Your cart is currently empty!

Understanding OBD2 Transfer Case Codes: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to diagnosing issues with your vehicle’s four-wheel drive or all-wheel drive system, understanding OBD2 transfer case codes is crucial. These codes provide valuable insights into the health and functionality of your transfer case, helping you pinpoint problems and get back on the road smoothly.
 Transfer Case Connected to OBD2 Scanner
Transfer Case Connected to OBD2 Scanner
What is a Transfer Case?
Before we delve into the codes themselves, let’s clarify what a transfer case does. In simplest terms, the transfer case is a component found in four-wheel drive and all-wheel drive vehicles that splits power from the engine and transmission and sends it to both the front and rear axles. This allows for enhanced traction and control, especially in challenging driving conditions like snow, mud, or off-road terrain.
The Importance of OBD2 Transfer Case Codes
Your vehicle’s onboard computer system, also known as the Engine Control Unit (ECU), continuously monitors various components, including the transfer case. When a malfunction or issue arises, the ECU generates a specific OBD2 code, storing it in its memory.
These codes act as a starting point for diagnosing the problem. By accessing these codes using an OBD2 scanner, you gain valuable information about the potential root cause of the issue, saving you time and effort in the diagnostic process.
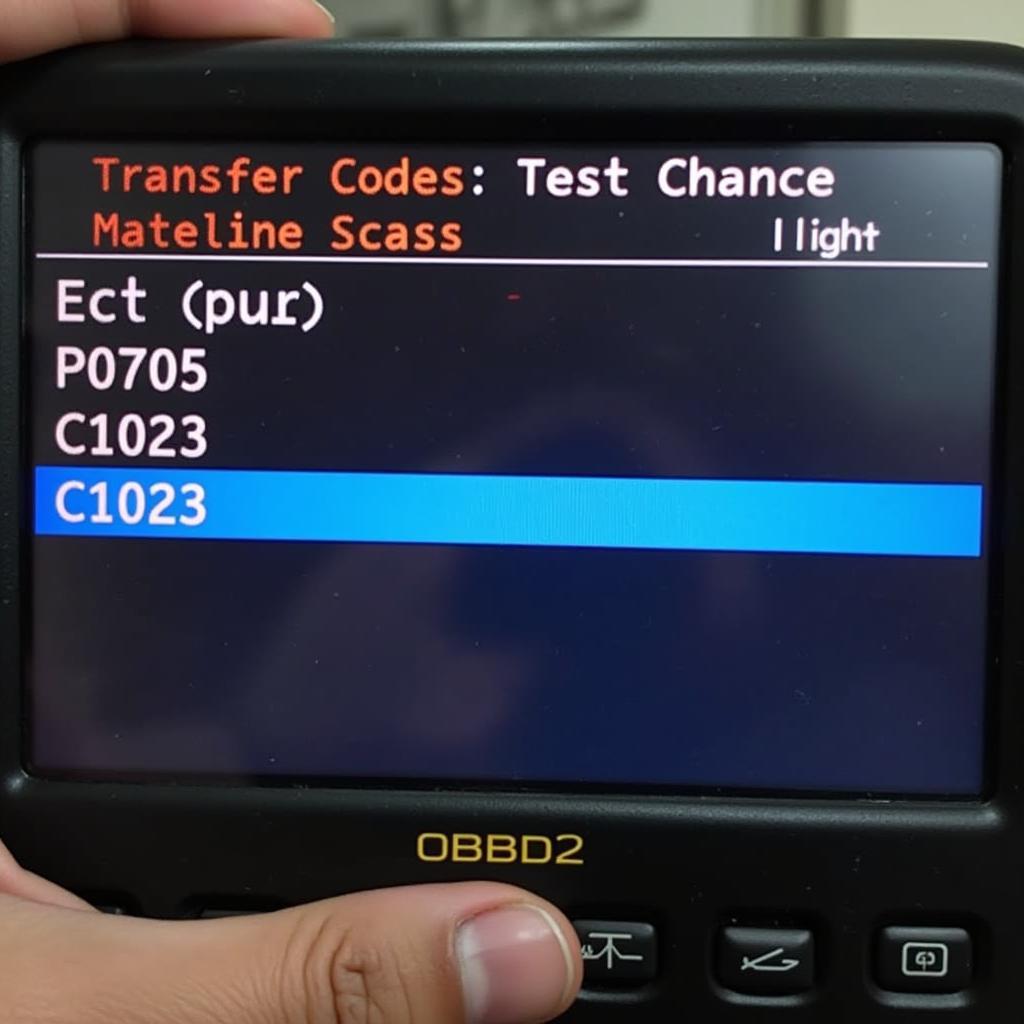 OBD2 Scanner Screen Showing a Transfer Case Code
OBD2 Scanner Screen Showing a Transfer Case Code
Common OBD2 Transfer Case Codes and Their Meanings
While the specific codes and their interpretations may vary depending on your vehicle’s make and model, here are some of the most common OBD2 transfer case codes and their general meanings:
- P0705: This code indicates a problem with the transfer case range sensor circuit. This sensor relays information to the ECU about the gear the transfer case is currently in (e.g., 2WD, 4WD High, 4WD Low).
- P0706: This code suggests an issue with the transfer case range sensor circuit itself, such as a faulty sensor or wiring problem.
- P0712: A P0712 code points to a problem with the transfer case input speed sensor circuit. This sensor monitors the speed of the input shaft coming from the transmission.
- P0713: Similar to P0712, this code indicates a fault within the transfer case input speed sensor circuit, potentially a faulty sensor or wiring issue.
- C1023: This code often relates to a malfunctioning actuator motor in the transfer case, which is responsible for engaging and disengaging four-wheel drive or switching between different drive modes.
Diagnosing Transfer Case Issues: Beyond the Codes
While OBD2 codes provide a valuable starting point, it’s essential to remember that they don’t always tell the whole story.
“Think of OBD2 codes as clues rather than definitive answers,” advises John Miller, a seasoned automotive technician with over 20 years of experience. “While they pinpoint the area of concern, further inspection and testing are often necessary to determine the exact cause and solution.”
 Mechanic Inspecting a Vehicle’s Transfer Case
Mechanic Inspecting a Vehicle’s Transfer Case
Here are some steps to take after retrieving OBD2 transfer case codes:
- Check for obvious signs: Before diving into complex diagnostics, visually inspect the transfer case for any leaks, damage, or loose connections.
- Consult your vehicle’s service manual: Your car’s service manual is a treasure trove of information, providing specific diagnostic procedures and wiring diagrams tailored to your vehicle model.
- Consider professional help: If you’re uncomfortable with advanced diagnostics or lack the necessary tools, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic specializing in transfer case repairs.
Conclusion
Understanding OBD2 transfer case codes is essential for anyone driving a four-wheel drive or all-wheel drive vehicle. By recognizing these codes and taking appropriate diagnostic steps, you can address potential issues early on, ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your vehicle’s drivetrain. Remember, while OBD2 codes are incredibly helpful, they are just one piece of the puzzle. Combining code reading with thorough inspections and, if needed, professional expertise is the key to keeping your vehicle running smoothly on all terrains.

Leave a Reply