OBD2 memory codes, also known as stored codes or pending codes, are snapshots of a vehicle’s performance history. Unlike active codes, which trigger the check engine light immediately, memory codes indicate a past issue that may or may not be recurring. Understanding these codes can be valuable for car owners and mechanics in diagnosing and addressing potential problems.
How Memory Codes Work
When your car’s onboard computer (ECU) detects a problem with a sensor, component, or system, it logs a corresponding diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in its memory. This code remains stored even if the issue resolves itself temporarily.
For instance, a loose gas cap might trigger a memory code. Tightening the cap might temporarily clear the issue, but the code remains logged in the system.
Types of Memory Codes
Hard Codes
Hard codes indicate a persistent issue. These codes reappear after clearing the codes and driving for a specific period or number of engine cycles. Hard codes generally require immediate attention, as they signal a consistent problem affecting your vehicle’s performance.
Soft Codes or Pending Codes
Soft codes represent intermittent or temporary issues. They might appear and disappear on their own, making them trickier to diagnose. While a soft code might not always indicate a major problem, it’s essential to monitor them, as they could develop into hard codes or indicate underlying issues.
Why Memory Codes Are Important
Memory codes offer several benefits for car maintenance and diagnosis:
- Early detection: They can reveal potential problems before they escalate into major issues, saving you costly repairs down the line.
- Historical data: They provide valuable information about your car’s past performance, which can help mechanics identify intermittent problems or patterns.
- DIY diagnostics: With an OBD2 scanner, you can read these codes yourself and gain insights into your car’s health.
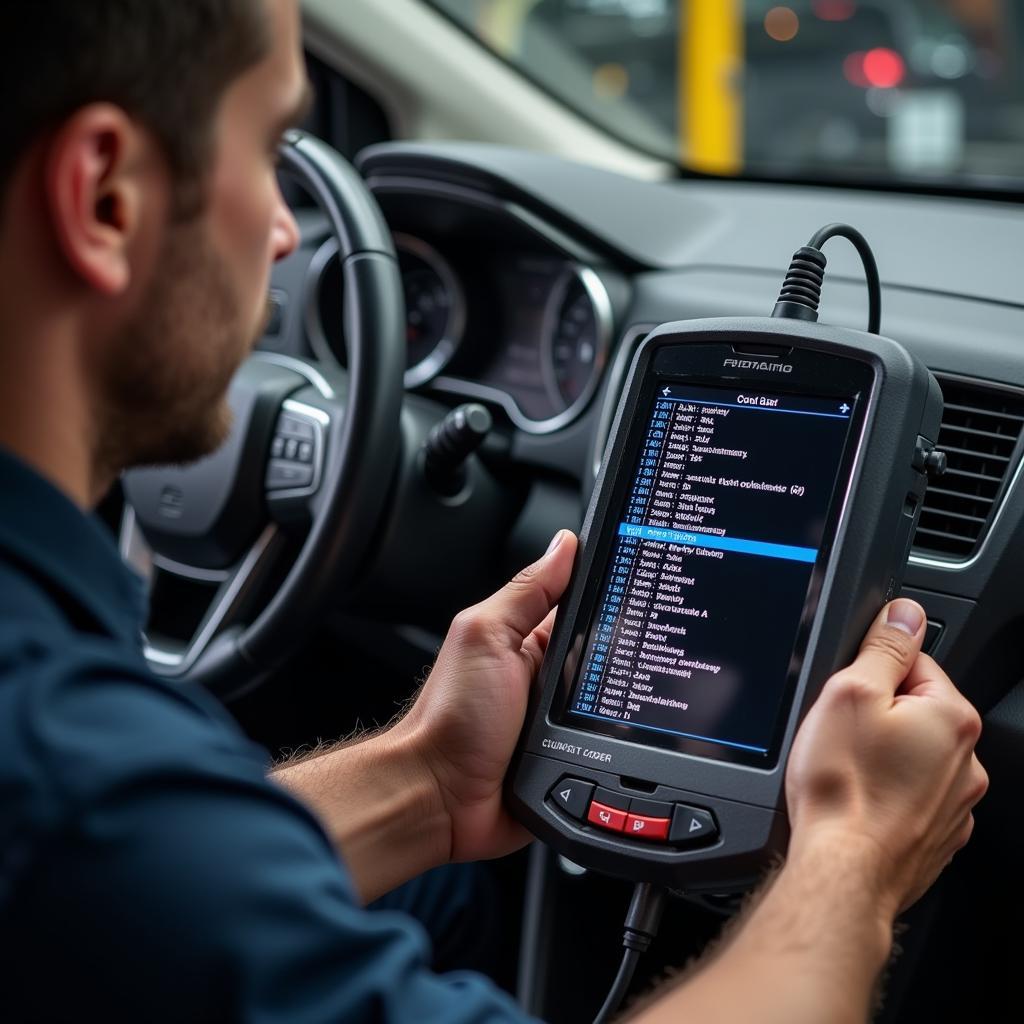
How to Read OBD2 Memory Codes
You can read OBD2 memory codes using a dedicated OBD2 code reader, which are available at various price points and functionalities.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Locate your car’s OBD2 port (usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side).
- Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn on the ignition (do not start the engine).
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to access the “Stored Codes” or “Memory Codes” section.
- The scanner will display the stored codes. Note down the codes or take a picture.
- Research the code definitions online or consult a repair manual.
Important Note: Clearing codes with a scanner will erase the stored data. If you haven’t addressed the underlying issue, the code will likely reappear.
Common OBD2 Memory Codes
While specific code definitions depend on the car make and model, here are some general categories and examples:
- Engine and Emission Control: P0171 (System Too Lean), P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected), P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold)
- Transmission: P0700 (Transmission Control System (TCS) Malfunction), P0715 (Input/Turbine Speed Sensor A Circuit Malfunction)
- Brakes: C1233 (Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Intermittent/Erratic)
- Airbag System: B1000 (Airbag System Malfunction)
“Regularly checking your vehicle’s memory codes can provide valuable insights into its health and help you address potential problems before they escalate,” says John Smith, Senior Automotive Engineer at XYZ Auto.
Conclusion
OBD2 memory codes offer a valuable glimpse into your car’s health. Understanding these codes can help you identify and address potential problems early on, saving you time, money, and potential headaches down the road. If you’re unsure about any code, always consult a qualified mechanic for accurate diagnosis and repair.
FAQs
Q: How often should I check my car’s memory codes?
A: It’s a good practice to check them monthly or whenever you experience unusual car behavior.
Q: Will disconnecting the battery clear memory codes?
A: Yes, but it’s not always a recommended solution as it might reset other essential settings.
Q: Can I drive my car with a memory code?
A: It depends on the code’s severity. Some codes might not affect drivability, while others require immediate attention.
Q: Are memory codes the same for all car brands?
A: While the OBD2 system is standardized, specific code definitions might vary slightly between manufacturers.
Q: Where can I find more information about specific OBD2 codes?
A: You can find detailed code definitions and troubleshooting tips on online resources like Equus OBD2 codes and forums.
Need more help with OBD2 codes or car diagnostics? Contact our expert team via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, or Email: [email protected]. We’re here to assist you 24/7.
Explore our website for further insights on OBD2 scanners and car diagnostics:
- Learn more about the features and benefits of Torque Pro OBD2 Car
- Discover how an OBD2 temperature alarm can prevent engine overheating.
- Explore the compatibility of AEM ECU Honda OBD2 systems.