The dreaded check engine light illuminates your dashboard, and your OBD2 scanner reveals the cryptic code: P0132. This indicates a problem with your vehicle’s oxygen sensor, specifically the oxygen sensor 1, bank 1, sensor 1 (O2 sensor B1S1) – a crucial component for fuel efficiency and emissions control. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the P0132 OBD2 fault code, its causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and solutions.
What Does the P0132 Code Mean?
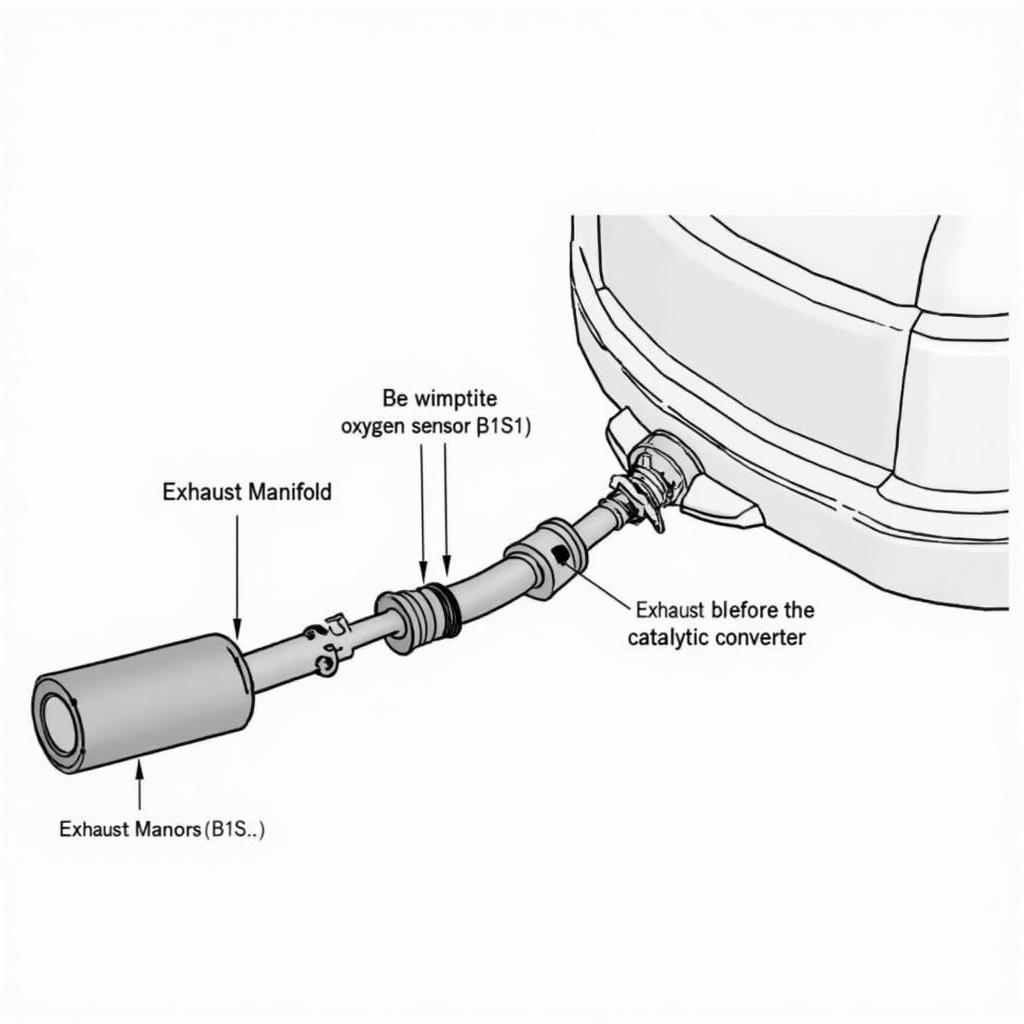
The P0132 code signifies a high voltage reading from the upstream oxygen sensor (B1S1). This sensor, located in the exhaust manifold before the catalytic converter, measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. This data is sent to the engine control module (ECM), which adjusts the air-fuel mixture accordingly. A high voltage signal usually indicates an excessively rich fuel mixture. Let’s dive deeper into understanding what causes this issue. After reading the initial description of the code, you might be wondering about similar issues on your VW. You can find helpful resources, like information on obd2 code p0134 vw, on our site.
Causes of the P0132 OBD2 Code
Several factors can trigger the P0132 code, ranging from simple fixes to more complex mechanical issues:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The most common culprit is a failing O2 sensor. Over time, these sensors can become contaminated or wear out, leading to inaccurate readings. If you suspect a faulty sensor, you may want to explore related articles like faulty sensor obd2.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system before the O2 sensor can introduce excess oxygen, disrupting the sensor’s readings.
- Fuel Pressure Regulator Issues: A malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator can cause excessive fuel delivery, leading to a rich mixture.
- Fuel Injector Problems: Leaky or clogged fuel injectors can disrupt the fuel-air ratio, triggering the P0132 code.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the engine’s vacuum system can affect the air intake, causing a rich mixture.
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor Issues: A faulty MAF sensor can provide incorrect air intake readings to the ECM, impacting fuel delivery.
- Engine Control Module (ECM) Problems: While less common, a faulty ECM can also contribute to the P0132 code.
Symptoms of the P0132 Code
Besides the illuminated check engine light, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Decreased Fuel Economy: A rich fuel mixture leads to higher fuel consumption.
- Rough Idle or Stalling: The engine may idle unevenly or stall due to the incorrect air-fuel mixture.
- Hesitation or Stumbling on Acceleration: The engine may hesitate or stumble when accelerating.
- Black Smoke from the Exhaust: A rich mixture can cause black smoke to be emitted from the tailpipe.
How to Diagnose and Fix the P0132 Code
Diagnosing the P0132 code requires a systematic approach:
- Visual Inspection: Check for obvious signs of exhaust leaks, damaged wiring, or a faulty O2 sensor.
- Scan Tool Diagnosis: Use an OBD2 scanner to confirm the P0132 code and check for other related codes. If you experience communication issues, reviewing resources on obd2 iso canbus protocol failed can be beneficial.
- Voltage Check: Using a multimeter, check the voltage of the O2 sensor. A high voltage reading confirms the problem.
- Fuel Pressure Test: Test the fuel pressure to ensure it’s within the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Vacuum Leak Test: Check for vacuum leaks using a smoke machine or a propane torch.
- MAF Sensor Inspection: Inspect the MAF sensor for contamination or damage.
Once the root cause is identified, the appropriate repair can be performed. This might involve replacing the O2 sensor, fixing exhaust leaks, repairing or replacing the fuel pressure regulator, cleaning or replacing fuel injectors, or addressing vacuum leaks.
Why is Fixing the P0132 Code Important?
Ignoring the P0132 code can lead to further engine damage, reduced fuel efficiency, and increased emissions. Addressing the issue promptly ensures optimal engine performance and minimizes potential long-term problems. It’s worth noting that other codes, like the obd2 code p1151, can also indicate sensor issues and should be addressed promptly.
Conclusion
The P0132 OBD2 fault code indicates a problem with the oxygen sensor B1S1, which can negatively impact your vehicle’s performance and emissions. Understanding the code, its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures is crucial for effective troubleshooting and repair. Don’t delay in addressing this issue to prevent further complications and maintain optimal vehicle operation.
FAQ
-
What does the P0132 code mean? It indicates a high voltage reading from the upstream oxygen sensor (B1S1).
-
What are the common causes of the P0132 code? A faulty oxygen sensor, exhaust leaks, fuel pressure regulator issues, or fuel injector problems are common causes.
-
What are the symptoms of the P0132 code? Decreased fuel economy, rough idle, hesitation on acceleration, and black smoke from the exhaust are potential symptoms.
-
How do I diagnose the P0132 code? Visual inspection, scan tool diagnosis, voltage checks, fuel pressure tests, and vacuum leak tests can help diagnose the problem.
-
How do I fix the P0132 code? The fix depends on the root cause and may involve replacing the O2 sensor, fixing leaks, or addressing fuel system issues.
-
Can I drive with the P0132 code? While you might be able to drive, it’s recommended to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage.
-
Is the P0132 code serious? Ignoring the code can lead to further engine damage and decreased fuel efficiency, so it should be addressed as soon as possible.
You might also find our resource on obd2 code 132 dodge ram helpful if you own a Dodge Ram.
Need further assistance? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected]. Our customer support team is available 24/7.