleshooting.
- What is the difference between the application and transport layers? The application layer interprets data, while the transport layer manages data flow.
- Where can I find more information about OBD2 scanners? Consider the bluedriver bluetooth professional obd2 page for a specific example.
For further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.