OBD2 and CAN bus are often mentioned together, leading to confusion about their relationship. This article clarifies the connection and differences between OBD2 and CAN bus, helping you understand their roles in modern vehicle diagnostics. We’ll explore the evolution of onboard diagnostics, delve into the intricacies of the CAN bus protocol, and highlight the benefits of using OBD2 scanners with CAN bus capabilities.
What is OBD2?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system that allows external devices, like OBD2 scanners, to access a vehicle’s diagnostic data. It was mandated in the United States for 1996 and newer model year vehicles to monitor emissions and identify malfunctions. OBD2 provides a common connector and communication protocol, enabling universal compatibility with diagnostic tools. This standardization simplified vehicle troubleshooting and repair, making it easier for mechanics and car owners alike to identify and fix problems. Learn more about how OBD2 is used with heavy trucks with our guide on obd2 scanner for heavy trucks.
How Does OBD2 Work?
OBD2 works by monitoring various sensors throughout the vehicle. These sensors collect data on everything from engine performance and emissions to transmission function and airbag systems. When a problem is detected, the OBD2 system stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in the vehicle’s computer. This DTC can then be retrieved using an OBD2 scanner, providing valuable information about the nature of the malfunction. Using an obd2 car tracker can further enhance your diagnostic capabilities by providing real-time data.
What is CAN Bus?
CAN bus, or Controller Area Network, is a robust vehicle communication system. Unlike traditional wiring harnesses, which require individual connections for each component, CAN bus utilizes a network architecture. This network allows various electronic control units (ECUs) within the vehicle to communicate with each other efficiently and reliably. CAN bus reduces the complexity of wiring and allows for more sophisticated features and functionalities within modern vehicles. You can learn more about OBD2 software options in our article on the best professional obd2 software.
CAN Bus and its Role in Modern Vehicles
CAN bus is essential for numerous functions in today’s vehicles, from engine management and transmission control to safety systems like anti-lock brakes (ABS) and airbags. Its high-speed data transfer capabilities and robust error detection mechanisms make it a critical component in ensuring safe and efficient vehicle operation.
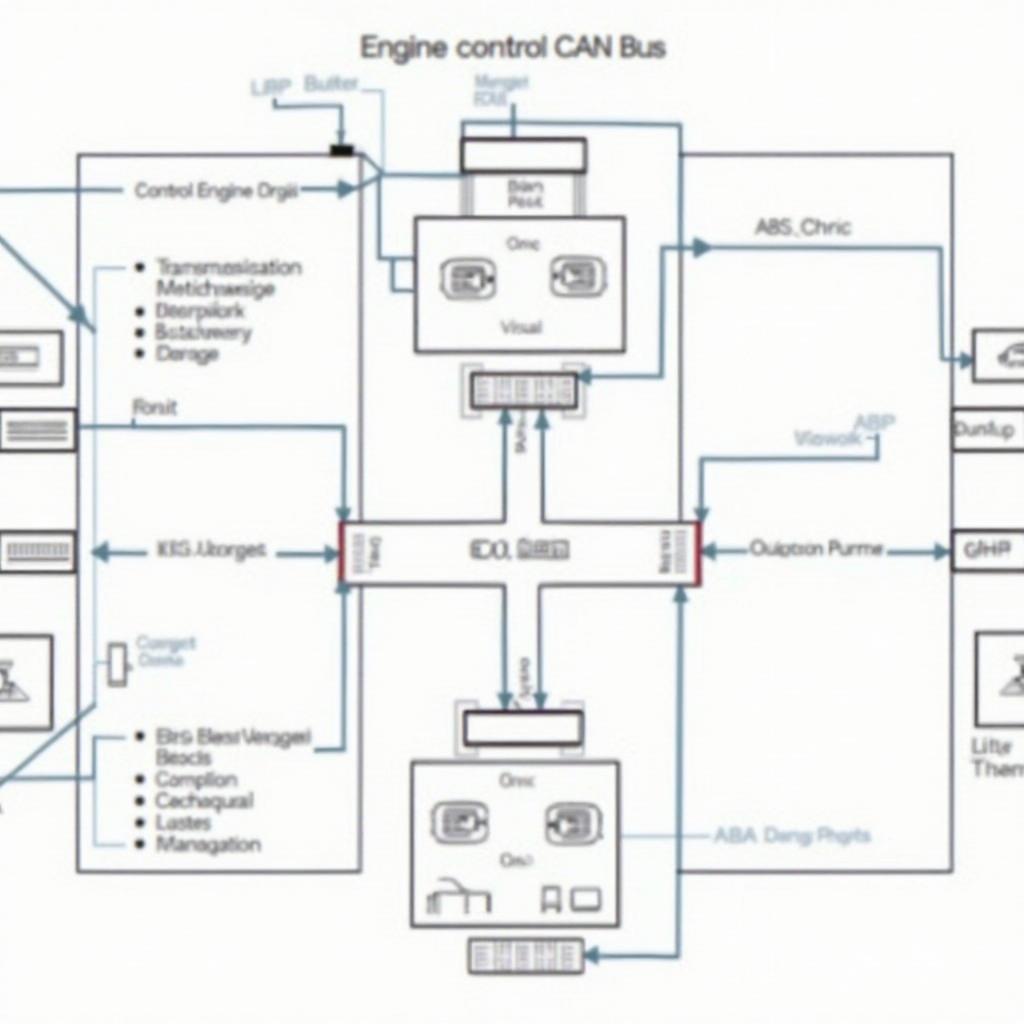 CAN Bus Diagram
CAN Bus Diagram
How OBD2 and CAN Bus Work Together
While distinct technologies, OBD2 and CAN bus are often intertwined. Many modern vehicles utilize CAN bus as the underlying communication protocol for OBD2. This means the OBD2 scanner connects to the vehicle’s CAN bus network to retrieve diagnostic data. The OBD2 standard defines how the scanner requests information and how the vehicle responds, ensuring compatibility across different makes and models. Explore the use of OBD2 with electric vehicles in our article obd2 c ev.
Why is this Connection Important?
The integration of OBD2 and CAN bus allows for more comprehensive diagnostics. By accessing the CAN bus data, OBD2 scanners can retrieve a wider range of information, providing a more detailed picture of the vehicle’s health. This advanced diagnostic capability is crucial for effectively troubleshooting complex issues in modern vehicles. GM vehicle owners might find our resource on gm obd2 software particularly helpful.
“Understanding the relationship between OBD2 and CAN bus is crucial for anyone working with modern vehicles. It’s the key to unlocking the wealth of diagnostic information available through the vehicle’s network,” says automotive expert, David Miller, from the Automotive Technology Institute.
Conclusion
OBD2 and CAN bus are crucial technologies in modern vehicle diagnostics. While OBD2 provides the standardized interface and communication protocol, CAN bus often serves as the underlying network facilitating the data exchange. Understanding their connection and differences is essential for anyone involved in vehicle maintenance and repair. Choosing the right OBD2 scanner with CAN bus compatibility allows for comprehensive diagnostics, enabling efficient troubleshooting and effective repairs.
FAQ
-
What is the difference between OBD2 and CAN bus?
OBD2 is a standardized diagnostic interface, while CAN bus is a vehicle communication network. OBD2 often uses CAN bus as its underlying communication protocol. -
Do all vehicles use CAN bus for OBD2?
While many modern vehicles use CAN bus for OBD2, older vehicles might use different communication protocols. -
Why is CAN bus important for OBD2?
CAN bus allows OBD2 scanners to access a wider range of diagnostic data, providing a more complete understanding of the vehicle’s status. -
What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner with CAN bus capability?
CAN bus-compatible OBD2 scanners can retrieve more comprehensive diagnostic information, aiding in more accurate and efficient troubleshooting. -
How do I know if my vehicle uses CAN bus?
You can check your vehicle’s owner’s manual or use an OBD2 scanner to identify the communication protocols used. -
Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my vehicle?
While the OBD2 connector is standardized, it’s crucial to choose a scanner compatible with your vehicle’s specific communication protocols, including CAN bus if applicable. -
What type of information can be accessed through OBD2 using CAN bus?
OBD2 scanners can access a wide range of information via CAN bus, including engine performance, emissions data, transmission status, ABS data, and airbag system information.
Common OBD2 and CAN Bus Related Issues
- Communication Errors: Difficulties retrieving data from the vehicle’s systems.
- Incompatible Scanners: Using an OBD2 scanner that doesn’t support the vehicle’s communication protocols.
- Intermittent Issues: Problems that occur sporadically, making diagnosis challenging.
Further Reading and Related Topics
- OBD2 for Hybrid Vehicles
- Advanced Diagnostic Techniques using OBD2 and CAN bus
- Understanding Vehicle Communication Protocols
Need further assistance? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880 or Email: [email protected]. Our 24/7 customer service team is ready to help.
