OBD2 vs. OBD1 is a common query among car enthusiasts and professionals. Understanding the key differences between these two onboard diagnostic systems is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and repair. This article will delve into the specifics of OBD1 and OBD2, exploring their functionalities, capabilities, and the significant advancements introduced with OBD2. We’ll explore everything from diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to connector types, providing a comprehensive overview of these essential automotive systems.
Decoding the Acronyms: OBD1 and OBD2
OBD stands for On-Board Diagnostics. These systems are designed to monitor various aspects of your vehicle’s performance, identify potential issues, and store relevant data for retrieval by diagnostic tools. OBD1, the predecessor, was a less standardized system, varying significantly between manufacturers and even models. This made diagnostics more complex and often required specialized equipment. OBD2, implemented in 1996 for gasoline vehicles and 1997 for diesel vehicles in the United States, revolutionized vehicle diagnostics with its standardized protocols, making it easier to diagnose and repair vehicles regardless of make or model.
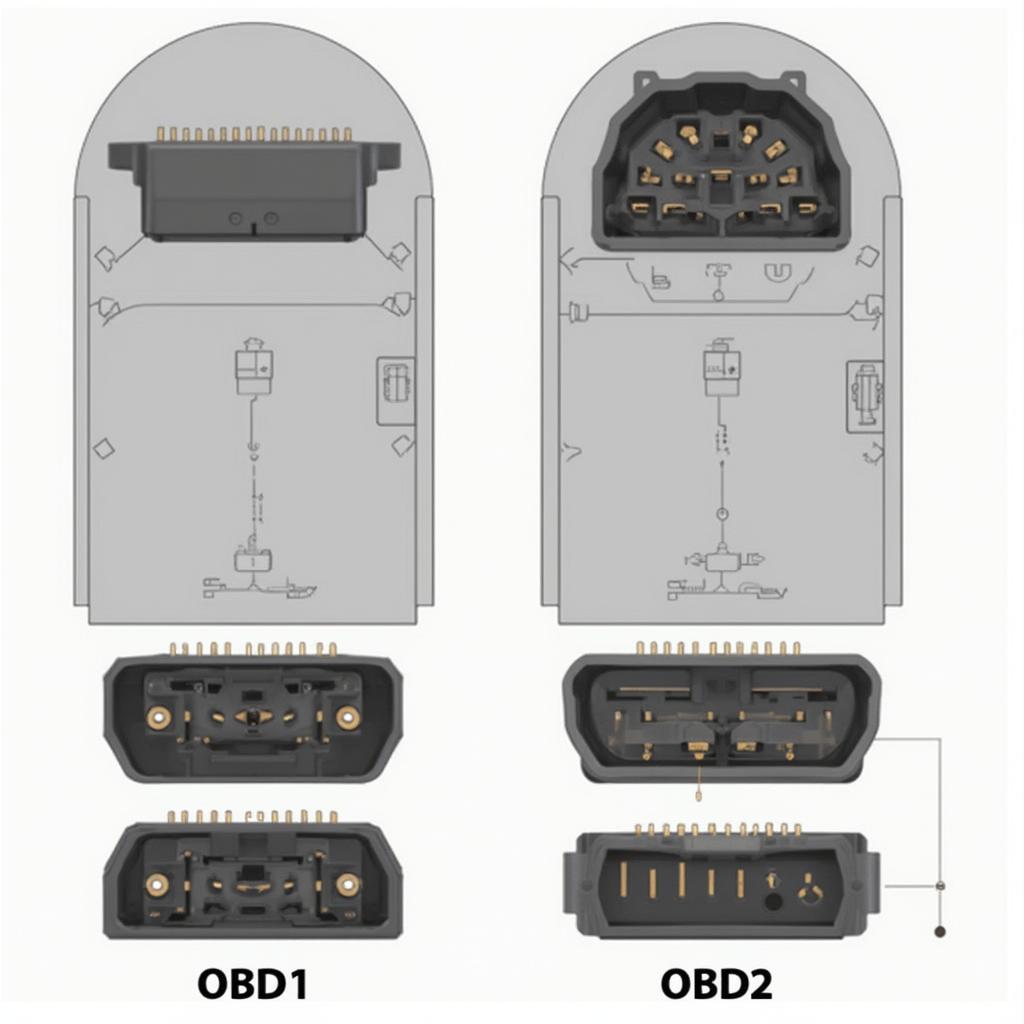
One of the key improvements of OBD2 was the standardization of the diagnostic connector. This universal connector, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, provides a consistent interface for connecting OBD2 scanners. This eliminated the need for multiple connectors and adapters, simplifying the diagnostic process for mechanics and car owners alike. This standardization was a significant step forward in vehicle diagnostics.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): OBD2’s Standardized Approach
Another major advancement of OBD2 was the standardization of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These codes, displayed by OBD2 scanners, pinpoint specific areas of malfunction within the vehicle’s systems. Unlike the less consistent codes of OBD1, OBD2 DTCs follow a specific alphanumeric format, making it easier to identify the nature of the problem. This standardized approach allows for quick and accurate diagnostics across different vehicle makes and models, simplifying the troubleshooting process.
What Does a DTC Look Like?
A typical OBD2 DTC consists of a letter and four numbers. The letter indicates the system affected (e.g., “P” for Powertrain, “B” for Body, “C” for Chassis, “U” for Network). The numbers provide more specific information about the fault. This standardized format allows technicians to quickly identify the problem area and begin the necessary repairs.
obd1 vs obd2 catalytic converter
OBD2: Enhanced Monitoring and Emissions Control
OBD2 systems monitor a wider range of vehicle components and systems than OBD1, including emissions-related components. This increased monitoring capability helps ensure compliance with stricter emissions regulations and contributes to a cleaner environment. OBD2 is crucial for detecting issues that can impact emissions, helping maintain a healthier atmosphere.
“The standardization brought by OBD2 was a game-changer,” says automotive expert, Michael Stevens. “It made diagnostics significantly easier and more efficient for everyone involved, from professional mechanics to everyday car owners.”
OBD1 vs. OBD2: Key Differences at a Glance
The shift from OBD1 to OBD2 brought about significant improvements in vehicle diagnostics. Here’s a table summarizing the key distinctions:
| Feature | OBD1 | OBD2 |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | Limited, varied by manufacturer | Standardized across all makes and models |
| Diagnostic Codes | Inconsistent, manufacturer-specific | Standardized DTCs |
| Connector | Varies by manufacturer | Standardized 16-pin connector |
| Monitoring Scope | Limited | Extensive, including emissions systems |

Conclusion: The OBD2 Advantage
The introduction of OBD2 marked a major advancement in vehicle diagnostics. Its standardized protocols, comprehensive monitoring, and readily accessible data have simplified the troubleshooting and repair process. While OBD1 served its purpose, OBD2 offers a more efficient and user-friendly approach to vehicle maintenance, making it a crucial tool for both professionals and car owners alike. Understanding the differences between OBD1 and OBD2 is essential for anyone working with modern vehicles.
FAQ
- What cars use OBD1? Generally, gasoline vehicles manufactured before 1996 in the US used OBD1.
- Is OBD2 better than OBD1? Yes, OBD2 offers significant improvements in standardization, monitoring, and data accessibility.
- What is a DTC? A DTC, or Diagnostic Trouble Code, is a code that indicates a specific malfunction within a vehicle’s systems.
- Where is the OBD2 port located? Typically under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Can I use an OBD2 scanner on an OBD1 car? No, you need an adapter or a scanner specifically designed for OBD1.
- What does the “P” in a DTC code mean? It signifies a Powertrain-related fault.
- Why is OBD2 important? OBD2 is essential for diagnostics, emissions control, and ensuring vehicle compliance with regulations.
For assistance, contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We offer 24/7 customer support.

