Your cart is currently empty!
Understanding P0138 OBD2 Code: Oxygen Sensor Issues and How to Fix Them
A “check engine” light glowing on your dashboard can be a nerve-wracking experience. It often signifies a problem with your car’s engine, leaving you wondering about the cause and potential costs. When you connect an OBD2 scanner and encounter the P0138 code, it points to an issue with your oxygen sensor, specifically the one located before the catalytic converter on Bank 1, Sensor 2.
But what does this code mean, and how serious is it?
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the P0138 OBD2 code, explaining its causes, symptoms, and providing actionable solutions to get your car running smoothly again.
What Does the P0138 Code Mean?
The P0138 code specifically refers to a “high voltage” problem detected in the oxygen sensor circuit for Bank 1, Sensor 2. Let’s break down what this means:
- Oxygen Sensor (O2 Sensor): These sensors, located in your car’s exhaust system, play a critical role in monitoring the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. They relay this information to your car’s computer, the Engine Control Unit (ECU), which adjusts the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion and emissions control.
- Bank 1: This refers to the side of the engine that contains cylinder #1. Most vehicles with a V engine configuration have two banks.
- Sensor 2: This indicates the downstream oxygen sensor, positioned after the catalytic converter. Its primary function is to monitor the catalytic converter’s efficiency.
- High Voltage: This means the voltage signal from the oxygen sensor is higher than the expected range, indicating a potential problem with the sensor itself, its wiring, or the circuit.
In essence, the P0138 code suggests that the downstream oxygen sensor on the side of the engine with cylinder #1 is sending an unusually high voltage signal to the ECU.
What Causes a P0138 Code?
Several factors can contribute to the P0138 code:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor is the most common culprit. Over time, the sensor can become contaminated with exhaust byproducts, leading to inaccurate readings and triggering the code.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring connections in the oxygen sensor circuit can disrupt the voltage signal, resulting in the P0138 code.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system, particularly before the downstream oxygen sensor, can introduce excess oxygen, throwing off the sensor readings.
- Faulty ECU: While less common, a malfunctioning ECU can misinterpret the signals from the oxygen sensor, leading to an erroneous P0138 code.
- Rich Fuel Mixture: A fuel mixture with too much fuel and not enough air can damage the oxygen sensor and trigger the code. This can be caused by problems with fuel injectors, fuel pressure regulators, or other components.
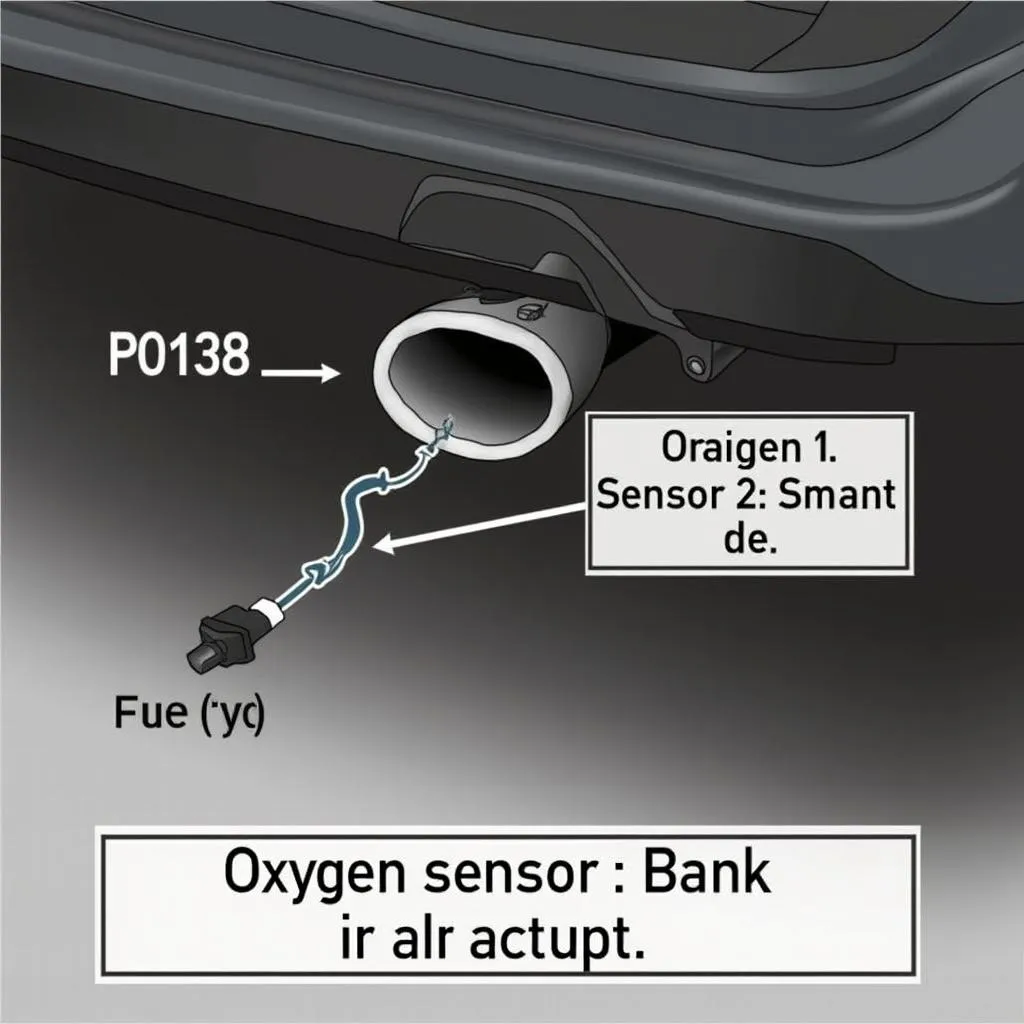
 P0138 OBD2 Code – Oxygen Sensor Location
P0138 OBD2 Code – Oxygen Sensor Location
Symptoms of a P0138 Code
While the “check engine” light is often the first indicator, other symptoms might accompany the P0138 code:
- Decreased Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to reduced fuel efficiency.
- Rough Engine Idle: You might experience a rough or uneven idling due to the incorrect air-fuel ratio caused by the faulty sensor.
- Increased Emissions: The P0138 code often indicates that your car is not effectively controlling emissions, potentially leading to a failed emissions test.
- Poor Engine Performance: A faulty oxygen sensor can affect engine performance, leading to hesitation, misfires, or reduced acceleration.
How to Diagnose a P0138 Code
While the P0138 code points towards the oxygen sensor, it’s crucial to perform a thorough diagnosis to confirm the issue:
- Read the Code: Use a reliable OBD2 scanner to retrieve the specific trouble codes stored in your car’s ECU. This will provide you with a starting point for your diagnosis.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine the wiring and connectors of the Bank 1 Sensor 2 oxygen sensor for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Repair or replace any faulty wiring.
- Check for Exhaust Leaks: Inspect the exhaust system for any leaks, particularly in the area before the downstream oxygen sensor. Repair any leaks before proceeding.
- Test the Oxygen Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the voltage signal from the oxygen sensor while the engine is running. Compare the readings with the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the sensor is functioning correctly.
- Inspect the Catalytic Converter: If the oxygen sensor readings are within the expected range, but the code persists, inspect the catalytic converter for damage or blockage.
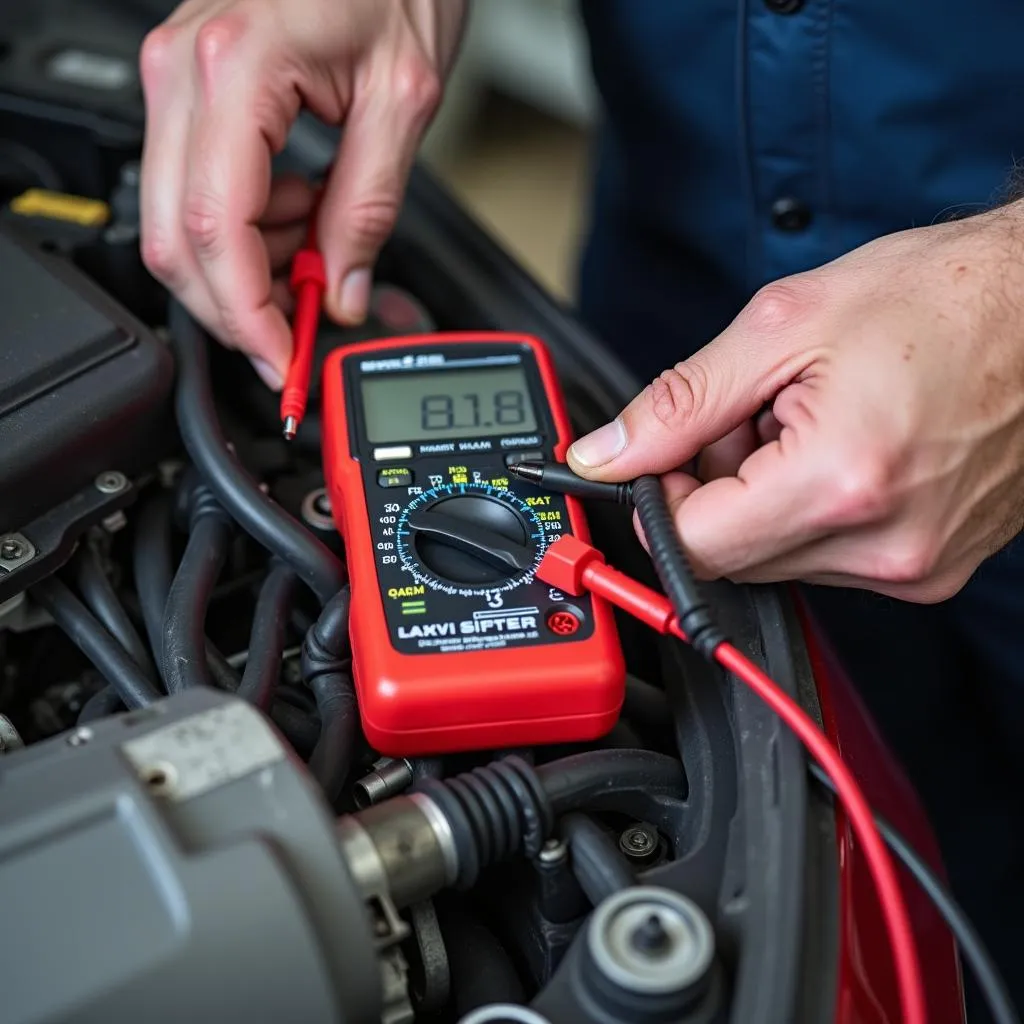 Mechanic Inspecting Oxygen Sensor with Multimeter
Mechanic Inspecting Oxygen Sensor with Multimeter
How to Fix a P0138 Code
The solution for a P0138 code depends on the underlying cause:
- Replace the Oxygen Sensor: In most cases, replacing the faulty oxygen sensor is the most effective solution. Ensure you use a high-quality sensor compatible with your car’s make, model, and year.
- Repair Wiring Issues: If you identified any wiring problems, repair or replace the affected wires or connectors.
- Fix Exhaust Leaks: Address any exhaust leaks promptly to ensure accurate oxygen sensor readings.
- Consult a Mechanic: If you suspect a faulty ECU or other complex issues, consult a qualified mechanic for diagnosis and repair.
P0138 Code: FAQs
Q: How much does it cost to fix a P0138 code?
A: The cost can range from $100 to $400 depending on whether you choose to DIY or visit a mechanic, the cost of the oxygen sensor, and labor charges.
Q: Can I drive with a P0138 code?
A: While you can drive short distances, it’s best to address the issue promptly. Prolonged driving with a faulty oxygen sensor can damage your catalytic converter, leading to expensive repairs.
Q: How long does it take to replace an oxygen sensor?
A: Replacing an oxygen sensor is a relatively straightforward process that can take 30 minutes to an hour.
Q: How do I prevent a P0138 code in the future?
A: Regular vehicle maintenance, including timely tune-ups and using high-quality fuel, can help prevent oxygen sensor issues and other engine problems.
Conclusion
Understanding the P0138 OBD2 code is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s optimal performance and minimizing emissions. While a faulty oxygen sensor is the most common culprit, a thorough diagnosis is essential to pinpoint the exact cause and implement the appropriate solution. If you lack the expertise or tools, don’t hesitate to consult a qualified mechanic for assistance. By addressing the issue promptly, you can prevent further damage to your car and costly repairs down the road.
For personalized support and expert guidance on all your OBD2 scanner needs, reach out to our team at OBDFree. We’re here to help you keep your car running smoothly. Contact us on WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, or Email: [email protected]. Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you.

Leave a Reply