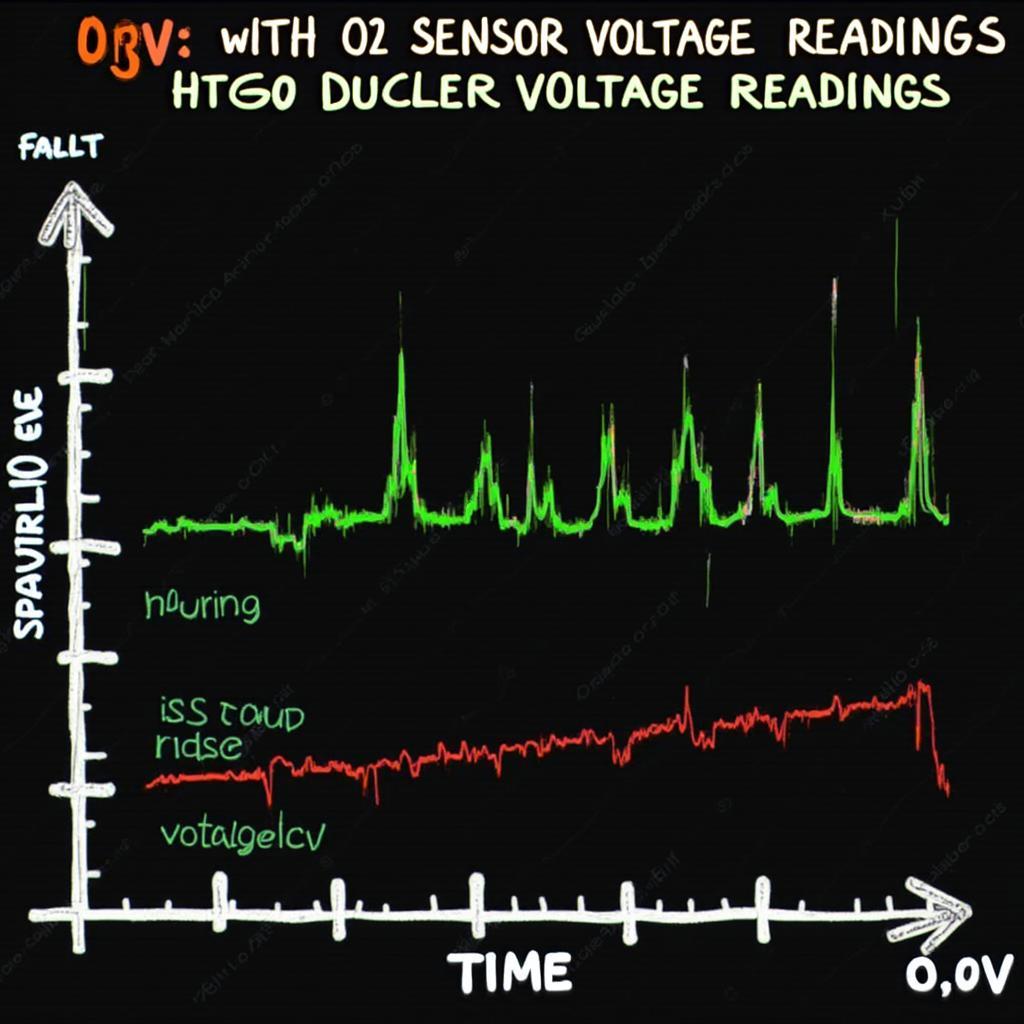
Understanding your O2 sensor readings through an OBD2 scanner is crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. An oxygen sensor, or O2 sensor, is a vital component of your vehicle’s emission control system. It measures the amount of unburned oxygen in the exhaust gases, providing data to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel mixture. Knowing what a normal reading looks like, and how to interpret abnormal readings, can save you time and money down the road.
Decoding O2 Sensor Readings with Your OBD2 Scanner
So, you’ve plugged in your OBD2 scanner and are staring at a screen full of numbers. What do they mean? O2 sensors generate voltage signals that fluctuate between 0.1 volts (lean) and 0.9 volts (rich). A healthy sensor rapidly switches between these values, indicating the engine is constantly adjusting the air-fuel ratio. A stuck sensor, on the other hand, will maintain a constant voltage, signaling a problem.
What Does a Normal O2 Sensor Reading Look Like?
A normal O2 sensor reading will fluctuate rapidly between 0.1 and 0.9 volts. This fluctuation signifies that the sensor is active and responding to changes in the exhaust stream. The frequency of these fluctuations is also important, typically varying between one and five times per second.
Identifying Abnormal O2 Sensor Readings
Several signs indicate a potential problem with your O2 sensor, including:
- Stuck Readings: A reading stuck at 0.1V, 0.9V, or somewhere in between indicates a faulty sensor.
- Slow Response Time: If the voltage changes slowly, the sensor might be failing.
- No Activity: A complete lack of voltage change points to a dead sensor.
- Out of Range Readings: Values consistently above 0.9V or below 0.1V are also abnormal.
Understanding O2 Sensor Location and Types
Most modern vehicles have multiple O2 sensors, typically located upstream and downstream of the catalytic converter. Upstream sensors (Sensor 1) monitor the air-fuel mixture before it enters the converter, while downstream sensors (Sensor 2) monitor the converter’s efficiency. Understanding the location and type of sensor you’re reading is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Upstream vs. Downstream O2 Sensors
The readings from upstream and downstream sensors will differ. Upstream sensors fluctuate rapidly, while downstream sensors should maintain a relatively steady voltage around 0.7V, indicating proper catalytic converter function. A fluctuating downstream sensor can indicate a faulty catalytic converter.
“Knowing the difference between upstream and downstream O2 sensor readings is essential for accurate diagnostics. Don’t jump to conclusions based on a single reading – consider the sensor’s location and function,” says Robert Johnson, a veteran automotive technician with over 20 years of experience.
Troubleshooting O2 Sensor Issues
If your OBD2 scanner reveals abnormal O2 sensor readings, several potential causes exist:
- Faulty O2 Sensor: The most common culprit is a worn-out sensor.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks can introduce excess oxygen into the exhaust stream, affecting readings.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the engine’s vacuum system can also disrupt air-fuel ratios.
- Fuel System Problems: Issues with fuel injectors, fuel pump, or fuel pressure regulator can also cause abnormal O2 sensor readings.
Conclusion
Understanding what is normal reading of a o2 sensor obd2 is vital for maintaining your vehicle’s health. By using an OBD2 scanner and interpreting the data correctly, you can identify potential problems early and prevent costly repairs. Regular monitoring of your O2 sensor readings can significantly improve fuel economy and extend the life of your catalytic converter.
FAQ
- How often should I check my O2 sensor readings?
- What tools do I need to check my O2 sensor readings?
- Can I replace an O2 sensor myself?
- How much does an O2 sensor replacement cost?
- What are the symptoms of a bad O2 sensor?
- Can a bad O2 sensor damage my engine?
- How can I prevent O2 sensor problems?
For further assistance please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.