OBD2 steering angle sensors play a crucial role in modern vehicle safety and performance. This article delves into the intricacies of these sensors, exploring their function, common issues, diagnostic procedures, and the importance of accurate readings for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). After reading this, you’ll have a deeper understanding of how these small but mighty components contribute to a safer and more controlled driving experience. We’ll explore everything from basic operation to advanced troubleshooting techniques.
Understanding the functionality of an sas obd2 is crucial for modern vehicle diagnostics. The steering angle sensor (SAS) is a critical component in many modern vehicles, providing data to various electronic control units (ECUs) that manage systems like electronic stability control (ESC), anti-lock brakes (ABS), and even adaptive cruise control. It precisely measures the angle of the steering wheel, allowing these systems to react accurately to driver inputs and road conditions. This data is essential for maintaining vehicle stability and enhancing safety features. For instance, if the vehicle starts to skid, the ESC system uses the steering angle sensor data, along with other inputs, to determine the appropriate braking and engine torque adjustments needed to regain control.
How Does the OBD2 Steering Angle Sensor Work?
The steering angle sensor typically uses one of two technologies: optical or magnetic. Optical sensors use a light source and a sensor to detect the position of a coded disc attached to the steering column. Magnetic sensors, on the other hand, utilize the Hall effect to measure changes in magnetic fields, providing information about the steering wheel’s position. Regardless of the technology used, the sensor generates a signal that corresponds to the steering wheel angle, which is then transmitted to the vehicle’s ECUs.
Common Problems with OBD2 Steering Angle Sensors
Several issues can arise with steering angle sensors, including:
- Sensor Malfunction: The sensor itself can fail due to internal component damage, wear and tear, or exposure to harsh environmental conditions.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring between the sensor and the ECUs can disrupt the signal transmission, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Calibration Errors: The steering angle sensor needs to be calibrated to ensure it provides accurate data. If the calibration is off, the ECUs may receive incorrect information, affecting the performance of various systems.
Diagnosing OBD2 Steering Angle Sensor Issues
Diagnosing steering angle sensor problems often involves using an OBD2 scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Codes related to the steering angle sensor can pinpoint the nature of the problem. For instance, a specific code might indicate a sensor malfunction, wiring issue, or calibration error. Specialized diagnostic tools might also be necessary to check the sensor’s output signal and verify its proper operation. Sometimes, a visual inspection of the wiring and connector can also reveal obvious problems.
Why is Accurate Steering Angle Sensor Data Important?
Accurate data from the steering angle sensor is critical for the proper function of several safety and performance systems:
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): ESC relies on precise steering angle information to determine the driver’s intended path and compare it to the vehicle’s actual trajectory.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): The ABS system uses steering angle data to optimize braking performance during turns, preventing wheel lockup and maintaining control.
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): In vehicles equipped with ACC, the steering angle sensor helps the system maintain a safe following distance and stay within the lane.
- Lane Keeping Assist (LKA): LKA systems use steering angle information to detect lane departures and provide corrective steering inputs.
John Doe, a seasoned automotive engineer at a major car manufacturer, emphasizes the importance of the steering angle sensor: “The steering angle sensor is a small but vital component. Its accuracy directly impacts the effectiveness of numerous safety systems, ensuring drivers maintain control and stability in various driving situations.”
Resetting and Calibrating the OBD2 Steering Angle Sensor
In some cases, resetting or recalibrating the steering angle sensor can resolve issues. This often requires using a specialized diagnostic tool or following specific procedures outlined in the vehicle’s service manual. An obd2 icarsoft vag ii might be useful for certain vehicle makes and models. Understanding these procedures and using the right tools is crucial for ensuring accurate calibration and proper system function.
Remember, if you’re unsure about any aspect of diagnosing or repairing steering angle sensor issues, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
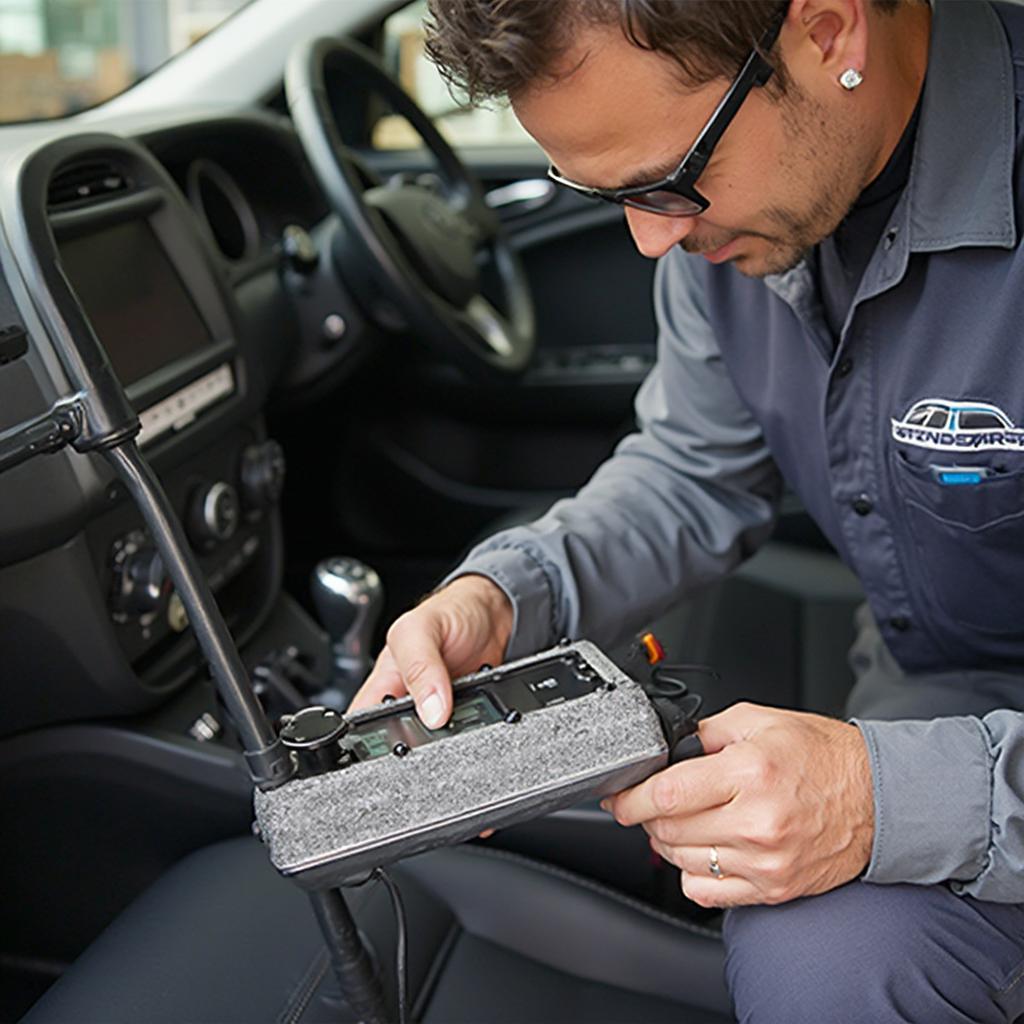 OBD2 Steering Angle Sensor Calibration Process
OBD2 Steering Angle Sensor Calibration Process
You can also check out these related resources: u11c2 obd2 code for a jeep patriot 2016 and obd2 c1513. Another resource that may be of interest is obd2 can controller breakout.
Conclusion
The OBD2 steering angle sensor is a crucial component in modern vehicles, playing a vital role in the proper function of various safety and performance systems. Understanding its operation, common problems, and diagnostic procedures can help ensure your vehicle remains safe and performs optimally. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any warning signs related to the steering system, including the steering angle sensor, are crucial for a safe and enjoyable driving experience. Remember, accurate obd2 steering angle information is essential for maintaining vehicle stability and maximizing the effectiveness of advanced driver-assistance systems.
FAQ
-
What is the OBD2 steering angle sensor?
- The OBD2 steering angle sensor measures the position of your steering wheel and relays this information to various vehicle systems.
-
What are the symptoms of a faulty steering angle sensor?
- Symptoms can include illuminated warning lights, malfunctioning stability control, and inaccurate speedometer readings.
-
How is the OBD2 steering angle sensor diagnosed?
- Diagnosis typically involves using an OBD2 scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes.
-
Can I replace the OBD2 steering angle sensor myself?
- While possible, it’s often recommended to have a qualified mechanic perform the replacement and calibration.
-
How is the OBD2 steering angle sensor calibrated?
- Calibration often requires a specialized diagnostic tool and following specific procedures outlined in the vehicle’s service manual.
-
Why is a functioning steering angle sensor important?
- It’s crucial for the proper function of safety systems like ESC, ABS, and advanced driver-assistance systems.
-
How can I prevent issues with my steering angle sensor?
- Regular vehicle maintenance and prompt attention to any steering system warning lights can help prevent problems.
Common Scenarios & Questions
- Scenario: My ESC light is on. Could it be the steering angle sensor? Answer: Yes, a faulty steering angle sensor can trigger the ESC light. It’s recommended to have it diagnosed.
- Question: How much does it cost to replace a steering angle sensor? Answer: The cost varies depending on the make and model of your vehicle, but it can range from a few hundred to over a thousand dollars.
For further information, explore our other articles on OBD2 systems and troubleshooting.
Need help? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer support team is available 24/7.