OBD1 and OBD2 scanners are essential tools for diagnosing car problems. This article delves into the differences between these two systems, their functionalities, and how they’ve revolutionized vehicle diagnostics. We’ll explore their evolution, benefits, and how you can leverage them for optimal car maintenance. After reading this, you’ll have a solid grasp of what OBD1 and OBD2 scanners are and how they empower you to understand your vehicle better. You might even be interested in an ebay obd2 scanner review after learning about them!
Understanding OBD1 Scanners
OBD1, or On-Board Diagnostics generation one, represents the initial stage of computerized car diagnostics. Introduced in the early 1980s, OBD1 systems varied significantly between manufacturers, lacking standardization. Each carmaker employed proprietary connectors, protocols, and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). This made diagnosis complex, requiring specialized equipment for each vehicle make and model. OBD1 primarily focused on monitoring emissions-related components and systems. Diagnostics often involved checking for stored fault codes using a basic code reader or by manipulating jumpers under the hood.
Limitations of OBD1
The lack of standardization was a major drawback of OBD1. Technicians needed multiple tools and extensive knowledge of different manufacturer systems. Retrieving codes often required consulting complicated manuals, and the limited data provided made pinpointing the root cause of a problem challenging.
The Evolution to OBD2: A Standardized Approach
OBD2, introduced in 1996 in the United States, marked a significant advancement in car diagnostics. This standardized system uses a universal 16-pin connector and a common set of DTCs. This standardization simplified diagnostics, enabling a single scanner to work across different vehicle makes and models. OBD2 expands beyond emissions monitoring to encompass a broader range of systems, including engine performance, transmission, and other critical components. It provides access to real-time data, allowing technicians to monitor sensor readings and identify issues more efficiently.
Advantages of OBD2
The key advantages of OBD2 include standardization, enhanced diagnostic capabilities, access to real-time data, and improved emissions control. This standardized approach simplifies diagnostics for technicians and empowers car owners to understand their vehicles better. OBD2 scanners can provide valuable insights into vehicle performance, allowing proactive maintenance and preventing potential issues.
How Does an OBD2 Scanner Work?
An OBD2 scanner connects to the vehicle’s diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard. It communicates with the vehicle’s onboard computer, retrieving stored DTCs and accessing real-time data from various sensors. The scanner then displays this information on its screen, allowing users to interpret the codes and understand the underlying issues. Some advanced scanners also offer features like live data graphing, freeze frame data, and emissions readiness checks. For instance, you can learn more about specific trouble codes like obd2 b codes.
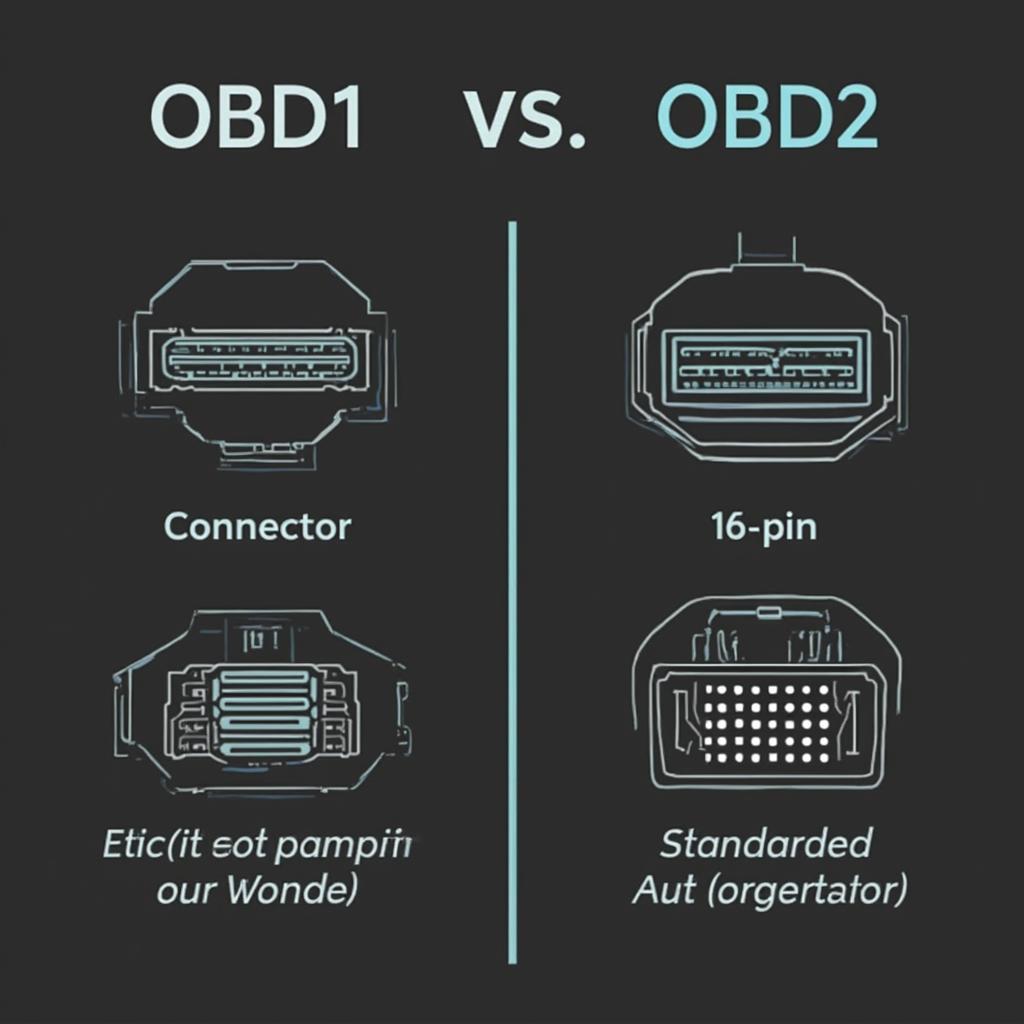
Key Differences Between OBD1 and OBD2
| Feature | OBD1 | OBD2 |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | Manufacturer-specific | Standardized |
| Connector | Varies | 16-pin |
| DTCs | Manufacturer-specific | Standardized |
| Data Access | Limited | Real-time data and stored codes |
| Systems Covered | Primarily emissions-related | Broader range, including engine, transmission |
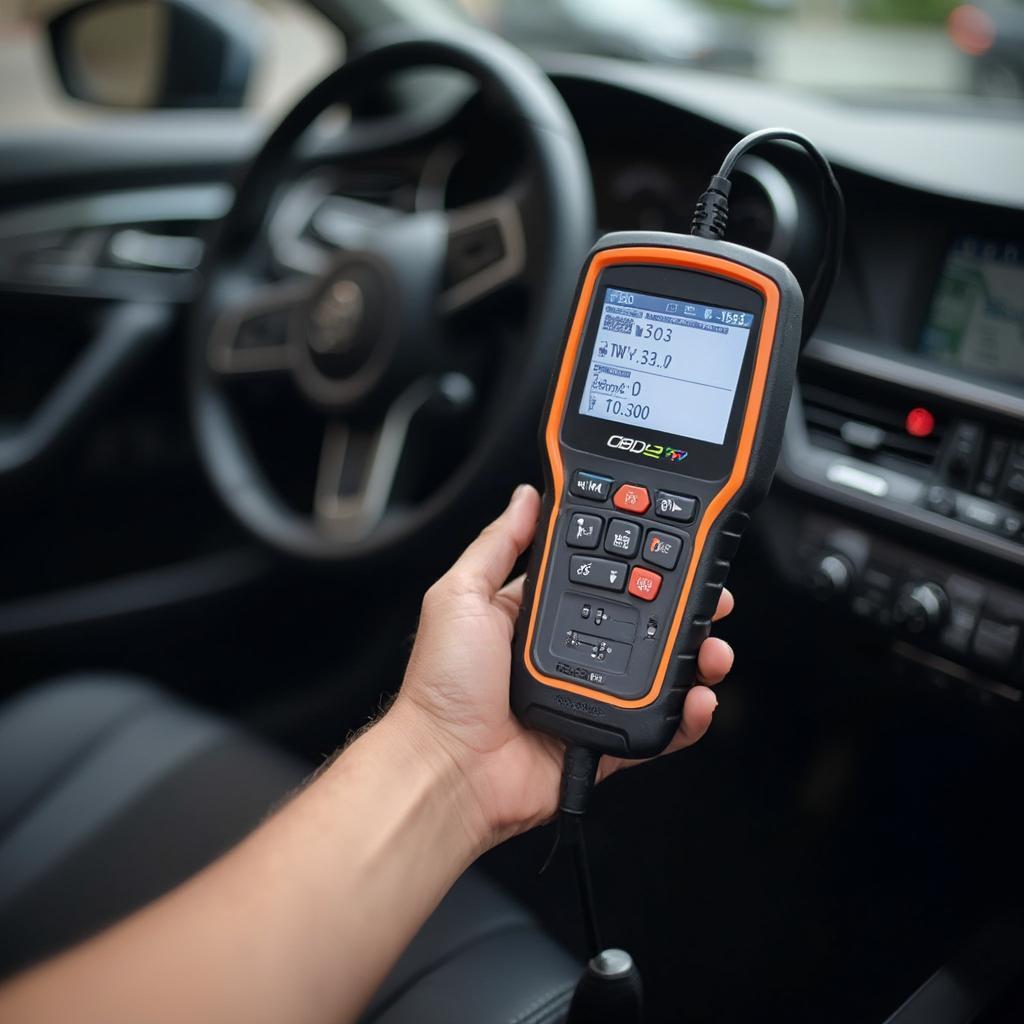


Common Uses for OBD2 Scanners
OBD2 scanners are valuable tools for various applications:
- Diagnosing Check Engine Light: Quickly identify the cause of the check engine light and take appropriate action.
- Monitoring Vehicle Performance: Track real-time data from various sensors, providing insights into engine performance, fuel efficiency, and other critical parameters.
- DIY Maintenance: Empower car owners to perform basic maintenance tasks and troubleshoot minor issues.
- Smog Check Readiness: Check if the vehicle is ready for emissions testing.
- Pre-Purchase Inspection: Evaluate the health of a used vehicle before buying. Sometimes, older cars require modifications, like a 95 eg convert to obd2.
You may even consider exploring an obd2 honda tuning app for more advanced functionalities. Furthermore, understanding specific codes, such as obd2 420, can be crucial for diagnosing emissions issues.
Conclusion
From the complexities of OBD1 to the standardized approach of OBD2, car diagnostics have come a long way. OBD2 scanners empower both technicians and car owners with the ability to understand and maintain their vehicles effectively. The advancements in OBD technology have revolutionized the automotive industry, leading to improved vehicle performance, enhanced safety, and better environmental protection. OBD1 and OBD2 scanners are indispensable tools for anyone involved in vehicle maintenance and repair.
FAQ
- What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2? OBD2 is standardized, offering a universal connector and DTCs, while OBD1 systems were manufacturer-specific.
- Where can I find the OBD2 port in my car? It’s typically located under the dashboard, near the steering wheel.
- Can I use an OBD2 scanner on an OBD1 car? No, you’ll need an adapter or a scanner specifically designed for OBD1 systems.
- What does a check engine light indicate? It signals a potential issue detected by the vehicle’s onboard computer.
- Are all OBD2 scanners the same? No, they vary in features and capabilities.
- Do I need professional training to use an OBD2 scanner? Basic usage is straightforward, but advanced features may require some technical knowledge.
- Can an OBD2 scanner clear trouble codes? Yes, most scanners have the capability to clear DTCs.
Common Scenarios with OBD1 and OBD2 questions
- Scenario 1: Check Engine Light is On: Use an OBD2 scanner to identify the specific trouble code causing the light to illuminate.
- Scenario 2: Poor Fuel Economy: Monitor fuel trim data using an OBD2 scanner to pinpoint potential issues affecting fuel efficiency.
- Scenario 3: Troubleshooting Engine Misfires: Use an OBD2 scanner to identify misfire counts and pinpoint the affected cylinder.
Further Exploration
For more information on OBD-related topics, consider researching topics like “OBD2 software,” “OBD2 protocols,” and “advanced OBD2 diagnostics.” These resources can provide a deeper understanding of OBD technology and its applications.
Need support? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected]. We offer 24/7 customer service.

