The OBD2 connector, a vital gateway to your vehicle’s diagnostics, relies on specific power and ground connections for proper function. Understanding these power and grounds obd2 connector pins is crucial for anyone working with vehicle diagnostics, from professional mechanics to DIY enthusiasts. This article will delve into the intricacies of the OBD2 connector’s power and ground setup, providing a comprehensive guide to their locations, functions, and importance.
Decoding the OBD2 Connector’s Power and Ground Pins
The OBD2 connector, a standardized 16-pin interface, houses several pins dedicated to power and ground. These pins provide the necessary electrical pathways for communication between the scan tool and the vehicle’s various control modules. Without these connections, retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and monitoring vehicle performance would be impossible.
Pin 16: The Battery Power Supply
Pin 16, often labeled as “battery positive,” provides the primary power source for the OBD2 connector. This constant 12V supply directly from the vehicle’s battery ensures continuous power to the connected scan tool, even when the ignition is off. This allows for certain diagnostic functions to be performed without the need to start the engine.
Pin 4: The Chassis Ground
Pin 4 serves as the primary chassis ground for the OBD2 system. This connection provides a stable return path for the electrical current, ensuring the integrity of the communication signals between the scan tool and the vehicle’s control modules. A proper ground connection is crucial for preventing electrical interference and ensuring accurate diagnostic readings.
Pin 5: The Signal Ground
Pin 5, designated as the signal ground, provides a dedicated ground path for the data signals transmitted between the scan tool and the vehicle’s control modules. This separate ground connection minimizes noise and interference, ensuring clear and reliable communication.
Why are Power and Ground Connections so Important?
The power and grounds obd2 connector pins are fundamental to the operation of the entire OBD2 system. Without a stable power supply and proper grounding, communication between the scan tool and the vehicle’s control modules would be unreliable or even impossible.
- Accurate Diagnostics: A stable power supply and ground connection ensure accurate data transmission, leading to reliable diagnostic readings.
- Preventing Damage: Proper grounding protects the scan tool and the vehicle’s electronic systems from potential damage caused by voltage spikes or electrical shorts.
- Consistent Communication: A continuous power supply ensures uninterrupted communication between the scan tool and the vehicle, allowing for real-time monitoring of vehicle parameters.
Troubleshooting Power and Ground Issues in the OBD2 Connector
Occasionally, you might encounter issues related to the power and ground connections of the OBD2 connector. These issues can manifest as communication errors or inability to connect to the vehicle’s control modules.
Common Problems and Solutions
- No Power at Pin 16: Check the vehicle’s battery voltage and ensure the fuse related to the OBD2 connector is not blown.
- Poor Ground Connection: Inspect the ground connections at pins 4 and 5 for corrosion or loose wires. Clean or tighten the connections as needed.
- Intermittent Communication: This could indicate a loose or damaged wire in the OBD2 connector’s wiring harness.
Ensuring Reliable OBD2 Communication
Maintaining the integrity of the OBD2 connector’s power and ground connections is essential for reliable vehicle diagnostics. Regular inspection and cleaning of the connector can prevent potential issues and ensure consistent communication.
“A well-maintained OBD2 connector is essential for accurate diagnostics and preventing potential electrical issues,” says automotive diagnostics expert, Michael Carter, ASE Master Technician. “Regularly checking the power and ground connections is a simple yet crucial step in ensuring reliable communication with your vehicle’s onboard computer.”
Conclusion
Understanding the power and grounds obd2 connector pins is critical for anyone working with vehicle diagnostics. By ensuring these connections are in good working order, you can ensure accurate diagnostic readings, prevent potential damage to your equipment and vehicle, and maintain reliable communication with your vehicle’s onboard computer.
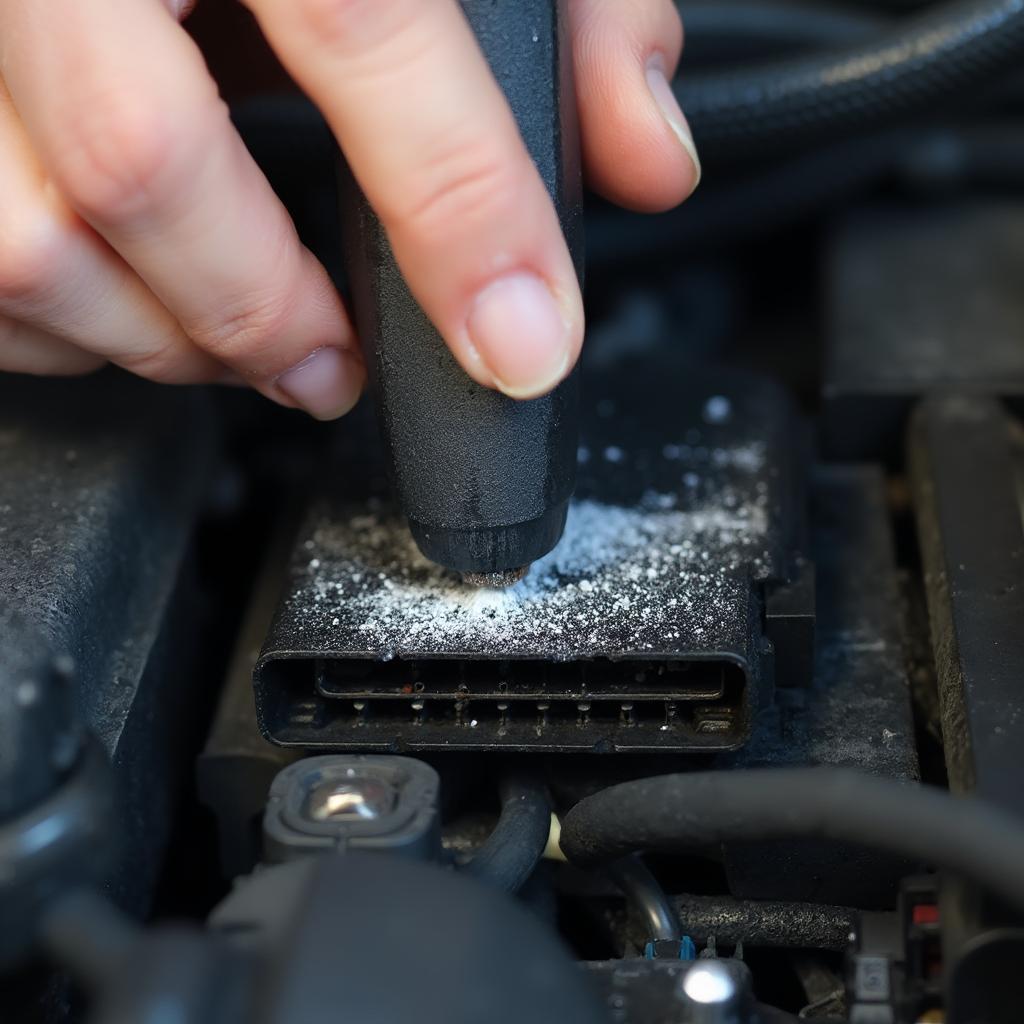 Maintaining the OBD2 Connector
Maintaining the OBD2 Connector
FAQs
- What voltage should be present at pin 16? (Around 12V)
- What happens if pin 4 is not properly grounded? (Communication errors or inability to connect)
- Can I use a standard multimeter to test the OBD2 connector’s power and ground? (Yes)
- What are the most common causes of OBD2 communication problems? (Loose connections, blown fuses, damaged wiring)
- How can I prevent corrosion in the OBD2 connector? (Regular cleaning and applying dielectric grease)
- What should I do if I suspect a problem with the OBD2 connector’s wiring harness? (Consult a qualified mechanic)
- Where can I find more information about OBD2 diagnostics? (OBDFree website)
For further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer support team is available 24/7.