The Volkswagen OBD2 ECU, or Engine Control Unit, is the heart of your vehicle’s electronic system. This sophisticated computer monitors and controls a vast range of engine functions, ensuring optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. Understanding how your Volkswagen’s OBD2 ECU works is essential for any car enthusiast or DIY mechanic.
Decoding the Volkswagen OBD2 ECU
The ECU constantly receives data from various sensors located throughout the engine and related systems. This data, including information on throttle position, engine speed, air intake, and oxygen levels, allows the ECU to make real-time adjustments to optimize engine performance.
For example, if you’re accelerating hard, the ECU will recognize the increased throttle input and adjust the fuel-to-air ratio accordingly to deliver maximum power. Conversely, when cruising at a constant speed, the ECU prioritizes fuel efficiency by leaning out the fuel mixture.
Accessing Your Volkswagen OBD2 ECU with a Scanner
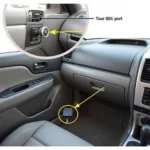
The OBD2 port, a standardized 16-pin connector usually located under the driver’s side dashboard, serves as the gateway to your Volkswagen’s ECU. By connecting an OBD2 scanner, you can tap into a wealth of information about your car’s engine and other systems.
OBD2 scanners range from basic code readers to advanced professional-grade tools. They allow you to:
- Read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs): These codes indicate potential issues within the engine or related systems.
- View live data streams: Monitor real-time sensor readings like engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor voltage.
- Perform actuator tests: Command various engine components, such as fuel injectors or the EGR valve, to test their functionality.
- Access advanced functions: Depending on the scanner and vehicle model, you might be able to perform tasks like key programming or module coding.
Common Volkswagen OBD2 Codes and What They Mean
While a complete list of Volkswagen OBD2 codes would be extensive, here are some common ones you might encounter:
- P0171 (System Too Lean Bank 1): Indicates that the engine is running lean, meaning there’s too much air compared to fuel.
- P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold Bank 1): Suggests a potential problem with the catalytic converter.
- P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected): Indicates that one or more cylinders are not firing properly.
- P0130 (Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction Bank 1 Sensor 1): Points to a problem with the oxygen sensor’s signal.
“It’s important to remember that OBD2 codes are just starting points for diagnosis,” says automotive engineer and diagnostics expert, Dr. Stefan Mueller. “Always research the code thoroughly and consider other symptoms before jumping to conclusions or replacing parts.”
Optimizing Your Volkswagen’s Performance with OBD2 Insights
By understanding the data provided by your Volkswagen’s OBD2 system, you can make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs. Regularly checking for trouble codes and monitoring live data can help you identify minor issues before they escalate into major problems, potentially saving you time and money in the long run.
Conclusion
The Volkswagen OBD2 ECU is a vital component that ensures your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. With the help of an OBD2 scanner and the knowledge of how to interpret the data, you can unlock a deeper understanding of your car’s health and performance.
Remember, early detection is key to keeping your Volkswagen on the road for years to come. Don’t hesitate to consult with a qualified mechanic for any issues beyond your comfort level.